
VERCKEN Elodie
- Institut Sophia Agrobiotech, INRA, Sophia Antipolis, France
- Biological control, Biological invasions, Demography, Dispersal & Migration, Evolutionary ecology, Experimental ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations
- recommender
Recommendations: 4
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 4
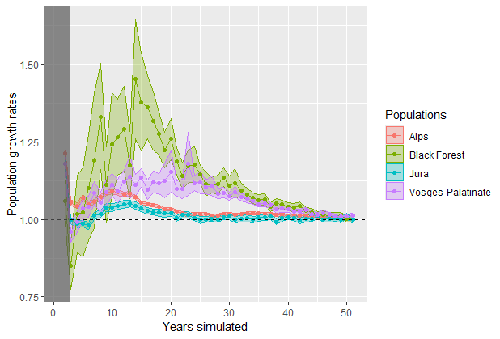
Modelling Eurasian lynx populations in Western Europe: What prospects for the next 50 years?
Glimmers of hope for the Eurasian lynx in Western Europe
Recommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by Hector Ruiz and Henrik AndrenThe conservation of large carnivores remains a challenge for biodiversity conservation (Ingeman et al. 2022), as they combine strict ecological requirements (large territories, sensitivity to human disturbance) with coexistence conflicts with human activities (livestock farming, hunting, risk perception). Although the Eurasian lynx is currently considered as “least concerned” by the IUCN Red List, this favorable status conceals major disparities between the remaining historical population nuclei in Northern and Eastern Europe and small, isolated populations in Western Europe resulting from reintroduction programs for which long-term persistence remains in jeopardy (Chapron et al. 2014).
Several ambitious conservation programs have been launched to try and improve the long-term demographic status of these still fragile populations (e.g., Swiss Lynx Project, French National Action Plan for the Eurasian Lynx), and conservation actors have a dire need for modelling of population dynamics to project demographic trajectories and compare scenarios of alternative conservation actions (Gatti 2022). A major challenge for making accurate demographic predictions is that lynx are characterized by extensive territories, and their demographic processes are expected to be strongly dependent on landscape characteristics. To address this challenge and capture the complexity of interactions between landscape structure and lynx dispersal, survival and reproduction, Bauduin et al. (2025) develop here a spatially explicit individual-based model for the four Western European populations of Eurasian lynx: Alps, Jura, Vosges and Black Forest. They use fine-scale data on movement and habitat use as well as road collisions to build a detailed spatial layer of habitat suitability and collision risk to predict the demographic trajectory and spatial repartition of the four Western European core populations over the next 50 years. Their simulations reveal an optimistic outlook offer for the future of the lynx : the sizes of the four population cores are predicted to increase steadily until stabilization at saturation within 20-40 years. Furthermore, the four populations are expected to act as a functional metapopulation, with regular exchanges of individuals between adjacent populations.
These results open up a wide range of perspectives. First, different conservation scenarios (e.g., reintroduction strategies, landscape evolution, changes in fragmentation) can be run using the framework of the model and compared to identify priority actions. Second, the predictions of lynx expansion into new areas (like Italian and French Alps) can be used to anticipate potential usage conflicts and develop coexistence strategies to improve social acceptance of the species in these target areas.
Although genetic information and the effects of inbreeding depression were not included in the model and could significantly lower the predicted growth rates in the long term, the conclusions are robust to a wide range of parameter values, and can be used both to inform lynx conservation strategies and to provide a priceless basis for the development of other SE-IBM for large mammals in human-inhabited landscapes.
References
Bauduin S, Germain E, Zimmermann F, Idelberger S, Herdtfelder M, Heurich M, Kramer-Schadt S, Duchamp C, Drouet-Hoguet N, Morand A, Blanc L, Charbonnel A, Gimenez O. 2025. Modelling Eurasian lynx populations in Western Europe: What prospects for the next 50 years?https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.22.465393
Chapron G, et al. 2014. Recovery of large carnivore in Europe’s modern human-dominated landscapes. Science 345: 1517-1519 https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1257553
Gatti S. 2022. National Action Plan for the Eurasian Lynx: restoring the Lynx to a favorable conservation status un France (2022-2026), 176 p.
Ingeman, K.E., Zhao, L.Z., Wolf, C. et al. 2022. Glimmers of hope in large carnivore recoveries.Sci Rep 12, 10005 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13671-7
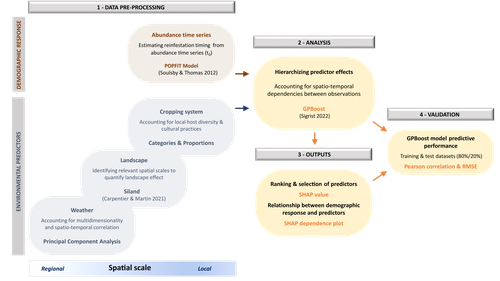
Hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effects on agricultural pest population dynamics: a case study on the annual onset of Bactrocera dorsalis population growth in Senegalese orchards
Uncovering the ecology in big-data by hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effects
Recommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron and Jianqiang SunAlong with the generalization of open-access practices, large, heterogeneous datasets are becoming increasingly available to ecologists (Farley et al. 2018). While such data offer exciting opportunities for unveiling original patterns and trends, they also raise new challenges regarding how to extract relevant information and actually improve our knowledge of complex ecological systems, beyond purely descriptive correlations (Dietze 2017, Farley et al. 2018).
In this work, Caumette et al. (2024) develop an original ecoinformatics approach to relate multi-scale environmental factors to the temporal dynamics of a major pest in mango orchards. Their method relies on the recent tree-boosting method GPBoost (Sigrist 2022) to hierarchize the influence of environmental factors of heterogeneous nature (e.g., orchard composition and management; landscape structure; climate) on the emergence date of the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. As boosting methods allows the analysis of high-dimensional data, they are particularly adapted to the exploration of such datasets, to uncover unexpected, potentially complex dependencies between ecological dynamics and multiple environmental factors (Farley et al. 2018). In this article, Caumette et al. (2024) make a special effort to guide the reader step by step through their complex analysis pipeline to make it broadly understandable to the average ecologist, which is no small feat. I particularly welcome this commitment, as making new, cutting-edge analytical methods accessible to a large community of science practitioners with varying degrees of statistical or programming expertise is a major challenge for the future of quantitative ecology.
The main result of Caumette et al. (2024) is that temperature and humidity conditions both at the local and regional scales are the main predictors of B. dorsalis emergence date, while orchard management practices seem to have relatively little influence. This suggests that favourable climatic conditions may allow the persistence of small populations of B. dorsalis over the dry season, which may then act as a propagule source for early re-infestations. However, as the authors explain, the resulting regression model is not designed for predictive purposes and should not at this stage be used for decision-making in pest management. Its main interest rather resides in identifying potential key factors favoring early infestations of B. dorsalis, and help focusing future experimental field studies on the most relevant levers for integrated pest management in mango orchards.
In a wider perspective, this work also provides a convincing proof-of-concept for the use of boosting methods to identify the most influential factors in large, multivariate datasets in a variety of ecological systems. It is also crucial to keep in mind that the current exponential growth in high-throughput environmental data (Lucivero 2020) could quickly come into conflict with the need to reduce the environmental footprint of research (Mariette et al. 2022). In this context, robust and accessible methods for extracting and exploiting all the information available in already existing datasets might prove essential to a sustainable pursuit of science.
References
Caumette C, Diatta P, Piry S, Chapuis M-P, Faye E, Sigrist F, Martin O, Papaïx J, Brévault T, Berthier K. 2024. Hierarchizing multi-scale environmental effects on agricultural pest population dynamics: a case study on the annual onset of Bactrocera dorsalis population growth in Senegalese orchards. bioRxiv 2023.11.10.566583, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.11.10.566583
Dietze MC. 2017. Ecological Forecasting. Princeton University Press
Farley SS, Dawson A, Goring SJ, Williams JW. 2018. Situating Ecology as a Big-Data Science: Current Advances, Challenges, and Solutions. BioScience, 68, 563–576, https://doi.org/10.1093/biosci/biy068
Lucivero F. 2020. Big Data, Big Waste? A Reflection on the Environmental Sustainability of Big Data Initiatives. Science and Engineering Ethics 26, 1009–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11948-019-00171-7
Mariette J, Blanchard O, Berné O, Aumont O, Carrey J, Ligozat A-L, Lellouch E, Roche P-E, Guennebaud G, Thanwerdas J, Bardou P, Salin G, Maigne E, Servan S, Ben-Ari T 2022. An open-source tool to assess the carbon footprint of research. Environmental Research: Infrastructure and Sustainability, 2022. https://dx.doi.org/10.1088/2634-4505/ac84a4
Sigrist F. 2022. Gaussian process boosting. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 23, 10565-10610. https://jmlr.org/papers/v23/20-322.html

Effects of climate warming on the pine processionary moth at the southern edge of its range: a retrospective analysis on egg survival in Tunisia
Even the current climate change winners could end up being losers
Recommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by Matt Hill, Philippe Louapre, José Hodar and Corentin IltisClimate change is accelerating (IPCC 2022), and so applies ever stronger selective pressures on biodiversity (Segan et al. 2016). Possible responses include range shifts or adaptations to new climatic conditions (Bellard et al. 2012), but there is still much uncertainty about the extent of most species' adaptive capacities and the impact of extreme climatic events.
The pine processionary is a major pest of pine trees in the Mediterranean area. It is notably one of the few species for which a clear link between recent climate change and its northward expansion has been established (Battisti et al. 2005), and as such is often considered as globally benefitting from climate change. However, recent results show a retraction of its range at the southern limit (Bourougaaoui et al. 2021), exposed to high warming (+1.4°C in Tunisia since 1901 as opposed to +1.12°C on average in the Northern hemisphere) and extreme summer temperature events (Verner et al. 2013). Thus, it is possible that the species' adaptive abilities are being challenged at the southern limit of its native range by the magnitude of observed climate change.
In this work, Bourougaaoui et al. (2022) investigate how climate change over the last 30 years has impacted the reproductive success of the pine processionary moth in Tunisia. A major methodological interest of this study is that they used data both from historical collections and from recent samplings, which raised a challenge for running a longitudinal analysis as sampling locations differed between the two periods. By applying a grouping method to local climatic data, the authors were able to define several large climatic clusters within the country, and analyze long-term data from different sites within the same clusters. They find that both fecundity and hatching rate decreased over the period, while at the same time both the average temperature increased and climate variability increased. One of the main conclusions is that recurrent episodes of extreme heat during summer might have a larger impact than the long-term increase of average temperature, which strongly echoes how the intensification of weather extremes is currently proving one of the most important dimensions of climate change.
However, a most interesting hypothesis also arises from the analysis of the differences between climatic clusters: preexisting adaptations to heat, for instance, phenological shifts that allow the most sensitive stages to develop earlier in the season before the extreme heat events are most likely to occur, might actually reduce impacts in the historically warmest areas. Thus the greatest climate vulnerability might not always stand where one expects it.
References
Battisti A, Stastny M, Netherer S, Robinet C, Schopf A, Roques A, Larsson S (2005) Expansion of Geographic Range in the Pine Processionary Moth Caused by Increased Winter Temperatures. Ecological Applications, 15, 2084–2096. https://doi.org/10.1890/04-1903
Bellard C, Bertelsmeier C, Leadley P, Thuiller W, Courchamp F (2012) Impacts of climate change on the future of biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 15, 365–377. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01736.x
Bourougaaoui A, Ben Jamâa ML, Robinet C (2021) Has North Africa turned too warm for a Mediterranean forest pest because of climate change? Climatic Change, 165, 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-021-03077-1
Bourougaaoui A, Robinet C, Jamaa MLB, Laparie M (2022) Effects of climate warming on the pine processionary moth at the southern edge of its range: a retrospective analysis on egg survival in Tunisia. bioRxiv, 2021.08.17.456665, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.17.456665
IPCC. 2022. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press. In Press.
Segan DB, Murray KA, Watson JEM (2016) A global assessment of current and future biodiversity vulnerability to habitat loss–climate change interactions. Global Ecology and Conservation, 5, 12–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2015.11.002
Verner D (2013) Tunisia in a Changing Climate : Assessment and Actions for Increased Resilience and Development. World Bank, Washington, DC. https://doi.org/10.1596/978-0-8213-9857-9

Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities
Unity makes strength: clustered extinctions have stronger, longer-lasting effects on metacommunities dynamics
Recommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker and Frederik De LaenderIn this article, Saade et al. (2021) investigate how the rate of local extinctions and their spatial distribution affect recolonization dynamics in metacommunities. They use an elegant combination of microcosm experiments with metacommunities of freshwater ciliates and mathematical modelling mirroring their experimental system. Their main findings are (i) that local patch extinctions increase both local (α-) and inter-patch (β-) diversity in a transient way during the recolonization process, (ii) that these effects depend more on the spatial distribution of extinctions (dispersed or clustered) than on their amount, and (iii) that they may spread regionally.
Microcosm experiments are already quite cool just by themselves and have contributed largely to conceptual advances in community ecology (see Fraser and Keddy 1997, or Jessup et al. 2004 for reviews on this topic), but they are here exploited to a whole further level by the fitting of a metapopulation dynamics model. The model allows both to identify the underlying mechanisms most likely to generate the patterns observed (here, competitive interactions) and to assess the robustness of these patterns when considering larger spatial or temporal scales. This release of experimental limitations allows here for the analysis of quantitative metrics of spatial structure, like the distance to the closest patch, which gives an interesting insight into the functional basis of the effect of the spatial distribution of extinctions.
A major strength of this study is that it highlights the importance of considering the spatial structure explicitly. Recent work on ecological networks has shown repeatedly that network structure affects the propagation of pathogens (Badham and Stocker 2010), invaders (Morel-Journel et al. 2019), or perturbation events (Gilarranz et al. 2017). Here, the spatial structure of the metacommunity is a regular grid of patches, but the distribution of extinction events may be either regularly dispersed (i.e., extinct patches are distributed evenly over the grid and are all surrounded by non-extinct patches only) or clustered (all extinct patches are neighbours). This has a direct effect on the neighbourhood of perturbed patches, and because perturbations have mostly local effects, their recovery dynamics are dominated by the composition of this immediate neighbourhood. In landscapes with dispersed extinctions, the neighbourhood of a perturbed patch is not affected by the amount of extinctions, and neither is its recovery time. In contrast, in landscapes with clustered extinctions, the amount of extinctions affects the depth of the perturbed area, which takes longer to recover when it is larger. Interestingly, the spatial distribution of extinctions here is functionally equivalent to differences in connectivity between perturbed and unperturbed patches, which results in contrasted “rescue recovery” and “mixing recovery” regimes as described by Zelnick et al. (2019).
Furthermore, this study focuses on local dynamics of competition and short-term, transient patterns that may have been overlooked by more classical, equilibrium-based approaches of dynamical systems of metacommunities. Indeed, in a metacommunity composed of several competitors, early theoretical work demonstrated that species coexistence is possible at the regional scale only, provided that spatial heterogeneity creates spatial variance in fitness or precludes the superior competitor from accessing certain habitat patches (Skellam 1951, Levins 1969). In the spatially homogeneous experimental system of Saade et al., one of the three ciliate species ends up dominating the community at equilibrium. However, following local, one-time extinction events, the community endures a recolonization process in which differences in dispersal may provide temporary spatial niches for inferior competitors. These transient patterns might prove essential to understand and anticipate the resilience of natural systems that are under increasing pressure, and enduring ever more frequent and intense perturbations (IPBES 2019). Spatial autocorrelation in extinction events was previously identified as a risk for stability and persistence of metacommunities (Ruokolainen 2013, Kahilainen et al. 2018). These new results show that autocorrelated perturbations also have longer-lasting effects, which is likely to increase their overall impact on metacommunity dynamics. As spatial and temporal autocorrelation of temperature and extreme climatic events are expected to increase (Di Cecco and Gouthier 2018), studies that investigate how metacommunities respond to the structure of the distribution of perturbations are more necessary than ever.
References
Badham J, Stocker R (2010) The impact of network clustering and assortativity on epidemic behaviour. Theoretical Population Biology, 77, 71–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tpb.2009.11.003
Di Cecco GJ, Gouhier TC (2018) Increased spatial and temporal autocorrelation of temperature under climate change. Scientific Reports, 8, 14850. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33217-0
Fraser LH, Keddy P (1997) The role of experimental microcosms in ecological research. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 12, 478–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-5347(97)01220-2
Gilarranz LJ, Rayfield B, Liñán-Cembrano G, Bascompte J, Gonzalez A (2017) Effects of network modularity on the spread of perturbation impact in experimental metapopulations. Science, 357, 199–201. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aal4122
IPBES (2019) Summary for policymakers of the global assessment report on biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. S. Díaz, J. Settele, E. S. Brondízio E.S., H. T. Ngo, M. Guèze, J. Agard, A. Arneth, P. Balvanera, K. A. Brauman, S. H. M. Butchart, K. M. A. Chan, L. A. Garibaldi, K. Ichii, J. Liu, S. M. Subramanian, G. F. Midgley, P. Miloslavich, Z. Molnár, D. Obura, A. Pfaff, S. Polasky, A. Purvis, J. Razzaque, B. Reyers, R. Roy Chowdhury, Y. J. Shin, I. J. Visseren-Hamakers, K. J. Willis, and C. N. Zayas (eds.). IPBES secretariat, Bonn, Germany. 56 pages. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3553579
Jessup CM, Kassen R, Forde SE, Kerr B, Buckling A, Rainey PB, Bohannan BJM (2004) Big questions, small worlds: microbial model systems in ecology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2004.01.008
Kahilainen A, van Nouhuys S, Schulz T, Saastamoinen M (2018) Metapopulation dynamics in a changing climate: Increasing spatial synchrony in weather conditions drives metapopulation synchrony of a butterfly inhabiting a fragmented landscape. Global Change Biology, 24, 4316–4329. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14280
Levins R (1969) Some Demographic and Genetic Consequences of Environmental Heterogeneity for Biological Control1. Bulletin of the Entomological Society of America, 15, 237–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/besa/15.3.237
Morel-Journel T, Assa CR, Mailleret L, Vercken E (2019) Its all about connections: hubs and invasion in habitat networks. Ecology Letters, 22, 313–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13192
Ruokolainen L (2013) Spatio-Temporal Environmental Correlation and Population Variability in Simple Metacommunities. PLOS ONE, 8, e72325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072325
Saade C, Kefi S, Gougat-Barbera C, Rosenbaum B, Fronhofer EA (2021) Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities. bioRxiv, 2020.12.03.409524, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.409524
Skellam JG (1951) Random Dispersal in Theoretical Populations. Biometrika, 38, 196–218. https://doi.org/10.2307/2332328
Zelnik YR, Arnoldi J-F, Loreau M (2019) The three regimes of spatial recovery. Ecology, 100, e02586. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2586