Direct submissions to PCI Ecology from bioRxiv.org are possible using the B2J service
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
27 Nov 2023
Modeling Tick Populations: An Ecological Test Case for Gradient Boosted TreesWilliam Manley, Tam Tran, Melissa Prusinski, Dustin Brisson https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.13.532443Gradient Boosted Trees can deliver more than accurate ecological predictionsRecommended by Timothée Poisot based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Tick-borne diseases are an important burden on public health all over the globe, making accurate forecasts of tick population a key ingredient in a successful public health strategy. Over long time scales, tick populations can undergo complex dynamics, as they are sensitive to many non-linear effects due to the complex relationships between ticks and the relevant (numerical) features of their environment. But luckily, capturing complex non-linear responses is a task that machine learning thrives on. In this contribution, Manley et al. (2023) explore the use of Gradient Boosted Trees to predict the distribution (presence/absence) and abundance of ticks across New York state. This is an interesting modelling challenge in and of itself, as it looks at the same ecological question as an instance of a classification problem (presence/absence) or of a regression problem (abundance). In using the same family of algorithm for both, Manley et al. (2023) provide an interesting showcase of the versatility of these techniques. But their article goes one step further, by setting up a multi-class categorical model that estimates jointly the presence and abundance of a population. I found this part of the article particularly elegant, as it provides an intermediate modelling strategy, in between having two disconnected models for distribution and abundance, and having nested models where abundance is only predicted for the present class (see e.g. Boulangeat et al., 2012, for a great description of the later). One thing that Manley et al. (2023) should be commended for is their focus on opening up the black box of machine learning techniques. I have never believed that ML models are more inherently opaque than other families of models, but the focus in this article on explainable machine learning shows how these models might, in fact, bring us closer to a phenomenological understanding of the mechanisms underpinning our observations. There is also an interesting discussion in this article, on the rate of false negatives in the different models that are being benchmarked. Although model selection often comes down to optimizing the overall quality of the confusion matrix (for distribution models, anyway), depending on the type of information we seek to extract from the model, not all types of errors are created equal. If the purpose of the model is to guide actions to control vectors of human pathogens, a false negative (predicting that the vector is absent at a site where it is actually present) is a potentially more damaging outcome, as it can lead to the vector population (and therefore, potentially, transmission) increasing unchecked. References
Boulangeat I, Gravel D, Thuiller W. Accounting for dispersal and biotic interactions to disentangle the drivers of species distributions and their abundances: The role of dispersal and biotic interactions in explaining species distributions and abundances. Ecol Lett. 2012;15: 584-593. Manley W, Tran T, Prusinski M, Brisson D. (2023) Modeling tick populations: An ecological test case for gradient boosted trees. bioRxiv, 2023.03.13.532443, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.13.532443 | Modeling Tick Populations: An Ecological Test Case for Gradient Boosted Trees | William Manley, Tam Tran, Melissa Prusinski, Dustin Brisson | <p style="text-align: justify;">General linear models have been the foundational statistical framework used to discover the ecological processes that explain the distribution and abundance of natural populations. Analyses of the rapidly expanding ... | Parasitology, Species distributions, Statistical ecology | Timothée Poisot | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2023-03-23 23:41:17 | View | |
24 Nov 2023
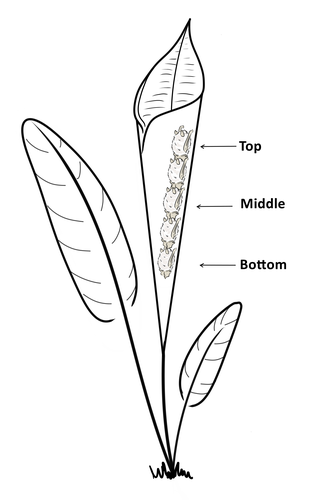
Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged batsGiada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223Consistent individual differences in habitat use in a tropical leaf roosting batRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Annemarie van der Marel and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Annemarie van der Marel and 2 anonymous reviewers
Consistent individual differences in habitat use are found across species and can play a role in who an individual mates with, their risk of predation, and their ability to compete with others (Stuber et al. 2022). However, the data informing such hypotheses come primarily from temperate regions (Stroud & Thompson 2019, Titley et al. 2017). This calls into question the generalizability of the conclusions from this research until further investigations can be conducted in tropical regions. Giacomini and colleagues (2023) tackled this task in an investigation of consistent individual differences in habitat use in the Central American tropics. They explored whether Spix’s disc-winged bats form positional hierarchies in roosts, which is an excellent start to learning more about the social behavior of this species - a species that is difficult to directly observe. They found that individual bats use their roosting habitat in predictable ways by positioning themselves consistently either in the bottom, middle, or top of the roost leaf. Individuals chose the same positions across time and across different roost sites. They also found that age and sex play a role in which sections individuals are positioned in. Their research shows that consistent individual differences in habitat use are present in a tropical system, and sets the stage for further investigations into social behavior in this species, particularly whether there is a dominance hierarchy among individuals and whether some positions in the roost are more protective and sought after than others. References Giacomini G, Chaves-Ramirez S, Hernandez-Pinson A, Barrantes JP, Chaverri G. (2023). Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223 Stroud, J. T., & Thompson, M. E. (2019). Looking to the past to understand the future of tropical conservation: The importance of collecting basic data. Biotropica, 51(3), 293-299. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12665 Stuber, E. F., Carlson, B. S., & Jesmer, B. R. (2022). Spatial personalities: a meta-analysis of consistent individual differences in spatial behavior. Behavioral Ecology, 33(3), 477-486. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arab147 Titley, M. A., Snaddon, J. L., & Turner, E. C. (2017). Scientific research on animal biodiversity is systematically biased towards vertebrates and temperate regions. PloS one, 12(12), e0189577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189577 | Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats | Giada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri | <p style="text-align: justify;">Individuals within both moving and stationary groups arrange themselves in a predictable manner; for example, some individuals are consistently found at the front of the group or in the periphery and others in the c... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Social structure, Zoology | Corina Logan | 2022-11-05 17:39:35 | View | |
21 Nov 2023
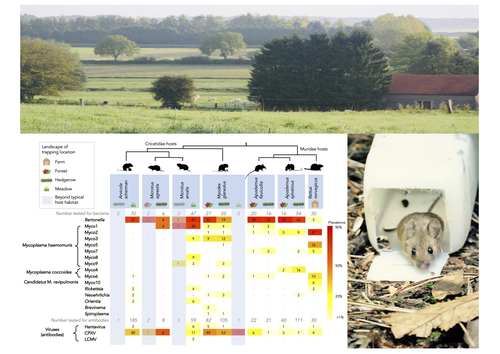
Pathogen community composition and co-infection patterns in a wild community of rodentsJessica Lee Abbate, Maxime Galan, Maria Razzauti, Tarja Sironen, Liina Voutilainen, Heikki Henttonen, Patrick Gasqui, Jean-François Cosson, Nathalie Charbonnel https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.09.940494Reservoirs of pestilence: what pathogen and rodent community analyses can tell us about transmission riskRecommended by Francois Massol based on reviews by Adrian Diaz, Romain Pigeault and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Adrian Diaz, Romain Pigeault and 1 anonymous reviewer
Rodents are well known as one of the main animal groups responsible for human-transmitted pathogens. As such, it seems logical to try and survey what kinds of pathogenic microbes might be harboured by wild rodents, in order to establish some baseline surveillance and prevent future zoonotic outbreaks (Bernstein et al., 2022). This is exactly what Abbate et al. (2023) endeavoured and their findings are intimidating. Based on quite a large sampling effort, they collected more than 700 rodents of seven species around two villages in northeastern France. They looked for molecular markers indicative of viral and bacterial infections and proceeded to analyze their pathogen communities using multivariate techniques. Variation in the prevalence of the different pathogens was found among host species, with e.g. signs of CPXV more prevalent in Cricetidae while some Mycoplasma strains were more prevalent in Muridae. Co-circulation of pathogens was found in all species, with some evidencing signs of up to 12 different pathogen taxa. The diversity of co-circulating pathogens was markedly different between host species and higher in adult hosts, but not affected by sex. The dataset also evinced some slight differences between habitats, with meadows harbouring a little more diversity of rodent pathogens than forests. Less intuitively, some pathogen associations seemed quite repeatable, such as the positive association of Bartonella spp. with CPXV in the montane water vole. The study allowed the authors to test several associations already described in the literature, including associations between different hemotropic Mycoplasma species. I strongly invite colleagues interested in zoonoses, emerging pandemics and more generally One Health to read the paper of Abbate et al. (2023) and try to replicate them across the world. To prevent the next sanitary crises, monitoring rodents, and more generally vertebrates, population demographics is a necessary and enlightening step (Johnson et al., 2020), but insufficient. Following the lead of colleagues working on rodent ectoparasites (Krasnov et al., 2014), we need more surveys like the one described by Abbate et al. (2023) to understand the importance of the dilution effect in the prevalence and transmission of microbial pathogens (Andreazzi et al., 2023) and the formation of epidemics. We also need other similar studies to assess the potential of different rodent species to carry pathogens more or less capable of infecting other mammalian species (Morand et al., 2015), in other places in the world. References Abbate, J. L., Galan, M., Razzauti, M., Sironen, T., Voutilainen, L., Henttonen, H., Gasqui, P., Cosson, J.-F. & Charbonnel, N. (2023) Pathogen community composition and co-infection patterns in a wild community of rodents. BioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.02.09.940494 Andreazzi, C. S., Martinez-Vaquero, L. A., Winck, G. R., Cardoso, T. S., Teixeira, B. R., Xavier, S. C. C., Gentile, R., Jansen, A. M. & D'Andrea, P. S. (2023) Vegetation cover and biodiversity reduce parasite infection in wild hosts across ecological levels and scales. Ecography, 2023, e06579. | Pathogen community composition and co-infection patterns in a wild community of rodents | Jessica Lee Abbate, Maxime Galan, Maria Razzauti, Tarja Sironen, Liina Voutilainen, Heikki Henttonen, Patrick Gasqui, Jean-François Cosson, Nathalie Charbonnel | <p style="text-align: justify;">Rodents are major reservoirs of pathogens that can cause disease in humans and livestock. It is therefore important to know what pathogens naturally circulate in rodent populations, and to understand the factors tha... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Community ecology, Eco-immunology & Immunity, Epidemiology, Host-parasite interactions, Population ecology, Species distributions | Francois Massol | 2020-02-11 12:42:28 | View | |
15 Nov 2023

The challenges of independence: ontogeny of at-sea behaviour in a long-lived seabirdKarine Delord, Henri Weimerskirch, Christophe Barbraud https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.23.465439On the road to adulthood: exploring progressive changes in foraging behaviour during post-fledging immaturity using remote trackingRecommended by Blandine Doligez based on reviews by Juliet Lamb and 1 anonymous reviewerIn most vertebrate species, the period of life spanning from departure from the growing site until reaching a more advanced life stage (immature or adult) is critical. During this period, juveniles are often highly vulnerable because they have not reached the morphological, physiological and behavioural maturity levels of adults yet and are therefore at high risk of mortality, e.g. through starvation, depredation or competition (e.g. Marchetti & Price 1989, Wunderle 1991, Naef-Daenzer & Grüebler 2016). In line with this, juvenile survival is most often far lower than adult survival (e.g. Wooller et al. 1992). In species with parental care, juveniles have to acquire behavioural independence from their parents and possibly establish their own territory during this period of life. Very often, this is also the period that is least well-known in the life cycle (Cox et al. 2014, Naef-Daenzer & Grüebler 2016) because of reduced accessibility to individuals and/or adoption of low conspicuous behaviours. Therefore, our understanding of how juveniles acquire typical adult behaviours and how this progressively increases their survival prospects is still very limited (Naef-Daenzer & Grüebler 2016), and questions such as the length of this transition period or the cognitive (e.g. learning, memorization) mechanisms involved remain largely unresolved. This is particularly true regarding the acquisition of independent foraging behaviour (Marchetti & Price 1989). Because direct observations of juvenile behaviours are usually very difficult except in specific situations or at the cost of an enormous effort, the use of remote tracking devices can be particularly appealing in this context (e.g. Ponchon et al. 2013, Kays et al. 2015). Over the past decades, technical advances have allowed the monitoring of not only individuals’ movements at both large and small spatial scales but also their activities and behaviours based on different parameters recording e.g. speed of movement or diving depth (Whitford & Klimley 2019). Device miniaturization has in particular allowed smaller species to be equipped and/or longer periods of time to be monitored (e.g. Naef-Daenzer et al. 2005). This has opened up whole fields of research, and has been particularly used on marine seabirds. In these species, individuals are most often inaccessible when at sea, representing most of the time outside (and even within) the breeding season, and the life cycle of these long-lived species can include an extended immature period (up to many years) during which most of them will remain unseen, until they come back as breeders or pre-breeders (e.g. Wooller et al. 1992, Oro & Martínez-Abraín 2009). Survival has been found to increase gradually with age in these species before reaching high values characteristic of the adult stage. However, the mechanisms underlying this increase are still to be deciphered. The study by Delord et al. (2023) builds upon the hypothesis that juveniles gradually learn foraging techniques and movement strategies, improving their foraging efficiency, as previous data on flight parameters seemed to show in different long-lived bird species. Yet, these previous studies obtained data over a limited period of time, i.e. a few months at best. Whether these data could capture the whole dynamics of the progressive acquisition of foraging and movement skills can only be assessed by measuring behaviour over a longer time period and comparing it to similar data in adults, to account for seasonal variation in relation to both resource availability and energetic demands, e.g. due to molt. The present study (Delord et al. 2023) addresses these questions by taking advantage of longer-lasting recordings of the location and activity of juvenile, immature and adult birds obtained simultaneously to investigate changes over time in juvenile behaviour and thereby provide hints about how young progressively acquire foraging skills. This study is performed on Amsterdam albatrosses, a highly endangered long-lived sea bird, with obvious conservation issues (Thiebot et al. 2015). The results show progressive changes in foraging effort over the first two months after departure from the birth colony, but large differences remain between life stages over a much longer time frame. They also reveal strong variations between sexes and over time in the year. Overall, this study, therefore, confirms the need for very long-term data to be collected in order to address the question of progressive behavioural maturation and associated survival consequences in such species with strongly deferred maturity. Ideally, the same individuals should be monitored over different life stages, from the juvenile period up to adulthood, but this would require further technical development to release the issue of powering duration limitation. As reviewers emphasized in the first review round, one main challenge now remains to ascertain the outcome of the observed behavioural changes in foraging behaviour: we expect them to reflect improvement in foraging skills and thus performance of juveniles over time, but this would need to be tested. Collecting data on foraging efficiency is yet another challenge, that future technical developments may also help overcome. Importantly also, data were available only for individuals that could be caught again because the tracking device had to be retrieved from the bird. Here, a substantial fraction of the loggers (one-fifth) could not be found again (Delord et al. 2023). To what extent the birds for which no data could be obtained are a random sample of the equipped birds would also need to be assessed. The further development of remote tracking techniques allowing data to be downloaded from a long distance should help further exploration of behavioural ontogeny of juveniles while maturing and its survival consequences. Because the maturation process explored here is likely to show very different characteristics (e.g. timing and speed) in smaller / shorter-lived species (see Cox et al. 2014, Naef-Daenzer & Grüebler 2016), the development of miniaturization is also expected to allow further investigation of post-fledging behavioural maturation in a wider range of bird species. Our understanding of this crucial life phase in different types of species should thus continue to progress in the coming years. References Cox W. A., Thompson F. R. III, Cox A. S. & Faaborg J. 2014. Post-fledging survival in passerine birds and the value of post-fledging studies to conservation. Journal of Wildlife Management, 78: 183-193. https://doi.org/10.1002/jwmg.670 Delord K., Weimerskirch H. & Barbraud C. 2023. The challenges of independence: ontogeny of at-sea behaviour in a long-lived seabird. bioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.23.465439 Kays R., Crofoot M. C., Jetz W. & Wikelski M. 2015. Terrestrial animal tracking as an eye on life and planet. Science, 348 (6240). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa2478 Marchetti K: & Price T. 1989. Differences in the foraging of juvenile and adult birds: the importance of developmental constraints. Biological Reviews, 64: 51-70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.1989.tb00638.x Naef-Daenzer B., Fruh D., Stalder M., Wetli P. & Weise E. 2005. Miniaturization (0.2 g) and evaluation of attachment techniques of telemetry transmitters. The Journal of Experimental Biology, 208: 4063–4068. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.01870 Naef-Daenzer B. & Grüebler M. U. 2016. Post-fledging survival of altricial birds: ecological determinants and adaptation. Journal of Field Ornithology, 87: 227-250. https://doi.org/10.1111/jofo.12157 Oro D. & Martínez-Abraín A. 2009. Ecology and behavior of seabirds. Marine Ecology, pp.364-389. Ponchon A., Grémillet D., Doligez B., Chambert T., Tveera T., Gonzàles-Solìs J & Boulinier T. 2013. Tracking prospecting movements involved in breeding habitat selection: insights, pitfalls and perspectives. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 4: 143-150. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210x.2012.00259.x Thiebot J.-B., Delord K., Barbraud C., Marteau C. & Weimerskirch H. 2015. 167 individuals versus millions of hooks: bycatch mitigation in longline fisheries underlies conservation of Amsterdam albatrosses. Aquatic Conservation 26: 674-688. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.2578 Whitford M & Klimley A. P. An overview of behavioral, physiological, and environmental sensors used in animal biotelemetry and biologging studies. Animal Biotelemetry, 7: 26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40317-019-0189-z Wooller R.D., Bradley J. S. & Croxall J. P. 1992. Long-term population studies of seabirds. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 7: 111-114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-5347(92)90143-y Wunderle J. M. 1991. Age-specific foraging proficiency in birds. Current Ornithology, 8: 273-324. | The challenges of independence: ontogeny of at-sea behaviour in a long-lived seabird | Karine Delord, Henri Weimerskirch, Christophe Barbraud | <p style="text-align: justify;">The transition to independent foraging represents an important developmental stage in the life cycle of most vertebrate animals. Juveniles differ from adults in various life history traits and tend to survive less w... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Foraging, Ontogeny | Blandine Doligez | 2021-10-26 07:51:49 | View | |
09 Nov 2023
Mark loss can strongly bias estimates of demographic rates in multi-state models: a case study with simulated and empirical datasetsFrédéric Touzalin, Eric J. Petit, Emmanuelle Cam, Claire Stagier, Emma C. Teeling, Sébastien J. Puechmaille https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.25.485763Marks lost in action, biased estimationsRecommended by Sylvain Billiard based on reviews by Olivier Gimenez, Devin Johnson and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Olivier Gimenez, Devin Johnson and 1 anonymous reviewer
Capture-Mark-Recapture (CMR) data are commonly used to estimate ecological variables such as abundance, survival probability, or transition rates from one state to another (e.g. from juvenile to adult, or migration from one site to another). Many studies have shown how estimations can be affected by neglecting one aspect of the population under study (e.g. the heterogeneity in survival between individuals) or one limit of the methodology itself (e.g. the fact that observers might not detect an individual although it is still alive). Strikingly, very few studies have yet assessed the robustness of one fundamental assumption of all CMR-based inferences: marks are supposed definitive and immutable. If they are not, how are estimations affected? Addressing this issue is the main goal of the paper by Touzalin et al. (2023), and they did a very nice work. But, because the answer is not that simple, it also calls for further investigations. When and why would mark loss bias estimation? In at least two situations. First, when estimating survival rates: if an individual loses its mark, it will be considered as dead, hence death rates will be overestimated. Second, more subtly, when estimating transition rates: if one individual loses its mark at the specific moment where its state changes, then a transition will be missed in data. The history of the marked individual would then be split into two independent CMR sequences as if there were two different individuals, including one which died. Touzalin et al. (2023) thoroughly studied these two situations by estimating ecological parameters on 1) well-thought simulated datasets, that cover a large range of possible situations inspired from a nice compilation of hundreds of estimations from fish and bats studies, and 2) on their own bats dataset, for which they had various sources of information about mark losses, i.e. different mark types on the same individuals, including mark based on genotypes, and marks found on the soil in the place where bats lived. Their main findings from the simulated datasets are that there is a general trend for underestimation of survival and transition rates if mark loss is not accounting for in the model, as it would be intuitively expected. However, they also showed from the bats dataset that biases do not show any obvious general trend, suggesting complex interactions between different ecological processes and/or with the estimation procedure itself. The results by Touzalin et al. (2023) strongly suggest that mark loss should systematically be included in models estimating parameters from CMR data. In addition to adapt the inferential models, the authors also recommend considering either a double marking, or even a single but ‘permanent’ mark such as one based on the genotypes. However, the potential gain of a double marking or of the use of genotypes is still to be evaluated both in theory and practice, and it seems to be not that obvious at first sight. First because double marking can be costly for experimenters but also for the marked animals, especially as several studies showed that marks can significantly affect survival or recapture rates. Second because multiple sources of errors can affect genotyping, which would result in wrong individual assignations especially in populations with low genetic diversity or high inbreeding, or no individual assignation at all, which would increase the occurrence of missing data in CMR datasets. Touzalin et al. (2023) supposed in their paper that there were no genotyping errors, but one can doubt it to be true in most situations. They have now important and interesting other issues to address. References Frédéric Touzalin, Eric J. Petit, Emmanuelle Cam, Claire Stagier, Emma C. Teeling, Sébastien J. Puechmaille (2023) Mark loss can strongly bias demographic rates in multi-state models: a case study with simulated and empirical datasets. BioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.03.25.485763 | Mark loss can strongly bias estimates of demographic rates in multi-state models: a case study with simulated and empirical datasets | Frédéric Touzalin, Eric J. Petit, Emmanuelle Cam, Claire Stagier, Emma C. Teeling, Sébastien J. Puechmaille | <p style="text-align: justify;">1. The development of methods for individual identification in wild species and the refinement of Capture-Mark-Recapture (CMR) models over the past few decades have greatly improved the assessment of population demo... | Conservation biology, Demography | Sylvain Billiard | 2022-04-12 18:49:34 | View | ||
06 Nov 2023
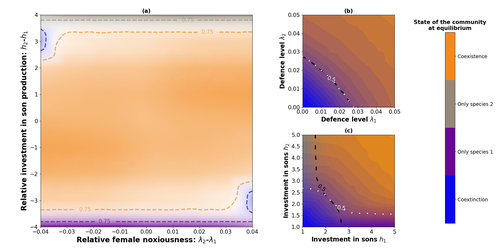
Influence of mimicry on extinction risk in Aculeata: a theoretical approachMaxime Boutin, Manon Costa, Colin Fontaine, Adrien Perrard, Violaine Llaurens https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.21.513153Mullerian and Batesian mimicry can influence population and community dynamicsRecommended by Amanda Franklin based on reviews by Jesus Bellver and 1 anonymous reviewerMimicry between species has long attracted the attention of scientists. Over a century ago, Bates first proposed that palatable species should gain a benefit by resembling unpalatable species (Bates 1862). Not long after, Müller suggested that there could also be a mutual advantage for two unpalatable species to mimic one another to reduce predator error (Müller 1879). These forms of mimicry, Batesian and Müllerian, are now widely studied, providing broad insights into behaviour, ecology and evolution. Numerous taxa, including both invertebrates and vertebrates, show examples of Batesian or Müllerian mimicry. Bees and wasps provide a particularly interesting case due to the differences in defence between females and males of the same species. While both males and females may display warning colours, only females can sting and inject venom to cause pain and allow escape from predators. Therefore, males are palatable mimics and can resemble females of their own species or females of another species (dual sex-limited mimicry). This asymmetry in defence could have impacts on both population structure and community assembly, yet research into mimicry largely focuses on systems without sex differences. Here, Boutin and colleagues (2023) use a differential equations model to explore the effect of mimicry on population structure and community assembly for sex-limited defended species. Specifically, they address three questions, 1) how do female noxiousness and sex-ratio influence the extinction risk of a single species?; 2) what is the effect of mimicry on species co-existence? and 3) how does dual sex-limited mimicry influence species co-existence? Their results reveal contexts in which populations with undefended males can persist, the benefit of Müllerian mimicry for species coexistence and that dual sex-limited mimicry can have a destabilising impact on species coexistence. The results not only contribute to our understanding of how mimicry is maintained in natural systems but also demonstrate how changes in relative abundance or population structure of one species could impact another species. Further insight into the population and community dynamics of insects is particularly important given the current population declines (Goulson 2019; Seibold et al 2019). References Bates, H. W. 1862. Contributions to the insect fauna of the Amazon Valley, Lepidoptera: Heliconidae. Trans. Linn. Soc. Lond. 23:495- 566. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1096-3642.1860.tb00146.x Boutin, M., Costa, M., Fontaine, C., Perrard, A., Llaurens, V. 2022 Influence of sex-limited mimicry on extinction risk in Aculeata: a theoretical approach. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.10.21.513153 Goulson, D. 2019. The insect apocalypse, and why it matters. Curr. Biol. 29: R967-R971. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.06.069 Müller, F. 1879. Ituna and Thyridia; a remarkable case of mimicry in butterflies. Trans. Roy. Entom. Roc. 1879:20-29. Seibold, S., Gossner, M. M., Simons, N. K., Blüthgen, N., Müller, J., Ambarlı, D., ... & Weisser, W. W. 2019. Arthropod decline in grasslands and forests is associated with landscape-level drivers. Nature, 574: 671-674. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1684-3 | Influence of mimicry on extinction risk in Aculeata: a theoretical approach | Maxime Boutin, Manon Costa, Colin Fontaine, Adrien Perrard, Violaine Llaurens | <p style="text-align: justify;">Positive ecological interactions, such as mutualism, can play a role in community structure and species co-existence. A well-documented case of mutualistic interaction is Mullerian mimicry, the convergence of colour... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Evolutionary ecology, Facilitation & Mutualism | Amanda Franklin | 2022-10-25 19:11:55 | View | |
23 Oct 2023
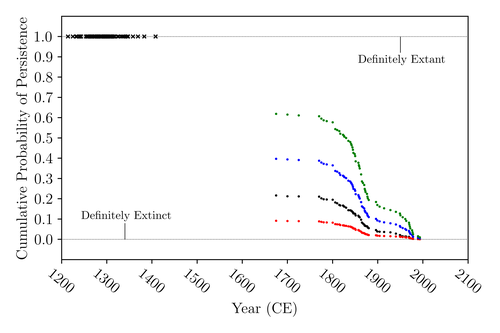
The Moa the Merrier: Resolving When the Dinornithiformes Went ExtinctFloe Foxon https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.07.552261Are Moas ancient Lazarus species?Recommended by Werner Ulrich based on reviews by Tim Coulson and Richard Holdaway based on reviews by Tim Coulson and Richard Holdaway
Ancient human colonisation often had catastrophic consequences for native fauna. The North American Megafauna went extinct shortly after humans entered the scene and Madagascar suffered twice, before 1500 CE and around 1700 CE after the Malayan and European colonisation. Maoris colonised New Zealand by about 1300 and a century later the giant Moa birds (Dinornithiformes) sharply declined. But did they went extinct or are they an ancient example of Lazarus species, species thought to be extinct but still alive? Scattered anecdotes of late sightings of living Moas even up to the 20th century seem to suggest the latter. The quest for later survival has also a criminal aspect. Who did it, the Maoris or the white colonisers in the late 18th century? The present work by Floe Foxon (2023) tries to settle this question. It uses a survival modelling approach and an assessment of the reliability of nearly 100 alleged sightings. The model favours the so-called overkill hypothesis, that Moas probably went extinct in the 15th century shortly after Maori colonisation. A small but still remarkable probability remained for survival up to 1770. Later sightings turned out to be highly unreliable. The paper is important as it does not rely on subjective discussions of late sightings but on a probabilistic modelling approach with sensitivity testing prior applied to marsupials. As common in probabilistic approaches, the study does not finally settle the case. A probability of as much as 20% remained for late survival after 1450 CE. This is not improbable as New Zealand was sufficiently unexplored in those days to harbour a few refuges for late survivors. However, in this respect, it is a bit unfortunate that at the end of the discussion, the paper cites Heuvelmans, the founder of cryptozoology, and it mentions the ivory-billed woodpecker, which has recently been redetected. No Moa remains were found after 1450. References Foxon F (2023) The Moa the Merrier: Resolving When the Dinornithiformes Went Extinct. bioRxiv, 2023.08.07.552261, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.07.552261 | The Moa the Merrier: Resolving When the Dinornithiformes Went Extinct | Floe Foxon | <p style="text-align: justify;">The Moa (Aves: Dinornithiformes) are an extinct group of the ratite clade from New Zealand. The overkill hypothesis asserts that the first New Zealand settlers hunted the Moa to extinction by 1450 CE, whereas the st... |  | Conservation biology, Human impact, Statistical ecology, Zoology | Werner Ulrich | Tim Coulson, Richard Holdaway | 2023-08-08 17:14:30 | View |
11 Oct 2023

Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysisCédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.02.516908Disentangling microbial exopolymer dynamics in intertidal sedimentsRecommended by Ute Risse-Buhl and Nils Rädecker based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) enables microorganisms to shape and interact with their environment [1]. EPS support cell adhesion and motility, offer protection from unfavorable conditions, and facilitate nutrient acquisition and transfer between microorganisms [2]. EPS production and consumption thus control the formation and structural organization of biofilms [3]. However, in marine environments, our understanding of the sources and composition of EPS is limited. References
| Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysis | Cédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe | <p style="text-align: justify;">Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) refer to a wide variety of high molecular weight molecules secreted outside the cell membrane by biofilm microorganisms. In the present study, EPS from marine microphytobenth... |  | Biodiversity, Ecological stoichiometry, Ecosystem functioning, Food webs, Marine ecology, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Soil ecology | Ute Risse-Buhl | 2022-12-06 14:13:11 | View | |
03 Oct 2023
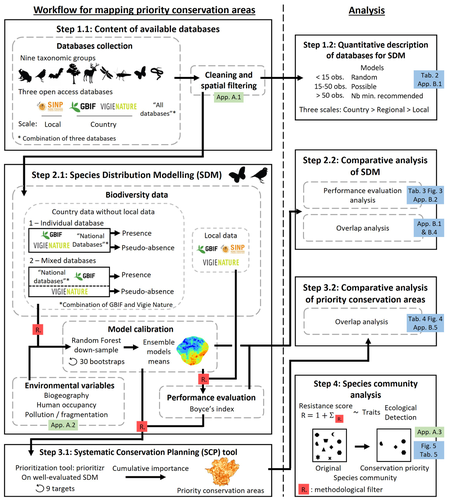
Integrating biodiversity assessments into local conservation planning: the importance of assessing suitable data sourcesThibaut Ferraille, Christian Kerbiriou, Charlotte Bigard, Fabien Claireau, John D. Thompson https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.09.539999Biodiversity databases are ever more numerous, but can they be used reliably for Species Distribution Modelling?Recommended by Nicolas Schtickzelle based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Proposing efficient guidelines for biodiversity conservation often requires the use of forecasting tools. Species Distribution Models (SDM) are more and more used to predict how the distribution of a species will react to environmental change, including any large-scale management actions that could be implemented. Their use is also boosted by the increase of publicly available biodiversity databases[1]. The now famous aphorism by George Box "All models are wrong but some are useful"[2] very well summarizes that the outcome of a model must be adjusted to, and will depend on, the data that are used to parameterize it. The question of the reliability of using biodiversity databases to parameterize biodiversity models such as SDM –but the question would also apply to other kinds of biodiversity models, e.g. Population Viability Analysis models[3]– is key to determine the confidence that can be placed in model predictions. This point is often overlooked by some categories of biodiversity conservation stakeholders, in particular the fact that some data were collected using controlled protocols while others are opportunistic. In this study[4], the authors use a collection of databases covering a range of species as well as of geographic scales in France and using different data collection and validation approaches as a case study to evaluate the impact of data quality when performing Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA). Among their conclusions, the fact that a large-scale database (what they call the “country” level) is necessary to reliably parameterize SDM. Besides this and other conclusions of their study, which are likely to be in part specific to their case study –unfortunately for its conservation, biodiversity is complex and varies a lot–, the merit of this work lies in the approach used to test the impact of data on model predictions. References 1. Feng, X. et al. A review of the heterogeneous landscape of biodiversity databases: Opportunities and challenges for a synthesized biodiversity knowledge base. Global Ecology and Biogeography 31, 1242–1260 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.13497 2. Box, G. E. P. Robustness in the Strategy of Scientific Model Building. in Robustness in Statistics (eds. Launer, R. L. & Wilkinson, G. N.) 201–236 (Academic Press, 1979). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-438150-6.50018-2. 3. Beissinger, S. R. & McCullough, D. R. Population Viability Analysis. (The University of Chicago Press, 2002). 4. Ferraille, T., Kerbiriou, C., Bigard, C., Claireau, F. & Thompson, J. D. (2023) Integrating biodiversity assessments into local conservation planning: the importance of assessing suitable data sources. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.05.09.539999 | Integrating biodiversity assessments into local conservation planning: the importance of assessing suitable data sources | Thibaut Ferraille, Christian Kerbiriou, Charlotte Bigard, Fabien Claireau, John D. Thompson | <p>Strategic Environmental Assessment (SEA) of land-use planning is a fundamental tool to minimize environmental impacts of artificialization. In this context, Systematic Conservation Planning (SCP) tools based on Species Distribution Models (SDM)... |  | Biodiversity, Conservation biology, Species distributions, Terrestrial ecology | Nicolas Schtickzelle | 2023-05-11 09:41:05 | View | |
01 Oct 2023
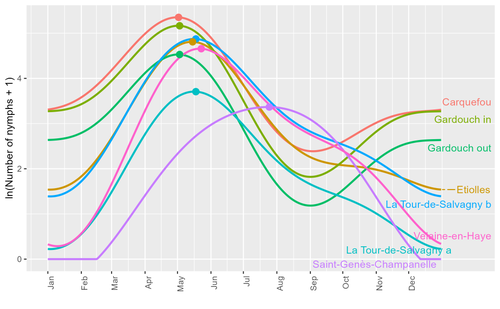
Seasonality of host-seeking Ixodes ricinus nymph abundance in relation to climateThierry Hoch, Aurélien Madouasse, Maude Jacquot, Phrutsamon Wongnak, Fréderic Beugnet, Laure Bournez, Jean-François Cosson, Frédéric Huard, Sara Moutailler, Olivier Plantard, Valérie Poux, Magalie René-Martellet, Muriel Vayssier-Taussat, Hélène Verheyden, Gwenaёl Vourc’h, Karine Chalvet-Monfray, Albert Agoulon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.25.501416Assessing seasonality of tick abundance in different climatic regionsRecommended by Nigel Yoccoz based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Tick-borne pathogens are considered as one of the major threats to public health – Lyme borreliosis being a well-known example of such disease. Global change – from climate change to changes in land use or invasive species – is playing a role in the increased risk associated with these pathogens. An important aspect of our knowledge of ticks and their associated pathogens is seasonality – one component being the phenology of within-year tick occurrences. This is important both in terms of health risk – e.g., when is the risk of encountering ticks high – and ecological understanding, as tick dynamics may depend on the weather as well as different hosts with their own dynamics and habitat use. Hoch et al. (2023) provide a detailed data set on the phenology of one species of tick, Ixodes ricinus, in 6 different locations of France. Whereas relatively cool sites showed a clear peak in spring-summer, warmer sites showed in addition relatively high occurrences in fall-winter, with a minimum in late summer-early fall. Such results add robust data to the existing evidence of the importance of local climatic patterns for explaining tick phenology. Recent analyses have shown that the phenology of Lyme borreliosis has been changing in northern Europe in the last 25 years, with seasonal peaks in cases occurring now 6 weeks earlier (Goren et al. 2023). The study by Hoch et al. (2023) is of too short duration to establish temporal changes in phenology (“only” 8 years, 2014-2021, see also Wongnak et al 2021 for some additional analyses; given the high year-to-year variability in weather, establishing phenological changes often require longer time series), and further work is needed to get better estimates of these changes and relate them to climate, land-use, and host density changes. Moreover, the phenology of ticks may also be related to species-specific tick phenology, and different tick species do not respond to current changes in identical ways (see for example differences between the two Ixodes species in Finland; Uusitalo et al. 2022). An efficient surveillance system requires therefore an adaptive monitoring design with regard to the tick species as well as the evolving causes of changes. References Goren, A., Viljugrein, H., Rivrud, I. M., Jore, S., Bakka, H., Vindenes, Y., & Mysterud, A. (2023). The emergence and shift in seasonality of Lyme borreliosis in Northern Europe. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 290(1993), 20222420. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2022.2420 Hoch, T., Madouasse, A., Jacquot, M., Wongnak, P., Beugnet, F., Bournez, L., . . . Agoulon, A. (2023). Seasonality of host-seeking Ixodes ricinus nymph abundance in relation to climate. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.25.501416 Uusitalo, R., Siljander, M., Lindén, A., Sormunen, J. J., Aalto, J., Hendrickx, G., . . . Vapalahti, O. (2022). Predicting habitat suitability for Ixodes ricinus and Ixodes persulcatus ticks in Finland. Parasites & Vectors, 15(1), 310. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-022-05410-8 Wongnak, P., Bord, S., Jacquot, M., Agoulon, A., Beugnet, F., Bournez, L., . . . Chalvet-Monfray, K. (2022). Meteorological and climatic variables predict the phenology of Ixodes ricinus nymph activity in France, accounting for habitat heterogeneity. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 7833. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-11479-z | Seasonality of host-seeking *Ixodes ricinus* nymph abundance in relation to climate | Thierry Hoch, Aurélien Madouasse, Maude Jacquot, Phrutsamon Wongnak, Fréderic Beugnet, Laure Bournez, Jean-François Cosson, Frédéric Huard, Sara Moutailler, Olivier Plantard, Valérie Poux, Magalie René-Martellet, Muriel Vayssier-Taussat, Hélène Ve... | <p style="text-align: justify;">There is growing concern about climate change and its impact on human health. Specifically, global warming could increase the probability of emerging infectious diseases, notably because of changes in the geographic... |  | Climate change, Population ecology, Statistical ecology | Nigel Yoccoz | 2022-10-14 18:43:56 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Vasilis Dakos (Representative)
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










