Intraspecific difference among herbivore lineages and their host-plant specialization drive the strength of trophic cascades
Arnaud Sentis, Raphaël Bertram, Nathalie Dardenne, Jean-Christophe Simon, Alexandra Magro, Benoit Pujol, Etienne Danchin and Jean-Louis Hemptinne
https://doi.org/10.1101/722140
Tell me what you’ve eaten, I’ll tell you how much you’ll eat (and be eaten)
Recommended by Sara Magalhães and Raul Costa-Pereira based on reviews by Bastien Castagneyrol and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Bastien Castagneyrol and 1 anonymous reviewer
Tritrophic interactions have a central role in ecological theory and applications [1-3]. Particularly, systems comprised of plants, herbivores and predators have historically received wide attention given their ubiquity and economic importance [4]. Although ecologists have long aimed to understand the forces that govern alternating ecological effects at successive trophic levels [5], several key open questions remain (at least partially) unanswered [6]. In particular, the analysis of complex food webs has questioned whether ecosystems can be viewed as a series of trophic chains [7,8]. Moreover, whether systems are mostly controlled by top-down (trophic cascades) or bottom-up processes remains an open question [6].
Traditionally, studies have addressed how species diversity at different food chain compartments affect the strength and direction of trophic cascades [9]. For example, many studies have tested whether biological control was more efficient with more than one species of natural enemies [10-12]. Much less attention has been given to the role of within-species variation in shaping trophic cascades [13]. In particular, whereas the impact of trait variation within species of plants or predators on successive trophic levels has been recently addressed [14,15], the impact of intraspecific herbivore variation is in its infancy (but see [16]). This is at odds with the resurgent acknowledgment of the importance of individual variation for several ecological processes operating at higher levels of biological organization [17].
Sources of variation within species can come in many flavours. In herbivores, striking ecological variation can be found among populations occurring on different host plants, which become genetically differentiated, thus forming host races [18,19]. Curiously, the impact of variation across host races on the strength of trophic cascades has, to date, not been explored. This is the gap that the manuscript by Sentis and colleagues [20] fills. They experimentally studied a curious tri-trophic system where the primary consumer, pea aphids, specializes in different plant hosts, creating intraspecific variation across biotypes. Interestingly, there is also ecological variation across lineages from the same biotype. The authors set up experimental food chains, where pea aphids from different lineages and biotypes were placed in their universal legume host (broad bean plants) and then exposed to a voracious but charming predator, ladybugs. The full factorial design of this experiment allowed the authors to measure vertical effects of intraspecific variation in herbivores on both plant productivity (top-down) and predator individual growth (bottom-up).
The results nicely uncover the mechanisms by which intraspecific differences in herbivores precipitates vertical modulation in food chains. Herbivore lineage and host-plant specialization shaped the strength of trophic cascades, but curiously these effects were not modulated by density-dependence. Further, ladybugs consuming pea aphids from different lineages and biotypes grew at distinct rates, revealing bottom-up effects of intraspecific variation in herbivores.
These findings are novel and exciting for several reasons. First, they show how intraspecific variation in intermediate food chain compartments can simultaneously reverberate both top-down and bottom-up effects. Second, they bring an evolutionary facet to the understanding of trophic cascades, providing valuable insights on how genetically differentiated populations play particular ecological roles in food webs. Finally, Sentis and colleagues’ findings [20] have critical implications well beyond their study systems. From an applied perspective, they provide an evident instance on how consumers’ evolutionary specialization matters for their role in ecosystems processes (e.g. plant biomass production, predator conversion rate), which has key consequences for biological control initiatives and invasive species management. From a conceptual standpoint, their results ignite the still neglected value of intraspecific variation (driven by evolution) in modulating the functioning of food webs, which is a promising avenue for future theoretical and empirical studies.
References
[1] Price, P. W., Bouton, C. E., Gross, P., McPheron, B. A., Thompson, J. N., & Weis, A. E. (1980). Interactions among three trophic levels: influence of plants on interactions between insect herbivores and natural enemies. Annual review of Ecology and Systematics, 11(1), 41-65. doi: 10.1146/annurev.es.11.110180.000353
[2] Olff, H., Brown, V.K. & Drent, R.H. (1999). Herbivores: between plants and predators. Blackwell Science, Oxford.
[3] Tscharntke, T. & Hawkins, B.A. (2002). Multitrophic level interactions. Cambridge University Press. doi: 10.1017/CBO9780511542190
[4] Agrawal, A. A. (2000). Mechanisms, ecological consequences and agricultural implications of tri-trophic interactions. Current opinion in plant biology, 3(4), 329-335. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5266(00)00089-3
[5] Pace, M. L., Cole, J. J., Carpenter, S. R., & Kitchell, J. F. (1999). Trophic cascades revealed in diverse ecosystems. Trends in ecology & evolution, 14(12), 483-488. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(99)01723-1
[6] Abdala‐Roberts, L., Puentes, A., Finke, D. L., Marquis, R. J., Montserrat, M., Poelman, E. H., ... & Mooney, K. (2019). Tri‐trophic interactions: bridging species, communities and ecosystems. Ecology letters, 22(12), 2151-2167. doi: 10.1111/ele.13392
[7] Polis, G.A. & Winemiller, K.O. (1996). Food webs. Integration of patterns and dynamics. Chapmann & Hall, New York. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7007-3
[8] Torres‐Campos, I., Magalhães, S., Moya‐Laraño, J., & Montserrat, M. (2020). The return of the trophic chain: Fundamental vs. realized interactions in a simple arthropod food web. Functional Ecology, 34(2), 521-533. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.13470
[9] Polis, G. A., Sears, A. L., Huxel, G. R., Strong, D. R., & Maron, J. (2000). When is a trophic cascade a trophic cascade?. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 15(11), 473-475. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(00)01971-6
[10] Sih, A., Englund, G., & Wooster, D. (1998). Emergent impacts of multiple predators on prey. Trends in ecology & evolution, 13(9), 350-355. doi: 10.1016/S0169-5347(98)01437-2
[11] Diehl, E., Sereda, E., Wolters, V., & Birkhofer, K. (2013). Effects of predator specialization, host plant and climate on biological control of aphids by natural enemies: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Applied Ecology, 50(1), 262-270. doi: 10.1111/1365-2664.12032
[12] Snyder, W. E. (2019). Give predators a complement: conserving natural enemy biodiversity to improve biocontrol. Biological control, 135, 73-82. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2019.04.017
[13] Des Roches, S., Post, D. M., Turley, N. E., Bailey, J. K., Hendry, A. P., Kinnison, M. T., ... & Palkovacs, E. P. (2018). The ecological importance of intraspecific variation. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 2(1), 57-64. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0402-5
[14] Bustos‐Segura, C., Poelman, E. H., Reichelt, M., Gershenzon, J., & Gols, R. (2017). Intraspecific chemical diversity among neighbouring plants correlates positively with plant size and herbivore load but negatively with herbivore damage. Ecology Letters, 20(1), 87-97. doi: 10.1111/ele.12713
[15] Start, D., & Gilbert, B. (2017). Predator personality structures prey communities and trophic cascades. Ecology letters, 20(3), 366-374. doi: 10.1111/ele.12735
[16] Turcotte, M. M., Reznick, D. N., & Daniel Hare, J. (2013). Experimental test of an eco-evolutionary dynamic feedback loop between evolution and population density in the green peach aphid. The American Naturalist, 181(S1), S46-S57. doi: 10.1086/668078
[17] Bolnick, D. I., Amarasekare, P., Araújo, M. S., Bürger, R., Levine, J. M., Novak, M., ... & Vasseur, D. A. (2011). Why intraspecific trait variation matters in community ecology. Trends in ecology & evolution, 26(4), 183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2011.01.009
[18] Drès, M., & Mallet, J. (2002). Host races in plant–feeding insects and their importance in sympatric speciation. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences, 357(1420), 471-492. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2002.1059
[19] Magalhães, S., Forbes, M. R., Skoracka, A., Osakabe, M., Chevillon, C., & McCoy, K. D. (2007). Host race formation in the Acari. Experimental and Applied Acarology, 42(4), 225-238. doi: 10.1007/s10493-007-9091-0
[20] Sentis, A., Bertram, R., Dardenne, N., Simon, J.-C., Magro, A., Pujol, B., Danchin, E. and J.-L. Hemptinne (2020) Intraspecific difference among herbivore lineages and their host-plant specialization drive the strength of trophic cascades. bioRxiv, 722140, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/722140
| Intraspecific difference among herbivore lineages and their host-plant specialization drive the strength of trophic cascades | Arnaud Sentis, Raphaël Bertram, Nathalie Dardenne, Jean-Christophe Simon, Alexandra Magro, Benoit Pujol, Etienne Danchin and Jean-Louis Hemptinne | <p>Trophic cascades, the indirect effect of predators on non-adjacent lower trophic levels, are important drivers of the structure and dynamics of ecological communities. However, the influence of intraspecific trait variation on the strength of t... |  | Community ecology, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Food webs, Population ecology | Sara Magalhães | | 2019-08-02 09:11:03 | View |
Interplay between the paradox of enrichment and nutrient cycling in food webs
Pierre Quévreux, Sébastien Barot and Élisa Thébault
https://doi.org/10.1101/276592
New insights into the role of nutrient cycling in food web dynamics
Recommended by Samraat Pawar based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi, Wojciech Uszko and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi, Wojciech Uszko and 1 anonymous reviewer
Understanding the factors that govern the relationship between structure, stability and functioning of food webs has been a central problem in ecology for many decades. Historically, apart from microbial and soil food webs, the role of nutrient cycling has largely been ignored in theoretical and empirical food web studies. A prime example of this is the widespread use of Lotka-Volterra type models in theoretical studies; these models per se are not designed to capture the effect of nutrients being released back into the system by interacting populations. Thus overall, we still lack a general understanding of how nutrient cycling affects food web dynamics.
A new study by Quévreux, Barot and Thébault [1] tackles this problem by building a new food web model. This model features some important biological details: trophic interactions and vital rates constrained by species' body masses (using Ecological Metabolic Theory), adaptive foraging, and stoichiometric rules to ensure meaningful conversion between carbon and nutrient flows. The authors analyze the model through detailed simulations combined with thorough sensitivity analyses of model assumptions and parametrizations (including of allometric scaling relationships). I am happy to recommend this preprint because of the novelty of the work and it's technical quality.
The study yields interesting and novel findings. Overall, nutrient cycling does have a strong effect on community dynamics. Nutrient recycling is driven mostly by consumers at low mineral nutrient inputs, and by primary producers at high inputs. The extra nutrients made available through recycling increases species' persistence at low nutrient input levels, but decreases persistence at higher input levels by increasing population oscillations (a new, nuanced perspective on the classical "paradox of enrichment"). Also, for the same level of nutrient input, food webs with nutrient recycling show more fluctuations in primary producer biomass (and less at higher trophic levels) than those without recycling, with this effect weakening in more complex food webs.
Overall, these results provide new insights, suggesting that nutrient cycling may enhance the positive effects of species richness on ecosystem stability, and point at interesting new directions for future theoretical and empirical studies.
References
[1] Quévreux, P., Barot, S. and E. Thébault (2020) Interplay between the paradox of enrichment and nutrient cycling in food webs. bioRxiv, 276592, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/276592
| Interplay between the paradox of enrichment and nutrient cycling in food webs | Pierre Quévreux, Sébastien Barot and Élisa Thébault | <p>Nutrient cycling is fundamental to ecosystem functioning. Despite recent major advances in the understanding of complex food web dynamics, food web models have so far generally ignored nutrient cycling. However, nutrient cycling is expected to ... |  | Biodiversity, Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning, Food webs, Interaction networks, Theoretical ecology | Samraat Pawar | | 2018-11-03 21:47:37 | View |
A community perspective on the concept of marine holobionts: current status, challenges, and future directions
Simon M. Dittami, Enrique Arboleda, Jean-Christophe Auguet, Arite Bigalke, Enora Briand, Paco Cárdenas, Ulisse Cardini, Johan Decelle, Aschwin Engelen, Damien Eveillard, Claire M.M. Gachon, Sarah Griffiths, Tilmann Harder, Ehsan Kayal, Elena Kazamia, Francois H. Lallier, Mónica Medina, Ezequiel M. Marzinelli, Teresa Morganti, Laura Núñez Pons, Soizic Pardo, José Pintado Valverde, Mahasweta Saha, Marc-André Selosse, Derek Skillings, Willem Stock, Shinichi Sunagawa, Eve Toulza, Alexey Vorobev, Cat...
10.5281/zenodo.3696771
Marine holobiont in the high throughput sequencing era
Recommended by Sophie Arnaud-Haond and Corinne Vacher based on reviews by Sophie Arnaud-Haond and Aurélie Tasiemski
The concept of holobiont dates back to more than thirty years, it was primarily coined to hypothesize the importance of symbiotic associations to generate significant evolutionary novelties. Quickly adopted to describe the now well-studied system formed by zooxanthella associated corals, this concept expanded much further after the emergence of High-Throughput Sequencing and associated progresses in metabarcoding and metagenomics.
Holobionts – defined as the association between an individual host and its microbiota - are now increasingly described at sea and on land. The opinion article by Dittami et al. [1] provides a synthetic overview of marine holobionts. It retraces the history of the holobiont concept, recalls the main mechanisms underlying the association between hosts and microbial communities, highlights the influence of these symbioses on marine ecosystem functioning, and outlines current tools and future lines of research.
In particular, the article discusses some particularities of marine systems, such as the strong connectivity allowing an exchange of microorganisms and chemical signals between and within holobionts.
The authors advocate the need to bridge the gap between large scale exploration studies and smaller scale mechanistic studies, by conducting interdisciplinary research (combining physiology, biochemistry, ecology, experimentation and computational modeling) on some keystone holobionts.
Finally, one strength of the paper by Dittami et al. [1] is that it places the concept of the holobiont in an applied research framework. Several possible applications of knowledge on host-microbiota interactions are suggested, both in the field of aquaculture and that of monitoring the health of marine ecosystems. This article contains all the necessary elements for someone who would like to jump into the study of the holobionths in the marine world.
References
[1] Dittami SM, Arboleda E, Auguet J, Bigalke A, Briand E, Cardenas P, Cardini U, Decelle J, Engelen AH, Eveillard D, Gachon CMM, Griffiths SM, Harder T, Kayal E, Kazamia E, Lallier FH, Medina M, Marzinelli E, Morganti T, Núñez Pons L, Prado S, Pintado J, Saha M, Selosse M, Skillings D, Stock W, Sunagawa S, Toulza E, Vorobev A, Leblanc C, Not F. (2020). A community perspective on the concept of marine holobionts: current status, challenges, and future directions. Zenodo, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3696771
| A community perspective on the concept of marine holobionts: current status, challenges, and future directions | Simon M. Dittami, Enrique Arboleda, Jean-Christophe Auguet, Arite Bigalke, Enora Briand, Paco Cárdenas, Ulisse Cardini, Johan Decelle, Aschwin Engelen, Damien Eveillard, Claire M.M. Gachon, Sarah Griffiths, Tilmann Harder, Ehsan Kayal, Elena Kazam... | Host-microbe interactions play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. However, we still have very little understanding of the mechanisms that govern these relationships, the evolutionary processes that shape them, and their ecological consequences. T... | 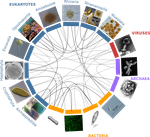 | Marine ecology, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Symbiosis | Sophie Arnaud-Haond | | 2019-02-05 17:57:11 | View |
The persistence in time of distributional patterns in marine megafauna impacts zonal conservation strategies
Charlotte Lambert, Ghislain Dorémus, Vincent Ridoux
https://doi.org/10.1101/790634
The importance of spatio-temporal dynamics on MPA's design
Recommended by Sergio Estay based on reviews by Ana S. L. Rodrigues and 1 anonymous reviewer
Marine protected areas (MPA) have arisen as the main approach for conservation of marine species. Fishes, marine mammals and birds can be conservation targets that justify the implementation of these areas. However, MPAs undergo many of the problems faced by their terrestrial equivalent. One of the major concerns is that these conservation areas are spatially constrained, by logistic reasons, and many times these constraints caused that key areas for the species (reproductive sites, refugees, migration) fall outside the limits, making conservation efforts even more difficult. Lambert et al. [1] evaluate at what point the Bay of Biscay MPA contains key ecological areas for several emblematic species. The evaluation incorporated a spatio-temporal dimension. To evaluate these ideas, authors evaluate two population descriptors: aggregation and persistence of several species of cetaceans and seabirds.
The authors determined that despite the MPA contains key areas for some species, for many others the key areas fall outside the MPA (aggregation sites) or observed aggregation sites are poorly persistent in time. They found that aggregation and persistence behave as two uncorrelated descriptors of the spatio-temporal distribution of populations. Variability of both characteristics was species-specific, but in all cases the message is clear: both features must be taken into account to evaluate the effectiveness of MPAs. Both conclusions pointed out to the difficulties that a strategy based on MPAs could face when the target are those species with low aggregation or those where key sites show low persistence in time.
Conceptually, the manuscript and its conclusions are very interesting, specially its recommendation of including temporal variability of species abundances and aggregation in the design of MPAs. However, despite the clear biological importance of persistence and aggregation of the conservation targets for the design of a MPA, its implementation will still be an extremely complex task. A first constraint is that important areas for one species could not be relevant for others, making the design of the MPA difficult because the more target species we include the larger the area needed for the MPA. As a consequence, the management of the MPA turns difficult and expensive as the area increases. These increased costs could be a key point for accepting/rejecting the implementation of these MPAs for governments. Also larger areas could imply highest level of conflict with local communities or stakeholders. In many the inclusion inside MPAs of areas with traditional social or economic use will be a major source of conflict with the people.
Despite these difficulties, the results of Lambert et al. [1] give us a key message for improving MPA’s design. The best strategy for including their conclusions in the effective implementation of these areas will be the next target in conservation research.
References
[1] Lambert, C., Dorémus, G. and V. Ridoux (2020) The persistence in time of distributional patterns in marine megafauna impacts zonal conservation strategies. bioRxiv, 790634, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/790634
| The persistence in time of distributional patterns in marine megafauna impacts zonal conservation strategies | Charlotte Lambert, Ghislain Dorémus, Vincent Ridoux | <p>The main type of zonal conservation approaches corresponds to Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), which are spatially defined and generally static entities aiming at the protection of some target populations by the implementation of a management pla... | 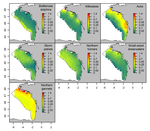 | Conservation biology, Habitat selection, Species distributions | Sergio Estay | | 2019-10-03 08:47:17 | View |
Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree
Sébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret
https://doi.org/10.1101/351197
Growth trajectories, better than organ-level functional traits, reveal intraspecific response to environmental variation
Recommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz
Functional traits are “morpho-physio-phenological traits which impact fitness indirectly via their effects on growth, reproduction and survival” [1]. Most functional traits are defined at organ level, e.g. for leaves, roots and stems, and reflect key aspects of resource acquisition and resource use by organisms for their development and reproduction [2]. More rarely, some functional traits can be related to spatial development, such as vegetative height and lateral spread in plants.
Organ-level traits are especially popular because they can be measured in a standard way and easily compared over many plants. But these traits can broadly vary during the life of an organism. For instance, Roggy et al. [3] found that Leaf Mass Area can vary from 30 to 140 g.m^(-2) between seedling and adult stages for the canopy tree Dicorynia guianensis in French Guiana. Fortunel et al. [4] have also showed that developmental stages much contribute to functional trait variation within several Micropholis tree species in lowland Amazonia.
The way plants grow and invest resources into organs is variable during life and allows defining specific developmental sequences and architectural models [5,6]. There is clear ontogenic variation in leaf number, leaf properties and ramification patterns. Ontogenic variations reflect changing adaptation of an individual over its life, depending on the changing environmental conditions.
In this regard, measuring a single functional trait at organ level in adult trees should miss the variation of resource acquisition and use strategies over time. Thus we should built a more integrative approach of ecological development, also called “eco-devo” approach [7].
Although the ecological significance of ontogeny and developmental strategies is now well known, the extent to which it contributes to explain species survival and coexistence in communities is still broadly ignored in functional ecology. Levionnois et al. [8] investigated intraspecific variation of functional traits and growth trajectories in a typical, early-successional tree species in French Guiana, Amazonia. This species, Cecropia obtusa, is generalist regarding soil type and can be found on both white sand and ferralitic soil. The study examines whether there in intraspecific variation in functional traits and growth trajectories of C. obtusa in response to the contrasted soil types.
The tree communities observed on the two types of soils include species with distinctive functional trait values, that is, there are changes in species composition related to different species strategies along the classical wood and leaf economic spectra. The populations of C. obtusa found on the two soils showed some difference in functional traits, but it did not concern traits related to the main economic spectra. Conversely, the populations showed different growth strategies, in terms of spatial and temporal development.
The major lessons we can learn from the study are:
(i) Functional traits measured at organ level cannot reflect well how long-lived plants collect and invest resources during their life. The results show the potential of considering architectural and developmental traits together with organ-level functional traits, to better acknowledge the variation in ecological strategies over plant life, and thus to better understand community assembly processes.
(ii) What makes functional changes between communities differs when considering interspecific and intraspecific variation. Species turnover should encompass different corteges of soil specialists. These specialists are sorted along economic spectra, as shown in tropical rainforests and globally [2]. Conversely, a generalist species such as C. obtusa does occur on contrasted soil, which entails that it can accommodate the contrasted ecological conditions. However, the phenotypic adjustment is not related to how leaves and wood ensure photosynthesis, water and nutrient acquisition, but regards the way the resources are allocated to growth and reproduction over time.
The results of the study stress the need to better integrate growth strategies and ontogeny in the research agenda of functional ecology. We can anticipate that organ-level functional traits and growth trajectories will be more often considered together in ecological studies. The integration should help better understand the temporal niche of organisms, and how organisms can coexist in space and time with other organisms during their life. Recently, Klimešová et al. [9] have proposed standardized protocols for collecting plant modularity traits. Such effort to propose easy-to-measure traits representing plant development and ontogeny, with clear functional roles, should foster the awaited development of an “eco-devo” approach.
References
[1] Violle, C., Navas, M. L., Vile, D., Kazakou, E., Fortunel, C., Hummel, I., & Garnier, E. (2007). Let the concept of trait be functional!. Oikos, 116(5), 882-892. doi: 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15559.x
[2] Díaz, S. et al. (2016). The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature, 529(7585), 167-171. doi: 10.1038/nature16489
[3] Roggy, J. C., Nicolini, E., Imbert, P., Caraglio, Y., Bosc, A., & Heuret, P. (2005). Links between tree structure and functional leaf traits in the tropical forest tree Dicorynia guianensis Amshoff (Caesalpiniaceae). Annals of forest science, 62(6), 553-564. doi: 10.1051/forest:2005048
[4] Fortunel, C., Stahl, C., Heuret, P., Nicolini, E. & Baraloto, C. (2020). Disentangling the effects of environment and ontogeny on tree functional dimensions for congeneric species in tropical forests. New Phytologist. doi: 10.1111/nph.16393
[5] Barthélémy, D., & Caraglio, Y. (2007). Plant architecture: a dynamic, multilevel and comprehensive approach to plant form, structure and ontogeny. Annals of botany, 99(3), 375-407. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl260
[6] Hallé, F., & Oldeman, R. A. (1975). An essay on the architecture and dynamics of growth of tropical trees. Kuala Lumpur: Penerbit Universiti Malaya.
[7] Sultan, S. E. (2007). Development in context: the timely emergence of eco-devo. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(11), 575-582. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2007.06.014
[8] Levionnois, S., Tysklind, N., Nicolini, E., Ferry, B., Troispoux, V., Le Moguedec, G., Morel, H., Stahl, C., Coste, S., Caron, H. & Heuret, P. (2020). Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree. bioRxiv, 351197, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/351197
[9] Klimešová, J. et al. (2019). Handbook of standardized protocols for collecting plant modularity traits. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 40, 125485. doi: 10.1016/j.ppees.2019.125485
| Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree | Sébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret | <p style="text-align: justify;">1- Trait-environment relationships have been described at the community level across tree species. However, whether interspecific trait-environment relationships are consistent at the intraspecific level is yet unkn... |  | Botany, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Habitat selection, Ontogeny, Tropical ecology | François Munoz | | 2018-06-21 17:13:17 | View |
A flexible pipeline combining clustering and correction tools for prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabarcoding
Miriam I Brandt, Blandine Trouche, Laure Quintric, Patrick Wincker, Julie Poulain, Sophie Arnaud-Haond
https://doi.org/10.1101/717355
A flexible pipeline combining clustering and correction tools for prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabarcoding
Recommended by Stefaniya Kamenova based on reviews by Tiago Pereira and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Tiago Pereira and 1 anonymous reviewer
High-throughput sequencing-based techniques such as DNA metabarcoding are increasingly advocated as providing numerous benefits over morphology‐based identifications for biodiversity inventories and ecosystem biomonitoring [1]. These benefits are particularly apparent for highly-diversified and/or hardly accessible aquatic and marine environments, where simple water or sediment samples could already produce acceptably accurate biodiversity estimates based on the environmental DNA present in the samples [2,3]. However, sequence-based characterization of biodiversity comes with its own challenges. A major one resides in the capacity to disentangle true biological diversity (be it taxonomic or genetic) from artefactual diversity generated by sequence-errors accumulation during PCR and sequencing processes, or from the amplification of non-target genes (i.e. pseudo-genes). On one hand, the stringent elimination of sequence variants might lead to biodiversity underestimation through the removal of true species, or the clustering of closely-related ones. On the other hand, a more permissive sequence filtering bears the risks of biodiversity inflation. Recent studies have outlined an excellent methodological framework for addressing this issue by proposing bioinformatic tools that allow the amplicon-specific error-correction as alternative or as complement to the more arbitrary approach of clustering into Molecular Taxonomic Units (MOTUs) based on sequence dissimilarity [4,5]. But to date, the relevance of amplicon-specific error-correction tools has been demonstrated only for a limited set of taxonomic groups and gene markers.
The study of Brandt et al. [6] successfully builds upon existing methodological frameworks for filling this gap in current literature. By proposing a bioinformatic pipeline combining Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASV) curation with MOTU clustering and additional post-clustering curation, the authors show that contrary to previous recommendations, ASV-based curation alone does not represent an adequate approach for DNA metabarcoding-based inventories of metazoans. Metazoans indeed, do exhibit inherently higher intra-specific and intra-individual genetic variability, necessarily leading to biased biodiversity estimates unbalanced in favor of species with higher intraspecific diversity in the absence of MOTU clustering. Interestingly, the positive effect of additional clustering showed to be dependent on the target gene region. Additional clustering had proportionally higher effect on the more polymorphic mitochondrial COI region (as compared to the 18S ribosomal gene). Thus, the major advantage of the study lies in the provision of optimal curation parameters that reflect the best possible balance between minimizing the impact of PCR/sequencing errors and the loss of true biodiversity across markers with contrasting levels of intragenomic variation. This is important as combining multiple markers is increasingly considered for improving the taxonomic coverage and resolution of data in DNA metabarcoding studies.
Another critical aspect of the study is the taxonomic assignation of curated OTUs (which is also the case for the majority of DNA metabarcoding-based biodiversity assessments). Facing the double challenge of focusing on taxonomic groups that are both highly diverse and poorly represented in public sequence reference databases, the authors failed to obtain high-resolution taxonomic assignments for several of the most closely-related species. As a result, taxa with low divergence levels were clustered as single taxonomic units, subsequently leading to underestimation of true biodiversity present. This finding adds to the argument that in order to be successful, sequence-based techniques still require the availability of comprehensive, high-quality reference databases.
Perhaps the only regret we might have with the study is the absence of mock community validation for the prokaryotes compartment. Even though the analyses of natural samples seem to suggest a positive effect of the curation pipeline, the concept of intra- versus inter-species variation in naturally occurring prokaryote communities remains at best ambiguous. Of course, constituting a representative sample of taxonomically-resolved prokaryote taxa from deep-sea habitats does not come without difficulties but has the benefit of opening opportunities for further studies on the matter.
References
[1] Porter, T. M., and Hajibabaei, M. (2018). Scaling up: A guide to high-throughput genomic approaches for biodiversity analysis. Molecular Ecology, 27(2), 313–338. doi: 10.1111/mec.14478
[2] Valentini, A., Taberlet, P., Miaud, C., Civade, R., Herder, J., Thomsen, P. F., … Dejean, T. (2016). Next-generation monitoring of aquatic biodiversity using environmental DNA metabarcoding. Molecular Ecology, 25(4), 929–942. doi: 10.1111/mec.13428
[3] Leray, M., and Knowlton, N. (2015). DNA barcoding and metabarcoding of standardized samples reveal patterns of marine benthic diversity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(7), 2076–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1424997112
[4] Callahan, B. J., McMurdie, P. J., and Holmes, S. P. (2017). Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. The ISME Journal, 11(12), 2639–2643. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2017.119
[5] Edgar, R. C. (2016). UNOISE2: improved error-correction for Illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. BioRxiv, 081257. doi: 10.1101/081257
[6] Brandt, M. I., Trouche, B., Quintric, L., Wincker, P., Poulain, J., and Arnaud-Haond, S. (2020). A flexible pipeline combining clustering and correction tools for prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabarcoding. BioRxiv, 717355, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/717355
| A flexible pipeline combining clustering and correction tools for prokaryotic and eukaryotic metabarcoding | Miriam I Brandt, Blandine Trouche, Laure Quintric, Patrick Wincker, Julie Poulain, Sophie Arnaud-Haond | <p>Environmental metabarcoding is an increasingly popular tool for studying biodiversity in marine and terrestrial biomes. With sequencing costs decreasing, multiple-marker metabarcoding, spanning several branches of the tree of life, is becoming ... | 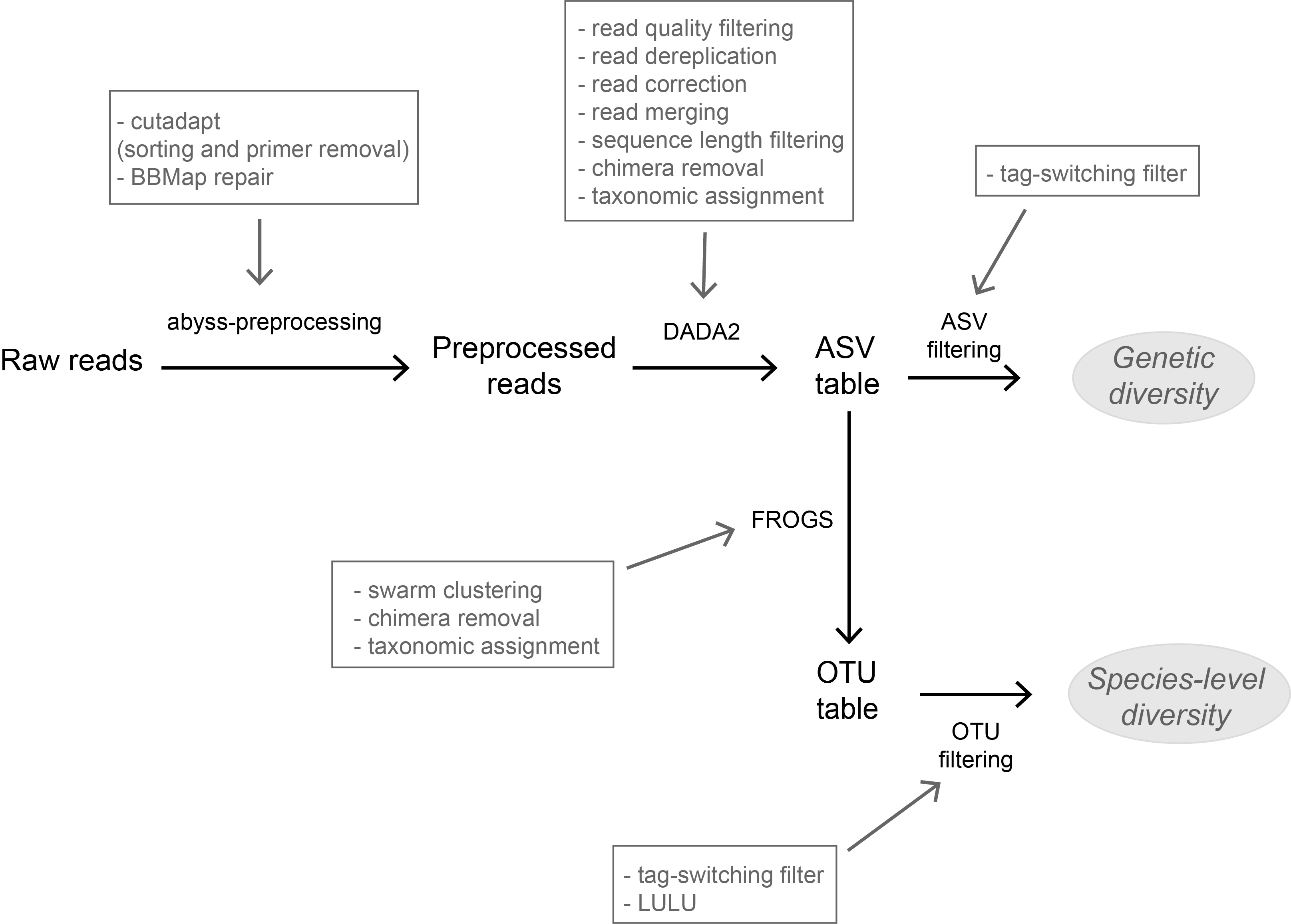 | Biodiversity, Community ecology, Marine ecology, Molecular ecology | Stefaniya Kamenova | | 2019-08-02 20:52:45 | View |
Touchy matter: the delicate balance between Morgan’s canon and open-minded description of advanced cognitive skills in the animal
Recommended by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor
In a recent paper published in PNAS, Fayet et al. [1] reported scarce field observations of two Atlantic puffins (four years apart) apparently scratching their bodies using sticks, which was interpreted by the authors as evidence of tool use in this species. In a short response, Benjamin Farrar [2] raises serious concerns about this interpretation and proposes simpler, more parsimonious, mechanisms explaining the observed behaviour: a textbook case of Morgan's canon.
In virtually all introductory lectures on animal behaviour, students are advised to exercise caution when interpreting empirical data and weighting alternative explanations. We are sometimes prisoner of our assumptions: our desire of beliefs in advanced cognitive skills in non-human species make us more receptive to facts confirming our preconceptions than to simpler, less exciting, interpretations (a phenomenon known as "confirmation bias" in psychology). We must resist the temptation to accept appealing explanations without enough critical thinking. Our students are thus taught to apply the Lloyd Morgan's canon, a variant of one of the most important heuristics in Science, the principle of parsimony or Occam's razor, rephrased by Morgan [3, page 53] in the context of animal behaviour: "In no case may we interpret an action as the outcome of a higher psychical faculty, if it can be interpreted as the outcome of the exercise of one that stands lower in the psychological scale". In absence of evidence to the contrary, one should postulate the simplest cognitive skill consistent with the observed behaviour. While sometimes criticized from an epistemological point of view [4-6], it remains an essential and largely accepted framework of animal cognition. It has repeatedly proved to be a useful guide in the minefield of comparative psychology. Classical ethology questions related to the existence of, for instance, meta-cognition [7], intentionality or problem solving [8] have been convincingly investigated using this principle.
Yet, there is a downside to this conservative approach. Blind reference to Morgan's canon may narrow our theoretical thinking about animal cognition [7,9]. It could be counter-productive to systematically deny advanced cognitive skills in animals. On the contrary, keeping our mind open to unplanned observations, unexpected discoveries, or serendipity [10], and being prepared to accept new hypotheses, sometimes fairly remote from the dominant paradigm, may be a fruitful research strategy. To quote Darwin's famous letter to Alfred Wallace: "I am a firm believer, that without speculation there is no good and original observation" [11]. Brief notes in specialized scientific journals, or even in grey literature (by enthusiast amateur ornithologists, ichthyologists, or entomologists), constitutes a rich array of anecdotal observations. For instance, Sol et al. [12] convincingly compared the innovation propensity across bird species by screening ornithology literature using keywords like 'never reported', 'not seen before', 'first report', 'unusual' or 'novel'. Even if "the plural of anecdote is not data" as the saying goes, such descriptions of novel behaviours, even single-subject observations, are indisputably precious: taxonomic ubiquity of a behaviour is a powerful argument in favour of evolutionary convergence. Of course, a race to the bottom, amplified by the inevitable media hypes around scientific articles questioning human exceptionalism, is another possible scientific trap for behavioural biologists in search of skills characteristic of so-called advanced species, but never described so far in supposedly cognitively simpler organisms. As stated by Franz de Waal [9]: "I have nothing against anecdotes, especially if they have been caught on camera or come from reputable observers who know their animals; but I do view them as a starting point of research, never an end point".
In the case of the two video observations of puffins apparently using sticks as scratching tool, it must be considered as a mere anecdote unless scientists systematically investigate this behaviour. In his constructive criticism of Fayet et al.'s paper, Benjamin Farrar [2] proposes interesting directions of research and testable predictions. A correlation between the background rate of stick picking and the rate of stick preening would indicate that this behaviour was more likely explained by fluke than genuine innovation in this species.
References
[1] Fayet, A. L., Hansen, E. S., and Biro, D. (2020). Evidence of tool use in a seabird. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(3), 1277–1279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918060117
[2] Farrar, B. G. (2020). Evidence of tool use in a seabird? PsyArXiv, 463hk, ver. 5 recommended and peer-reviewed by Peer Community In Ecology. doi: 10.31234/osf.io/463hk
[3] Morgan, C. L. (1894). An introduction to comparative psychology. London, UK: Walter Scott, Ltd. Retrieved from https://archive.org/details/introductiontoco00morg/page/53/mode/2up
[4] Meketa, I. (2014). A critique of the principle of cognitive simplicity in comparative cognition. Biology and Philosophy, 29(5), 731–745. doi: 10.1007/s10539-014-9429-z
[5] Fitzpatrick, S. (2017). Against Morgan's Canon. In K. Andrews and J. Beck (Eds.), The Routledge handbook of philosophy of animal minds (pp. 437–447). London, UK: Routledge, Taylor and Francis Group. doi: 10.4324/9781315742250.ch42
[6] Starzak, T. (2017). Interpretations without justification: a general argument against Morgan's Canon. Synthese, 194(5), 1681–1701. doi: 10.1007/s11229-016-1013-4
[7] Arbilly, M., and Lotem, A. (2017). Constructive anthropomorphism: a functional evolutionary approach to the study of human-like cognitive mechanisms in animals. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1865), 20171616. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1616
[8] Taylor, A. H., Knaebe, B., and Gray, R. D. (2012). An end to insight? New Caledonian crows can spontaneously solve problems without planning their actions. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 279(1749), 4977–4981. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.1998
[9] de Waal, F. (2016). Are we smart enough to know how smart animals are? New-York, USA: W. W. Norton and Company.
[10] Scheffer, M. (2014). The forgotten half of scientific thinking. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(17), 6119–6119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404649111
[11] Darwin, C. R. (1857). Letter to A. R. Wallace, 22 December 1857. Retrieved 30 January 2020, from https://www.darwinproject.ac.uk/letter/DCP-LETT-2192.xml
[12] Sol, D., Lefebvre, L., and Rodríguez-Teijeiro, J. D. (2005). Brain size, innovative propensity and migratory behaviour in temperate Palaearctic birds. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 272(1571), 1433–1441. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2005.3099
| Evidence of tool use in a seabird? | Benjamin G. Farrar | Fayet, Hansen and Biro (1) provide two observations of Atlantic puffins, *Fratercula arctica*, performing self-directed actions while holding a stick in their beaks. The authors interpret this as evidence of tool use as they suggest that the stick... |  | Behaviour & Ethology | Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont | | 2020-01-22 11:55:27 | View |
Diapause is not selected as a bet-hedging strategy in insects: a meta-analysis of reaction norm shapes
Jens Joschinski and Dries Bonte
10.1101/752881
When to diapause or not to diapause? Winter predictability is not the answer
Recommended by Bastien Castagneyrol based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron, Md Habibur Rahman Salman and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron, Md Habibur Rahman Salman and 1 anonymous reviewer
Winter is a harsh season for many organisms that have to cope with food shortage and potentially lethal temperatures. Many species have evolved avoidance strategies. Among them, diapause is a resistance stage many insects use to overwinter. For an insect, it is critical to avoid lethal winter temperatures and thus to initiate diapause before winter comes, while making the most of autumn suitable climatic conditions [1,2]. Several cues can be used to appreciate that winter is coming, including day length and temperature [3]. But climate changes, temperatures rise and become more variable from year to year, which imposes strong pressure upon insect phenology [4]. How can insects adapt to changes in the mean and variance of winter onset?
In this paper, Jens Joschinski and Dries Bonte [5] address this question by using a well conducted meta-analysis of 458 diapause reaction norms obtained from 60 primary studies. They first ask first if insect mean diapause timing is tuned to match winter onset. They further ask if insects adapt to climatic unpredictability through a bet-hedging strategy by playing it safe and avoid risk (conservative bet-hedging) or on the contrary by avoiding to put all their eggs in one basket and spread the risk among their offspring (diversified bet-hedging). From published papers, the authors extracted data on mean diapause timing and information on latitude from which they retrieved day length inducing diapause, the date of winter onset and the day length at winter onset.
They found a positive correlation between latitude and the day length inducing diapause. On the contrary they found positive but (very) weak correlation between the date of winter onset and the date of diapause, thus indicating that diapause timing is not as optimally adapted to local environments as expected, particularly at high latitudes. They only found weak correlations between climate unpredictability and variability in diapause timing, and no correlation between climate unpredictability and deviation from optimal diapause timing. Together, these findings go against the hypothesis that insects use diversified or conservative bet-hedging strategies to cope with uncertainty in climatic conditions.
This is what makes the study thought provoking: the results do not match the theory well. Not because of a lack of data or a narrow scope, but because diapause is a complex trait that is determined by a large array of physiological and ecological factors [3]. Determining what are these factors is of particular interest in the face of the current climate change. This study shows what does not determine the timing of insect diapause. Researchers now know where to look at to improve our understanding of this key aspect of insect adaptation to climatic conditions.
References
[1] Dyck, H. V., Bonte, D., Puls, R., Gotthard, K., and Maes, D. (2015). The lost generation hypothesis: could climate change drive ectotherms into a developmental trap? Oikos, 124(1), 54–61. doi: 10.1111/oik.02066
[2] Gallinat, A. S., Primack, R. B., and Wagner, D. L. (2015). Autumn, the neglected season in climate change research. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 30(3), 169–176. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2015.01.004
[3] Tougeron, K. (2019). Diapause research in insects: historical review and recent work perspectives. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 167(1), 27–36. doi: 10.1111/eea.12753
[4] Bale, J. S., and Hayward, S. a. L. (2010). Insect overwintering in a changing climate. Journal of Experimental Biology, 213(6), 980–994. doi: 10.1242/jeb.037911
[5] Joschinski, J., and Bonte, D. (2020). Diapause is not selected as a bet-hedging strategy in insects: a meta-analysis of reaction norm shapes. BioRxiv, 752881, ver. 3 recommended and peer-reviewed by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/752881
| Diapause is not selected as a bet-hedging strategy in insects: a meta-analysis of reaction norm shapes | Jens Joschinski and Dries Bonte | Many organisms escape from lethal climatological conditions by entering a resistant resting stage called diapause, and it is essential that this strategy remains optimally timed with seasonal change. Climate change therefore exerts selection press... | 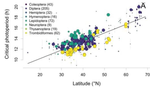 | Maternal effects, Meta-analyses, Phenotypic plasticity, Terrestrial ecology | Bastien Castagneyrol | | 2019-09-20 11:47:47 | View |
Stoichiometric constraints modulate the effects of temperature and nutrients on biomass distribution and community stability
Arnaud Sentis, Bart Haegeman, and José M. Montoya
https://doi.org/10.1101/589895
On the importance of stoichiometric constraints for understanding global change effects on food web dynamics
Recommended by Elisa Thebault based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The constraints associated with the mass balance of chemical elements (i.e. stoichiometric constraints) are critical to our understanding of ecological interactions, as outlined by the ecological stoichiometry theory [1]. Species in ecosystems differ in their elemental composition as well as in their level of elemental homeostasis [2], which can determine the outcome of interactions such as herbivory or decomposition on species coexistence and ecosystem functioning [3, 4].
Despite their importance, stoichiometric constraints are still often ignored in theoretical studies exploring the consequences of environmental perturbations on food web stability. Meanwhile, drivers of global change strongly alter biochemical cycles and the balance of chemical elements in ecosystems [5]. An important challenge is thus to understand how stoichiometric constraints affect food web responses to global changes.
The study of Sentis et al. [6] makes a step in that direction. This article investigates how stoichiometric constraints affect the response of consumer-resource dynamics to increasing temperature and nutrient inputs. It shows that the stoichiometric flexibility of the resource, coupled with lower consumer assimilation efficiency when stoichiometric unbalance between the resource and the consumer is higher, dampens the destabilizing effects of nutrient enrichment on species dynamics but reduces consumer persistence at extreme temperatures. Interestingly, these effects of stoichiometric constraints arise not only from changes in species assimilation efficiencies and carrying capacities but also from stoichiometric negative feedback loops on resource and consumer populations.
The results of this study are a call to further include stoichiometric constraints into food web models to better understand and predict the consequences of global changes on ecological communities. Many perspectives exist on that issue. For instance, it would be interesting to assess the effects of other stoichiometric mechanisms (e.g. changes in the element limiting growth [3]) on food web stability and its response to nutrient enrichment, as well as the effects of other global change drivers associated with altered biochemical cycles (e.g. carbon dioxide increase).
References
[1] Sterner, R. W. and Elser, J. J. (2017). Ecological Stoichiometry, The Biology of Elements from Molecules to the Biosphere. doi: 10.1515/9781400885695
[2] Elser, J. J., Sterner, R. W., Gorokhova, E., Fagan, W. F., Markow, T. A., Cotner, J. B., Harrison, J.F., Hobbie, S.E., Odell, G.M., Weider, L. W. (2000). Biological stoichiometry from genes to ecosystems. Ecology Letters, 3(6), 540–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2000.00185.x
[3] Daufresne, T., and Loreau, M. (2001). Plant–herbivore interactions and ecological stoichiometry: when do herbivores determine plant nutrient limitation? Ecology Letters, 4(3), 196–206. doi: 10.1046/j.1461-0248.2001.00210.x
[4] Zou, K., Thébault, E., Lacroix, G., and Barot, S. (2016). Interactions between the green and brown food web determine ecosystem functioning. Functional Ecology, 30(8), 1454–1465. doi: 10.1111/1365-2435.12626
[5] Peñuelas, J., Poulter, B., Sardans, J., Ciais, P., van der Velde, M., Bopp, L., Boucher, O., Godderis, Y., Hinsinger, P., Llusia, J., Nardin, E., Vicca, S., Obersteiner, M., Janssens, I. A. (2013). Human-induced nitrogen–phosphorus imbalances alter natural and managed ecosystems across the globe. Nature Communications, 4(1), 1–10. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3934
[6] Sentis, A., Haegeman, B. & Montoya, J.M. (2020). Stoichiometric constraints modulate the effects of temperature and nutrients on biomass distribution and community stability. bioRxiv, 589895, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/589895
| Stoichiometric constraints modulate the effects of temperature and nutrients on biomass distribution and community stability | Arnaud Sentis, Bart Haegeman, and José M. Montoya | <p>Temperature and nutrients are two of the most important drivers of global change. Both can modify the elemental composition (i.e. stoichiometry) of primary producers and consumers. Yet their combined effect on the stoichiometry, dynamics, and s... |  | Climate change, Community ecology, Food webs, Theoretical ecology, Thermal ecology | Elisa Thebault | | 2019-08-08 12:20:08 | View |
Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits
Legay Nicolas, Grassein Fabrice, Arnoldi Cindy, Segura Raphaël, Laîné Philippe, Lavorel Sandra, Clément Jean-Christophe
https://doi.org/10.1101/372235
Nitrate or not nitrate. That is the question
Recommended by Sébastien Barot based on reviews by Vincent Maire and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Vincent Maire and 1 anonymous reviewer
The article by Legay et al. [1] addresses two main issues: the links between belowground and aboveground plant traits and the links between plant strategies (as defined by these traits) and the capacity to absorb nitrate and ammonium. I recommend this work because these are important and current issues. The literature on plant traits is extremely rich and the existence of a leaf economic spectrum linked to a gradient between conservative and acquisitive plants is now extremely well established [2-3]. Many teams are now working on belowground traits and possible links with the aboveground gradients [4-5]. It seems indeed that there is a root economic spectrum but this spectrum is apparently less pronounced than the leaf economic spectrum. The existence of links between the two spectrums are still controversial and are likely not universal as suggested by discrepant results and after all a plant could have a conservative strategy aboveground and an acquisitive strategy belowground (or vice-versa) because, indeed, constraints are different belowground and aboveground (for example because in given ecosystem/vegetation type light may be abundant but not water or mineral nutrients). The various results obtained also suggest that we do not full understand the diversity of belowground strategies, what is at stake with these strategies, and the links with root characteristics.
Each time I give a conference on the work we are carrying out on African grasses that likely absorb ammonium preferentially because they inhibit nitrification [6-7], somebody asks me a question about the fact that plant essentially absorb nitrate because ammonium is toxic and nitrate more available in the soil. The present article confirms that this is not the case and that, though there are currently some teams working on the subject, we do not really know for the moment whether plants absorb nitrate or ammonium, in which proportion, how plastic this proportion is within individuals and within species. This subject seems to me crucial because it is linked to (1) the capacity of ecosystems to conserve nitrogen [8], because nitrate, much more than ammonium, goes out of ecosystems through leaching and denitrification, (2) to carbon cycling and plant energy budget because absorbing nitrate requires spending mucho more energy than absorbing ammonium because nitrate must be reduced before being incorporated in plant biomass, which is very energy costly. These two issues are naturally very relevant to develop efficient cropping systems in terms of carbon and nitrogen.
Interestingly, the present article, comparing three grass species in different sites, suggests that there is no trade-off between the absorption of nitrate and ammonium: more acquisitive individuals tend to absorb more ammonium and nitrate. This is contrary to hypotheses we made to predict the outcome of competition between plants absorbing nitrate and ammonium in different proportions [9] but should be tested in the future comparing many different types of plants. The results also suggest that more conservative plants absorb relatively more ammonium, which makes sense because this allows them to spare the energy necessary to reduce nitrate. This leads to the question of the effect of these strategies on nitrogen retention within the ecosystem. If nitrification is high (low), absorbing ammonium is not efficient and likely leads to high (low) nitrogen losses. This should be tested in the future. Moreover, the authors have measured the absorption of nitrate and ammonium through measurements at the root scale on cut roots. This should be complemented by measurements at the whole plant scale.
References
[1] Legay, N., Grassein, F., Arnoldi, C., Segura, R., Laîné, P., Lavorel, S. and Clément, J.-C. (2020). Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits. bioRxiv, 372235, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/372235
[2] Shipley, B., Lechowicz, M.J., Wright, I. & Reich, P.B. (2006) Fundamental trade-offs generating the worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Ecology, 87, 535-541. doi: 10.1890/05-1051
[3] Reich, P.B. (2014) The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. J. Ecol., 102, 275-301. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12211
[4] Maire, V., Gross, N., Pontes, L.D.S., Picon-Cochard, C. & Soussana, J.F. (2009) Trade-off between root nitrogen acquisition and shoot nitrogen utilization across 13 co-occurring pasture grass species. Func. Ecol., 23, 668-679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2009.01557.x
[5] Roumet, C., Birouste, M., Picon-Cochard, C., Ghestem, M., Osman, N., Vrignon-Brenas, S., Cao, K.F. & Stokes, A. (2016) Root structure-function relationships in 74 species: evidence of a root economics spectrum related to carbon economy. New. Phytol., 210, 815-826. doi: 10.1111/nph.13828
[6] Lata, J.-C., Degrange, V., Raynaud, X., Maron, P.-A., Lensi, R. & Abbadie, L. (2004) Grass populations control nitrification in savanna soils. Funct. Ecol., 18, 605-611. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00880.x
[7] Srikanthasamy, T., Leloup, J., N’Dri, A.B., Barot, S., Gervaix, J., Koné, A.W., Koffi, K.F., Le Roux, X., Raynaud, X. & Lata, J.-C. (2018) Contrasting effects of grasses and trees on microbial N-cycling in an African humid savanna. Soil Biol. Biochem., 117, 153-163. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.11.016
[8] Boudsocq, S., Lata, J.C., Mathieu, J., Abbadie, L. & Barot, S. (2009) Modelling approach to analyze the effects of nitrification inhibition on primary production. Func. Ecol., 23, 220-230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01476.x
[9] Boudsocq, S., Niboyet, A., Lata, J.-C., Raynaud, X., Loeuille, N., Mathieu, J., Blouin, M., Abbadie, L. & Barot, S. (2012) Plant preference for ammonium versus nitrate: a neglected determinant of ecosystem functioning? Am. Nat., 180, 60-69. doi: 10.1086/665997
| Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits | Legay Nicolas, Grassein Fabrice, Arnoldi Cindy, Segura Raphaël, Laîné Philippe, Lavorel Sandra, Clément Jean-Christophe | <p>The leaf economics spectrum (LES) is based on a suite of leaf traits related to plant functioning and ranges from resource-conservative to resource-acquisitive strategies. However, the relationships with root traits, and the associated belowgro... |  | Community ecology, Physiology, Terrestrial ecology | Sébastien Barot | | 2018-07-19 14:22:28 | View |

 based on reviews by Bastien Castagneyrol and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Bastien Castagneyrol and 1 anonymous reviewer

 based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi, Wojciech Uszko and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi, Wojciech Uszko and 1 anonymous reviewer





 based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz
based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz


 based on reviews by Tiago Pereira and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Tiago Pereira and 1 anonymous reviewer


 based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor
based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor

 based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron, Md Habibur Rahman Salman and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron, Md Habibur Rahman Salman and 1 anonymous reviewer



 based on reviews by Vincent Maire and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Vincent Maire and 1 anonymous reviewer











