Direct submissions to PCI Ecology from bioRxiv.org are possible using the B2J service
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
26 Aug 2024
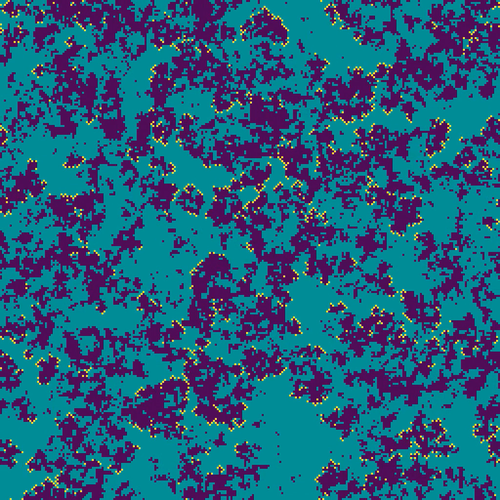
Easy, fast and reproducible Stochastic Cellular Automata with choucaAlexandre Génin, Guillaume Dupont, Daniel Valencia, Mauro Zucconi, M. Isidora Ávila-Thieme, Sergio A. Navarrete, Evie A. Wieters https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.08.566206An R package for flexible and fast Stochastic Cellular Automata modelingRecommended by Samuel Alizon based on reviews by Broder Breckling and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Broder Breckling and 1 anonymous reviewer
Stochastic Cellular Automata (SCA) are a popular modelling tool because in, spite of their simplicity, they can generate a variety of spatial patterns. This makes them particularly appreciated, for instance, to validate the insights of analytical or semi-analytical spatial models that make simplifying assumptions, e.g. moment equations models. A first limit to SCA are that as soon as details are added to the model, reproducibility issues may occur. Computation speed is also an issue, especially for large populations. The work by Génin et al. addresses these two issues through the development of an R package, chouca. The use of the package is designed to be as smooth as possible: users only need to define the type of possible transitions along with their rates, the parameter values, the number of neighbours, and the initial state of the landscape. The main function returns the population dynamics of each state and even the final state of the landscape. In addition to its flexibility, an asset of chouca resides in its use of the Rcpp package, which compiles the model designed by the user in C++. This allows for high computation speed, which can be further boosted by using parallelising options from R. In their manuscript, the authors use ecological models to illustrate the more advanced possibilities opened by chouca, e.g. in terms of graphical interpretation or even to estimate parameter values by computing likelihood functions (the implementation in R does make it very appropriate for statistical inference in general). The package still has some limitations, and, for example, it currently only applied to 2D rectangular grids and it cannot include elaborate movement processes. However, some of these could be addressed in future releases and chouca already has the potential to become central for SCA modelling, both for beginners and expert users, especially in ecology. References Alexandre Génin, Guillaume Dupont, Daniel Valencia, Mauro Zucconi, M. Isidora Ávila-Thieme, Sergio A. Navarrete, Evie A. Wieters (2024) Easy, fast and reproducible Stochastic Cellular Automata with chouca. bioRxiv, ver.6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.08.566206 | Easy, fast and reproducible Stochastic Cellular Automata with chouca | Alexandre Génin, Guillaume Dupont, Daniel Valencia, Mauro Zucconi, M. Isidora Ávila-Thieme, Sergio A. Navarrete, Evie A. Wieters | <p style="text-align: justify;">Stochastic cellular automata (SCA) are models that describe spatial dynamics using a grid of cells that switch between discrete states over time. They are widely used to understand how small-scale processes scale up... |  | Community ecology, Landscape ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Statistical ecology, Theoretical ecology | Samuel Alizon | 2024-03-11 10:54:39 | View | |
26 Aug 2024

Urban Cepaea nemoralis snails are less likely to have nematodes trapped within their shellsMaxime Dahirel, Hannah Reyné, Katrien De Wolf, Dries Bonte https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.07.583959Urbanisation linked to a decline in the proportion of snails with trapped nematodes in their shellRecommended by Alison Duncan based on reviews by Robbie Rae and 1 anonymous reviewerUrbanisation modifies species’ habitats affecting their density, distribution, fitness, and behaviour with knock-on effects for their parasites’ abundance and transmission (Bradley & Altizer 2007). A meta-analysis found that changes in resource provisioning due to anthropogenic change can have both positive and negative effects on parasite infection in wildlife populations, but that feeding on urban waste had an effect of reducing infection, especially for helminths and protozoa (Becker, Streicker & Altizer 2015). Another study found that urbanisation reduced ectoparasite load in birds, but had no effect on endoparasites or avian flu (Reid et al. 2024). These changes may be due to novel diets reducing transmission via predation upon trophic hosts (Becker, Streicker & Altizer 2015) or behavioural, leading to more time available to preen (Reid et al. 2024). Less is known about how urbanisation affects invertebrates (but see Lewthwaite et al., 2024) and their parasites. This is important considering that invertebrates are often intermediate hosts of, and/or vector other parasites. Recent work has found that snails and slugs can trap nematodes in their shells to prevent infection (Rae 2017). This newly discovered resistance mechanism reveals that the shell serves an immune defence function. It also provides a record of nematode exposure and documents incidences of resistance to infection as the trapped nematode becomes fixed onto the shell surface (Rae 2017). Dahirel and co-authors exploit this to investigate whether snail-nematode interactions change in response to increasing levels of urbanisation (Dahirel et al. 2024). They explore whether the proportion of Cepaea nemoralis snails with trapped nematodes in their shell changes across an urbanisation gradient. They also explore whether different phenotypic snail traits, notably shell size, colour, band number and fusion explain the likelihood of having trapped nematodes in their shells. An increase in urbanisation was associated with a decrease in the proportion of snails with trapped nematodes in their shells. At the same time larger shells were more likely to have trapped nematodes, but this effect did not change across the urbanisation gradient. The authors discuss that reduced nematode encapsulation in urban environments may be due to lower encounter rate due to either fewer nematodes in urban environments, changes in snail behaviour reducing exposure, or alternatively that urban snails were less resistant to nematode infection. It will be interesting to investigate how this resistance mechanism is related to other forms of snail immunity and whether high rates of nematode encapsulation are an indicator of high resistance or high exposure. This will enable nematode trapping to be used as a marker to indicate environments and/or snail populations harbouring high levels of parasitism and further exploitation of museum collections to understand host-parasite interactions in the past (Rae 2017). References Becker, D.J., Streicker, D.G. & Altizer, S. (2015) Linking anthropogenic resources to wildlife-pathogen dynamics: a review and meta-analysis. Ecol Lett, 18, 483-495. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12428 Bradley, C.A. & Altizer, S. (2007) Urbanization and the ecology of wildlife diseases. Trends Ecol Evol, 22, 95-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.11.001 Maxime Dahirel, Hannah Reyné, Katrien De Wolf, Dries Bonte (2024) Urban Cepaea nemoralis snails are less likely to have nematodes trapped within their shells. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.07.583959 Lewthwaite, J.M.M., Baiotto, T.M., Brown, B.V., Cheung, Y.Y., Baker, A.J., Lehnen, C., McGlynn, T.P., Shirey, V., Gonzalez, L., Hartop, E., Kerr, P.H., Wood, E. & Guzman, L.M. (2024) Drivers of arthropod biodiversity in an urban ecosystem. Sci Rep, 14, 390. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-50675-3 Rae, R. (2017) The gastropod shell has been co-opted to kill parasitic nematodes. Sci Rep, 7, 4745. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-04695-5 Reid, R., Capilla-Lasheras, P., Haddou, Y., Boonekamp, J. & Dominoni, D.M. (2024) The impact of urbanization on health depends on the health metric, life stage and level of urbanization: a global meta-analysis on avian species. Proc Biol Sci, 291, 20240617. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2024.0617 | Urban *Cepaea nemoralis* snails are less likely to have nematodes trapped within their shells | Maxime Dahirel, Hannah Reyné, Katrien De Wolf, Dries Bonte | <p style="text-align: justify;">Urbanisation is a major human-induced environmental change which can impact not only individual species, but also the way these species interact with each other. As a group, terrestrial molluscs interact frequently ... |  | Host-parasite interactions, Human impact | Alison Duncan | 2024-03-11 11:35:15 | View | |
20 Aug 2024
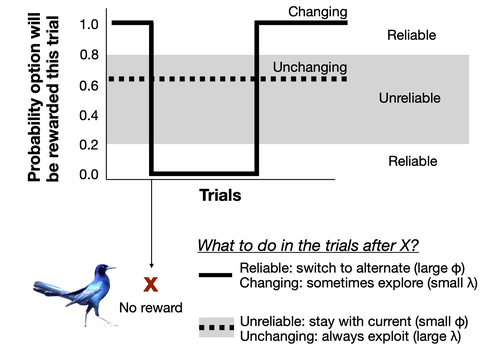
Bayesian reinforcement learning models reveal how great-tailed grackles improve their behavioral flexibility in serial reversal learning experimentsDieter Lukas, Kelsey B. McCune, Aaron P. Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Maggie MacPherson, Benjamin M. Seitz, Augustus Sevchik, Corina J. Logan https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/4ycpsChanges in behavioral flexibility to cope with environment instability: theoretical and empirical insights from serial reversal learning experimentsRecommended by Aurélie Coulon based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and 1 anonymous reviewer
Behavioral flexibility, i.e. the “ability to adapt behavior to new circumstances through packaging information and making it available to other cognitive processes” (Logan et al. 2023), appears as one of the crucial elements of responses of animal species to changing environments. Behavioral flexibility can change within the life of individuals, depending on their experience on the degree of variability and predictability of their surrounding environment. But little is known on the cognitive processes involved in these temporal changes in behavioral flexibility within individuals. This is what Lukas et al. (2024) investigated very thoroughly, using the framework of serial reversal learning experiments on great-tailed grackles to study different aspects of the question. Behavioral flexibility as involved in serial reversal learning experiments was previously modeled as being made of two primary parameters: the rate of updating associations, phi (i.e. how fast individuals learn the associations between a cue and its associated reward or danger); and the sensitivity to the learned associations, lambda (i.e. how strong do individuals make their choices based on the associations they learned). Lukas et al. (2024)* used a Bayesian reinforcement model to infer phi and lambda in individuals going through serial reversal learning experiments, to understand which of these two parameters explains most of the variation in grackle performance in serial reversal learning, how correlated they are, how they can change along time depending on an individual’s experience, how variable they can be among individuals, and whether they can predict performance in other contexts. But beforehand, the authors used an individual-based model to assess the ability of the Bayesian reinforcement model to correctly assess phi and lambda in their experimental design. They also used the Bayesian model to infer the range of values of phi and lambda an individual needs to exhibit to reduce errors in the serial reversal learning experiment. Among other results, this study shows that in a context of rapidly changing but strongly reliable cues, the variation in the success of grackles is more associated with the rate of updating associations (phi) than the sensitivity to learned associations (lambda). Besides, phi increased within individuals along the serial reversal learning experiment, while lambda only slightly decreased. However, it is very interesting to note that different approaches could be adopted by different individuals through the training, leading them eventually to the same final performance: slightly different combinations of changes in lambda and phi lead to different behaviours but compensate each other in the end in the final success rate. References Coulon, A. (2019) Can context changes improve behavioral flexibility? Towards a better understanding of species adaptability to environmental changes. Peer Community in Ecology, 100019. https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100019 Logan, CJ, Lukas D, Bergeron L, Folsom M, McCune, K. (2019). Is behavioral flexibility related to foraging and social behavior in a rapidly expanding species? In Principle Acceptance by PCI Ecology of the Version on 6 Aug 2019. http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_flexmanip.html Dieter Lukas, Kelsey B. McCune, Aaron P. Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Maggie MacPherson, Benjamin M. Seitz, Augustus Sevchik, Corina J. Logan (2024) Bayesian reinforcement learning models reveal how great-tailed grackles improve their behavioral flexibility in serial reversal learning experiments. ecoevoRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/4ycps | Bayesian reinforcement learning models reveal how great-tailed grackles improve their behavioral flexibility in serial reversal learning experiments | Dieter Lukas, Kelsey B. McCune, Aaron P. Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Maggie MacPherson, Benjamin M. Seitz, Augustus Sevchik, Corina J. Logan | <p>Environments can change suddenly and unpredictably and animals might benefit from being able to flexibly adapt their behavior through learning new associations. Serial (repeated) reversal learning experiments have long been used to investigate ... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Phenotypic plasticity, Preregistrations, Zoology | Aurélie Coulon | 2022-08-15 21:04:14 | View | |
16 Aug 2024
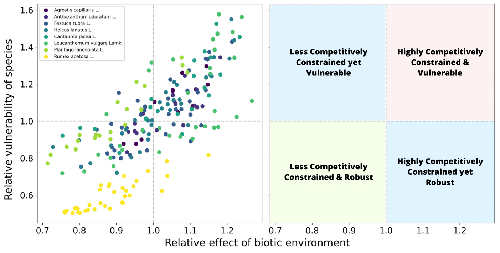
The distribution of distances to the edge of species coexistenceMario Desallais, Michel Loreau, Jean-François Arnoldi https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.21.575550How environmental perturbations affect coexistenceRecommended by Frederik De Laender based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Oscar Godoy, Pablo Lechon and 1 anonymous reviewer Understanding the effects of environmental perturbations on coexistence is a key challenge in ecology, and models have played an important role in structuring our ideas and generating predictions, leading to quantitative hypotheses. In such models, environmental perturbations are often captured by changes in parameter values, such as the intrinsic growth rates of species (1–3). The question then becomes how much one can change these parameters without breaking coexistence and thus losing species (4). References 1. Baert, J.M., Janssen, C.R., Sabbe, K., and De Laender, F. (2016). Per capita interactions and stress tolerance drive stress-induced changes in biodiversity effects on ecosystem functions. Nat. Commun. 7, 12486. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12486 8. Desallais M, Loreau M, Arnoldi J.F. (2024) The distribution of distances to the edge of species coexistence. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.21.575550 | The distribution of distances to the edge of species coexistence | Mario Desallais, Michel Loreau, Jean-François Arnoldi | <p>In Lotka-Volterra community models, given a set of biotic interactions, recent approaches have analysed the probability of finding a set of species intrinsic growth rates (representing intraspecific demographic features) that will allow coexist... |  | Coexistence, Community ecology, Competition, Facilitation & Mutualism, Interaction networks, Theoretical ecology | Frederik De Laender | 2024-02-15 14:17:32 | View | |
09 Aug 2024
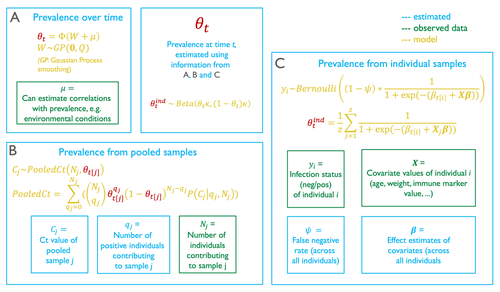
Reconstructing prevalence dynamics of wildlife pathogens from pooled and individual samplesBenny Borremans, Caylee A. Falvo, Daniel E. Crowley, Andrew Hoegh, James O. Lloyd-Smith, Alison J. Peel, Olivier Restif, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena, Raina K. Plowright https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.02.565200Pooled samples hold information about the prevalence of wildlife pathogensRecommended by Timothée Poisot based on reviews by Megan Griffiths and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Megan Griffiths and 2 anonymous reviewers
Although monitoring the prevalence of pathogens in wildlife is crucial, there are logistical constraints that make this difficult, costly, and unpractical. This problem is often compounded when attempting to measure the temporal dynamics of prevalence. To improve the detection rate, a commonly used technique is pooling samples, where multiple individuals are analyzed at once. Yet, this introduces further potential biases: low-prevalence samples are effectively diluted through pooling, creating a false negative risk; negative samples are masked by the inclusion of positive samples, possibly artificially inflating the estimate of prevalence (and masking the inter-sample variability). In their contribution, Borremans et al. (2024) come up with a modelling technique to provide accurate predictions of prevalence dynamics using a mix of pooled and individual samples. Because this model represents the pooling of individual samples as a complete mixing process, it can accurately estimate the prevalence dynamics from pooled samples only. It is particularly noteworthy that the model provides an estimation of the false negative rate of the test. When there are false negatives (or more accurately, when the true rate at which false negatives happens), the value of the effect coefficients for individual-level covariates are likely to be off, potentially by a substantial amount. But besides more accurate coefficient estimation, the actual false negative rate is important information about the overall performance of the infection test. The model described in this article also allows for a numerical calculation of the probability density function of infection. It is worth spending some time on how this is achieved, as I found the approach relying on combinatorics to be particularly interesting. When pooling, both the number of individuals that are mixed is known, and so is the measurement made on the pooled samples. The question is to figure out the number of individuals that because they are infectious, contribute to this score. The approach used by the authors is to draw (with replacement) possible positive and negative test outcomes assuming a number of positive individuals, and from this to estimate a pathogen concentration in the positive samples. This pathogen concentration can be transformed into its test outcome, and this value taken over all possible combinations is a conditional estimate of the test outcome, knowing the number of pooled individuals, and estimating the number of positive ones. This approach is where the use of individual samples informs the model: by providing additional corrections for the relative volume of sample each individual provides, and by informing the transformation of test values into virus concentrations. The authors make a strong case that their model can provide robust estimates of prevalence even in the presence of common field epidemiology pitfalls, and notably incomplete individual-level information. More importantly, because the model can work from pooled samples only, it gives additional value to samples that would otherwise have been discarded because they did not allow for prevalence estimates. References Benny Borremans, Caylee A. Falvo, Daniel E. Crowley, Andrew Hoegh, James O. Lloyd-Smith, Alison J. Peel, Olivier Restif, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena, Raina K. Plowright (2024) Reconstructing prevalence dynamics of wildlife pathogens from pooled and individual samples. bioRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.02.565200 | Reconstructing prevalence dynamics of wildlife pathogens from pooled and individual samples | Benny Borremans, Caylee A. Falvo, Daniel E. Crowley, Andrew Hoegh, James O. Lloyd-Smith, Alison J. Peel, Olivier Restif, Manuel Ruiz-Aravena, Raina K. Plowright | <p style="text-align: justify;">Pathogen transmission studies require sample collection over extended periods, which can be challenging and costly, especially in the case of wildlife. A useful strategy can be to collect pooled samples, but this pr... |  | Epidemiology, Statistical ecology | Timothée Poisot | Joshua Hewitt | 2023-11-21 23:16:20 | View |
29 Jun 2024
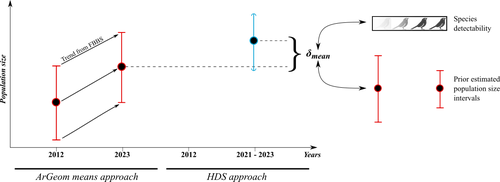
Reassessment of French breeding bird population sizes using citizen science and accounting for species detectabilityJean Nabias, Luc Barbaro, Benoit Fontaine, Jérémy Dupuy, Laurent Couzi, Clément Vallé, Romain Lorrillière https://hal.science/hal-04478371Reassessment of French breeding bird population sizes: from citizen science observations to nationwide estimatesRecommended by Nigel Yoccoz based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Estimating populations size of widespread, common species in a relatively large and heterogeneous country like France is difficult for several reasons, from having a sample covering well the diverse ecological gradients to accounting for detectability, the fact that absence of a species may represent a false negative, the species being present but not detected. Bird communities have been the focus of a very large number of studies, with some countries like the UK having long traditions of monitoring both common and rare species. Nabias et al. use a large, structured citizen science project to provide new estimates of common bird species, accounting for detectability and using different habitat and climate covariates to extrapolate abundance to non-sampled areas. About 2/3 of the species had estimates higher than what would have been expected using a previous attempt at estimating population size based in part on expert knowledge and projected using estimates of trends to the period covered by the citizen science sampling. Some species showed large differences between the two estimates, which could be in part explained by accounting for detectability. This paper uses what is called model-based inference (as opposed to design-based inference, that uses the design to make inferences about the whole population; Buckland et al. 2000), both in terms of detectability and habitat suitability. The estimates obtained depend on how well the model components approximate the underlying processes, which in a complex dataset like this one is not easy to assess. But it clearly shows that detectability may have substantial implications for the population size estimates. This is of course not new but has rarely been done at this scale and using a large sample obtained on many species. Interesting further work could focus on testing the robustness of the model-based approach by for example sampling new plots and compare the expected values to the observed values. Such a sampling could be stratified to maximize the discrimination between expected low and high abundances, at least for species where the estimates might be considered as uncertain, or for which estimating population sizes is deemed important. References Buckland, S. T., Goudie, I. B. J., & Borchers, D. L. (2000). Wildlife Population Assessment: Past Developments and Future Directions. Biometrics, 56(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00001.x Nabias, J., Barbaro, L., Fontaine, B., Dupuy, J., Couzi, L., et al. (2024) Reassessment of French breeding bird population sizes using citizen science and accounting for species detectability. HAL, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://hal.science/hal-04478371 | Reassessment of French breeding bird population sizes using citizen science and accounting for species detectability | Jean Nabias, Luc Barbaro, Benoit Fontaine, Jérémy Dupuy, Laurent Couzi, Clément Vallé, Romain Lorrillière | <p style="text-align: justify;">Higher efficiency in large-scale and long-term biodiversity monitoring can be obtained through the use of Essential Biodiversity Variables, among which species population sizes provide key data for conservation prog... |  | Biogeography, Macroecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Species distributions, Statistical ecology | Nigel Yoccoz | 2024-02-26 18:10:27 | View | |
28 Jun 2024
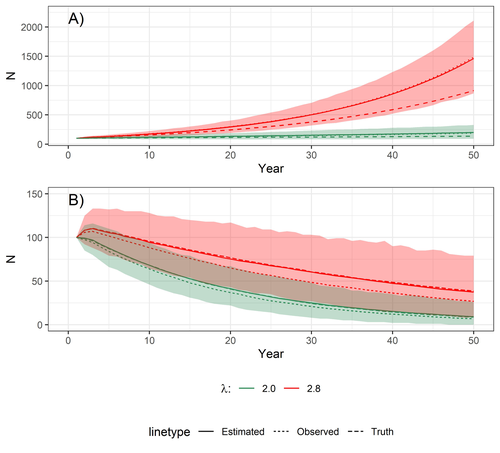
Accounting for observation biases associated with counts of young when estimating fecundity: case study on the arboreal-nesting red kite (Milvus milvus)Sollmann Rahel, Adenot Nathalie, Spakovszky Péter, Windt Jendrik, Brady J. Mattsson https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.01.569571Accounting for observation biases associated with counts of young: you may count too many or too few...Recommended by Nigel Yoccoz based on reviews by Steffen Oppel and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Steffen Oppel and 1 anonymous reviewer
Most species are hard to observe, and different methods are required to estimate demographic parameters such as the number of young individuals produced (one measure of breeding success) and survival. In the former case, and in particular for birds of prey, it often relies upon direct observations of breeding pairs on their nests. Two problems can then occur, that some young are missed and therefore the breeding success is underestimated (“false negatives”), but it is also possible that because for example of the nest structure or vegetation surrounding the nest, more young birds than in fact are present are counted (“false positives”). Sollmann et al. (2024) address this problem by using data where the truth is known as each nest was also accessed after climbing the tree, and a hierarchical model accounting for both undercounts and overcounts. Finally, they assess the impact of this correction on projected population size using simulations. This paper is a solid contribution to the panoply of methods and models that are available for monitoring populations, and has potential applications for many species for which both false positives and false negatives can be a problem. The results on the projected population sizes – showing that for growing populations correcting for bias can lead to large differences in population sizes after a few decades – may seem counterintuitive as population growth rate of long-lived species such as birds of prey is not very sensitive to a change in breeding success (as compared to adult survival). However, one should just be reminded that a small difference in population growth rate may translate to a large difference after many years – for example a growth rate of 1.05 after 50 years mean than population size is multiplied by 11.5, whereas a growth of 1.03 after 50 years mean a multiplication by 4.4, more than twice less individuals. Small differences may matter a lot if they are sustained, and a key aspect of management is to ensure that they are. Of course, management actions having an impact on survival may be more effective, but they might be harder to achieve than for example ensuring that birds of prey breed successfully. References Sollmann Rahel, Adenot Nathalie, Spakovszky Péter, Windt Jendrik, Mattsson Brady J. 2024. Accounting for observation biases associated with counts of young when estimating fecundity. bioRxiv, v. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.12.01.569571
| Accounting for observation biases associated with counts of young when estimating fecundity: case study on the arboreal-nesting red kite (*Milvus milvus*) | Sollmann Rahel, Adenot Nathalie, Spakovszky Péter, Windt Jendrik, Brady J. Mattsson | <p style="text-align: justify;">Counting the number of young in a brood from a distance is common practice, for example in tree-nesting birds. These counts can, however, suffer from over and undercounting, which can lead to biased estimates of fec... |  | Demography, Statistical ecology | Nigel Yoccoz | 2023-12-11 08:52:22 | View | |
20 Jun 2024

Spider mites collectively avoid plants with cadmium irrespective of their frequency or the presence of competitorsDiogo Prino Godinho, Ines Fragata, Maud Charlery de la Masseliere, Sara Magalhaes https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.17.553707We are better together: Spider mites running away from Cadmium contaminated plants make better decisions collectively than individuallyRecommended by Ruben Heleno based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Hyperaccumulator plants can concentrate heavy metals present on the soil in their tissues, avoiding their toxic effects and potentially discouraging herbivores (Martens & Boyd, 1994). But not all herbivores are necessarily discouraged, and access to locally abundant resources with low interspecific competition from other herbivores, can affect feeding choices. Godinho et al. performed a series of controlled laboratorial trials to evaluate if herbivores (spider mites) avoid tomato plants with high concentrations of Cadmium under alternative scenarios, namely: the presence/absence of conspecifics, the presence/absence of a competitor species (a congeneric mite), and the relative abundance of contaminated plants. They found that when looking for plants to lay their eggs, individual spider-mites (females) do not seem to discriminate between plants with or without cadmium, despite a significantly lower performance on the former. However, they consistently chose plants without Cadmium in set-ups where 200 mites are faced with this decision together. This preference was consistent and independent from the relative abundance of cadmium-free plants, but only when mites do this decision collectively. In addition, this preference was stronger than that for plants where interspecific competition was lower, with mites preferring to face high competition from congeneric herbivores than laying their eggs on Cadmium contaminated plants. Taken together these experiments suggest that aggregation is a key mechanism by which spider mites can avoid metal contaminated plants. As good research often does, these experiments open several important questions that will need to be addressed in the future. In particular, it will be important to clarify what are the sensorial and behavioural mechanisms that allow this decision/outcome when spider mites make this choice collectively but lead to a different outcome (no choice) when they face this decision alone. Additionally, it will be interesting to explore the potentially adaptive (or non-adaptive) consequences of this behaviour in terms of individual and inclusive fitness. One thing seems certain: both the abiotic and the biotic context can affect spider mite choices, and both need to be considered to advance our understanding about the trade-offs between plant defence mechanisms and associated herbivore decisions and fitness. References Martens, S. N., & Boyd, R. S. (1994). The ecological significance of nickel hyperaccumulation: a plant chemical defense. Oecologia, 98(3–4), 379–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00324227 Godinho, D. P., I. Fragata, M. C. de la Masseliere, S. Magalhaes 2024 Spider mites collectively avoid plants with cadmium irrespective of their frequency or the presence of competitors. bioRxiv, ver. 4, peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology 2023.08.17.553707. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.17.553707
| Spider mites collectively avoid plants with cadmium irrespective of their frequency or the presence of competitors | Diogo Prino Godinho, Ines Fragata, Maud Charlery de la Masseliere, Sara Magalhaes | <p>1. Plants can accumulate heavy metals from polluted soils on their shoots and use this to defend themselves against herbivory. One possible strategy for herbivores to cope with the reduction in performance imposed by heavy metal accumulation in... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Competition, Habitat selection, Herbivory | Ruben Heleno | 2023-11-09 11:52:58 | View | |
14 Jun 2024
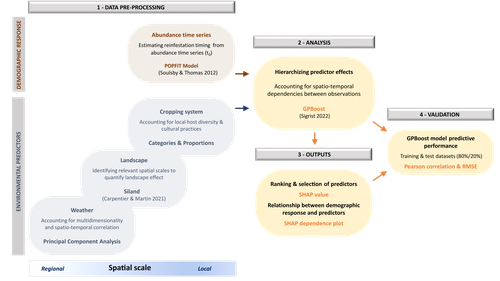
Hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effects on agricultural pest population dynamics: a case study on the annual onset of Bactrocera dorsalis population growth in Senegalese orchardsCécile Caumette, Paterne Diatta, Sylvain Piry, Marie-Pierre Chapuis, Emile Faye, Fabio Sigrist, Olivier Martin, Julien Papaïx, Thierry Brévault, Karine Berthier https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.10.566583Uncovering the ecology in big-data by hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effectsRecommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron and Jianqiang SunAlong with the generalization of open-access practices, large, heterogeneous datasets are becoming increasingly available to ecologists (Farley et al. 2018). While such data offer exciting opportunities for unveiling original patterns and trends, they also raise new challenges regarding how to extract relevant information and actually improve our knowledge of complex ecological systems, beyond purely descriptive correlations (Dietze 2017, Farley et al. 2018). In this work, Caumette et al. (2024) develop an original ecoinformatics approach to relate multi-scale environmental factors to the temporal dynamics of a major pest in mango orchards. Their method relies on the recent tree-boosting method GPBoost (Sigrist 2022) to hierarchize the influence of environmental factors of heterogeneous nature (e.g., orchard composition and management; landscape structure; climate) on the emergence date of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. As boosting methods allows the analysis of high-dimensional data, they are particularly adapted to the exploration of such datasets, to uncover unexpected, potentially complex dependencies between ecological dynamics and multiple environmental factors (Farley et al. 2018). In this article, Caumette et al. (2024) make a special effort to guide the reader step by step through their complex analysis pipeline to make it broadly understandable to the average ecologist, which is no small feat. I particularly welcome this commitment, as making new, cutting-edge analytical methods accessible to a large community of science practitioners with varying degrees of statistical or programming expertise is a major challenge for the future of quantitative ecology. The main result of Caumette et al. (2024) is that temperature and humidity conditions both at the local and regional scales are the main predictors of B. dorsalis emergence date, while orchard management practices seem to have relatively little influence. This suggests that favourable climatic conditions may allow the persistence of small populations of B. dorsalis over the dry season, which may then act as a propagule source for early re-infestations. However, as the authors explain, the resulting regression model is not designed for predictive purposes and should not at this stage be used for decision-making in pest management. Its main interest rather resides in identifying potential key factors favoring early infestations of B. dorsalis, and help focusing future experimental field studies on the most relevant levers for integrated pest management in mango orchards. In a wider perspective, this work also provides a convincing proof-of-concept for the use of boosting methods to identify the most influential factors in large, multivariate datasets in a variety of ecological systems. It is also crucial to keep in mind that the current exponential growth in high-throughput environmental data (Lucivero 2020) could quickly come into conflict with the need to reduce the environmental footprint of research (Mariette et al. 2022). In this context, robust and accessible methods for extracting and exploiting all the information available in already existing datasets might prove essential to a sustainable pursuit of science. References Dietze MC. 2017. Ecological Forecasting. Princeton University Press Mariette J, Blanchard O, Berné O, Aumont O, Carrey J, Ligozat A-L, Lellouch E, Roche P-E, Guennebaud G, Thanwerdas J, Bardou P, Salin G, Maigne E, Servan S, Ben-Ari T 2022. An open-source tool to assess the carbon footprint of research. Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability, 2022. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/2634-4505/ac84a4 | Hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effects on agricultural pest population dynamics: a case study on the annual onset of *Bactrocera dorsalis* population growth in Senegalese orchards | Cécile Caumette, Paterne Diatta, Sylvain Piry, Marie-Pierre Chapuis, Emile Faye, Fabio Sigrist, Olivier Martin, Julien Papaïx, Thierry Brévault, Karine Berthier | <p>Implementing integrated pest management programs to limit agricultural pest damage requires an understanding of the interactions between the environmental variability and population demographic processes. However, identifying key environmental ... |  | Demography, Landscape ecology, Statistical ecology | Elodie Vercken | 2023-12-11 17:02:08 | View | |
05 Jun 2024
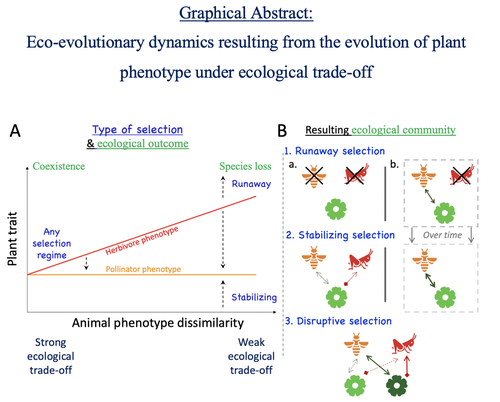
Attracting pollinators vs escaping herbivores: eco-evolutionary dynamics of plants confronted with an ecological trade-offYoussef Yacine, Nicolas Loeuille https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.02.470900Plant-herbivore-pollinator ménage-à-trois: tell me how well they match, and I'll tell you if it's made to lastRecommended by Sylvain Billiard based on reviews by Marcos Mendez and Yaroslav Ispolatov based on reviews by Marcos Mendez and Yaroslav Ispolatov
How would a plant trait evolve if it is involved in interacting with both a pollinator and an herbivore species? The answer by Yacine and Loeuille is straightforward: it is not trivial, but it can explain many situations found in natural populations. Yacine and Loeuille applied the well-known Adaptive Dynamics framework to a system with three interacting protagonists: a herbivore, a pollinator, and a plant. The evolution of a plant trait is followed under the assumption that it regulates the frequency of interaction with the two other species. As one can imagine, that is where problems begin: interacting more with pollinators seems good, but what if at the same time it implies interacting more with herbivores? And that's not a silly idea, as there are many cases where herbivores and pollinators share the same cues to detect plants, such as colors or chemical compounds. They found that depending on the trade-off between the two types of interactions and their density-dependent effects on plant fitness, the possible joint ecological and evolutionary outcomes are numerous. When herbivory prevails, evolution can make the ménage-à-trois ecologically unstable, as one or even two species can go extinct, leaving the plant alone. Evolution can also make the coexistence of the three species more stable when pollination services prevail, or lead to the appearance of a second plant species through branching diversification of the plant trait when herbivory and pollination are balanced. Yacine and Loeuille did not only limit themselves to saying "it is possible," but they also did much work evaluating when each evolutionary outcome would occur. They numerically explored in great detail the adaptive landscape of the plant trait for a large range of parameter values. They showed that the global picture is overall robust to parameter variations, strengthening the plausibility that the evolution of a trait involved in antagonistic interactions can explain many of the correlations between plant and animal traits or phylogenies found in nature. Are we really there yet? Of course not, as some assumptions of the model certainly limit its scope. Are there really cases where plants' traits evolve much faster than herbivores' and pollinators' traits? Certainly not, but the model is so general that it can apply to any analogous system where one species is caught between a mutualistic and a predator species, including potential species that evolve much faster than the two others. And even though this limitation might cast doubt on the generality of the model's predictions, studying a system where a species' trait and a preference trait coevolve is possible, as other models have already been studied (see Fritsch et al. 2021 for a review in the case of evolution in food webs). We can bet this is the next step taken by Yacine and Loeuille in a similar framework with the same fundamental model, promising fascinating results, especially regarding the evolution of complex communities when species can accumulate after evolutionary branchings. Relaxing another assumption seems more challenging as it would certainly need to change the model itself: interacting species generally do not play fixed roles, as being mutualistic or antagonistic might generally be density-dependent (Holland and DeAngelis 2010). How would the exchange of resources between three interacting species evolve? It is an open question. References Fritsch, C., Billiard, S., & Champagnat, N. (2021). Identifying conversion efficiency as a key mechanism underlying food webs adaptive evolution: a step forward, or backward? Oikos, 130(6), 904-930. Yacine, Y., & Loeuille, N. (2024) Attracting pollinators vs escaping herbivores: eco-evolutionary dynamics of plants confronted with an ecological trade-off. bioRxiv 2021.12.02.470900; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.02.470900 | Attracting pollinators vs escaping herbivores: eco-evolutionary dynamics of plants confronted with an ecological trade-off | Youssef Yacine, Nicolas Loeuille | <p style="text-align: justify;">Many plant traits are subject to an ecological trade-off between attracting pollinators and escaping herbivores. The interplay of both plant-animal interaction types determines their evolution. As most studies focus... |  | Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Herbivory, Pollination, Theoretical ecology | Sylvain Billiard | 2023-03-21 14:23:12 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Vasilis Dakos (Representative)
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










