Three points of consideration before testing the effect of patch connectivity on local species richness: patch delineation, scaling and variability of metrics
F. Laroche, M. Balbi, T. Grébert, F. Jabot & F. Archaux
https://doi.org/10.1101/640995
Good practice guidelines for testing species-isolation relationships in patch-matrix systems
Recommended by Damaris Zurell based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
Conservation biology is strongly rooted in the theory of island biogeography (TIB). In island systems where the ocean constitutes the inhospitable matrix, TIB predicts that species richness increases with island size as extinction rates decrease with island area (the species-area relationship, SAR), and species richness increases with connectivity as colonisation rates decrease with island isolation (the species-isolation relationship, SIR)[1]. In conservation biology, patches of habitat (habitat islands) are often regarded as analogous to islands within an unsuitable matrix [2], and SAR and SIR concepts have received much attention as habitat loss and habitat fragmentation are increasingly threatening biodiversity [3,4].
The existence of SAR in patch-matrix systems has been confirmed in several studies, while the relative importance of SIR remains debated [2,5] and empirical evidence is mixed. For example, Thiele et al. [6] showed that connectivity effects are trait specific and more important to explain species richness of short-distant dispersers and of specialist species for which the matrix is less permeable. Some authors have also cautioned that the relative support for or against the existence of SIR may depend on methodological decisions related to connectivity metrics, patch classification, scaling decisions and sample size [7].
In this preprint, Laroche and colleagues [8] argue that methodological limits should be fully understood before questioning the validity of SIR in patch-matrix systems. In consequence, they used a virtual ecologist approach [9] to qualify different methodological aspects and derive good practice guidelines related to patch delineation, patch connectivity indices, and scaling of indices with species dispersal distance.
Laroche et al. [8] simulated spatially-explicit neutral meta-communities with up to 100 species in artificial fractal (patch-matrix) landscapes. Each habitat cell could hold up to 100 individuals. In each time step, some individuals died and were replaced by an individual from the regional species pool depending on relative local and regional abundance as well as dispersal distance to the nearest source habitat cell. Different scenarios were run with varying degrees of spatial autocorrelation in the fractal landscape (determining the clumpiness of habitat cells), the proportion of suitable habitat, and the species dispersal distances (with all species showing the same dispersal distance). Laroche and colleagues then sampled species richness in the simulated meta-communities, computed different local connectivity indices for the simulated landscapes (Buffer index with different radii, dIICflux index and dF index, and, finally, related species richness to connectivity.
The complex simulations allowed Laroche and colleagues [8] to test how methodological choices and landscape features may affect SIR. Overall, they found that patch delineation is crucial and should be fine enough to exclude potential within-patch dispersal limitations, and the scaling of the connectivity indices (in simplified words, the window of analyses) should be tailored to the dispersal distance of the species group. Of course, tuning the scaling parameters will be more complicated when dispersal distances vary across species but overall these results corroborate empirical findings that SIR effects are trait specific [6]. Additionally, the results by Laroche and colleagues [8] indicated that indices based on Euclidian rather than topological distance are more performant and that evidence of SIR is more likely if Buffer indices are highly variable between sampled patches.
Although the study is very technical due to the complex simulation approach and the different methods tested, I hope it will not only help guiding methodological choices but also inspire ecologists to further test or even revisit SIR (and SAR) hypotheses for different systems. Also, Laroche and colleagues propose many interesting avenues that could still be explored in this context, for example determining the optimal grid resolution for the patch delineation in empirical studies.
References
[1] MacArthur, R.H. and Wilson, E.O. (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
[2] Fahrig, L. (2013) Rethinking patch size and isolation effects: the habitat amount hypothesis. Journal of Biogeography, 40(9), 1649-1663. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12130
[3] Hanski, I., Zurita, G.A., Bellocq, M.I. and Rybicki J (2013) Species–fragmented area relationship. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences U.S.A., 110(31), 12715-12720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1311491110
[4] Giladi, I., May, F., Ristow, M., Jeltsch, F. and Ziv, Y. (2014) Scale‐dependent species–area and species–isolation relationships: a review and a test study from a fragmented semi‐arid agro‐ecosystem. Journal of Biogeography, 41(6), 1055-1069. doi: 10.1111/jbi.12299
[5] Hodgson, J.A., Moilanen, A., Wintle, B.A. and Thomas, C.D. (2011) Habitat area, quality and connectivity: striking the balance for efficient conservation. Journal of Applied Ecology, 48(1), 148-152. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2664.2010.01919.x
[6] Thiele, J., Kellner, S., Buchholz, S., and Schirmel, J. (2018) Connectivity or area: what drives plant species richness in habitat corridors? Landscape Ecology, 33, 173-181. doi: 10.1007/s10980-017-0606-8
[7] Vieira, M.V., Almeida-Gomes, M., Delciellos, A.C., Cerqueira, R. and Crouzeilles, R. (2018) Fair tests of the habitat amount hypothesis require appropriate metrics of patch isolation: An example with small mammals in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Biological Conservation, 226, 264-270. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2018.08.008
[8] Laroche, F., Balbi, M., Grébert, T., Jabot, F. and Archaux, F. (2020) Three points of consideration before testing the effect of patch connectivity on local species richness: patch delineation, scaling and variability of metrics. bioRxiv, 640995, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/640995
[9] Zurell, D., Berger, U., Cabral, J.S., Jeltsch, F., Meynard, C.N., Münkemüller, T., Nehrbass, N., Pagel, J., Reineking, B., Schröder, B. and Grimm, V. (2010) The virtual ecologist approach: simulating data and observers. Oikos, 119(4), 622-635. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0706.2009.18284.x
| Three points of consideration before testing the effect of patch connectivity on local species richness: patch delineation, scaling and variability of metrics | F. Laroche, M. Balbi, T. Grébert, F. Jabot & F. Archaux | <p>The Theory of Island Biogeography (TIB) promoted the idea that species richness within sites depends on site connectivity, i.e. its connection with surrounding potential sources of immigrants. TIB has been extended to a wide array of fragmented... | 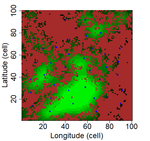 | Biodiversity, Community ecology, Dispersal & Migration, Landscape ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Damaris Zurell | | 2019-05-20 16:03:47 | View |
Trophic cascade driven by behavioural fine-tuning as naïve prey rapidly adjust to a novel predator
Chris J Jolly, Adam S Smart, John Moreen, Jonathan K Webb, Graeme R Gillespie and Ben L Phillips
https://doi.org/10.1101/856997
While the quoll’s away, the mice will play… and the seeds will pay
Recommended by Denis Réale based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
A predator can strongly influence the demography of its prey, which can have profound carryover effects on the trophic network; so-called density-mediated indirect interactions (DMII; Werner and Peacor 2003; Schmitz et al. 2004; Trussell et al. 2006). Furthermore, a novel predator can alter the phenotypes of its prey for traits that will change prey foraging efficiency. These trait-mediated indirect interactions may in turn have cascading effects on the demography and features of the basal resources consumed by the intermediate consumer (TMIII; Werner and Peacor 2003; Schmitz et al. 2004; Trussell et al. 2006), but very few studies have looked for these effects (Trusell et al. 2006). The study “Trophic cascade driven by behavioural fine-tuning as naïve prey rapidly adjust to a novel predator”, by Jolly et al. (2020) is therefore a much-needed addition to knowledge in this field. The authors have profited from a rare introduction of Northern quolls (Dasyurus hallucatus) on an Australian island, to examine both the density-mediated and trait-mediated indirect interactions with grassland melomys (Melomys burtoni) and the vegetation of their woodland habitat.
Jolly et al. (2020) compared melomys populations in four quoll-invaded and three quoll-free sites on the same island. Using capture-mark-recapture methods, they found a lower survival and decreased population size in quoll-invaded sites compared to quoll-free sites. Although they acknowledge that this decline could be attributable to either the direct effects of the predator or to a wildfire that occurred early in the experiment in the quoll-invaded sites, the authors argue that the wildfire alone cannot explain all of their results.
Beyond demographic effects, Jolly et al. (2020) also examined risk taking, foraging behaviour, and predator avoidance in melomys. Quoll presence was first associated with a strong decrease in risk taking in melomys, but the difference disappeared over the three years of study, indicating a possible adjustment by the prey. In quoll-invaded sites, though, melomys continued to be more neophobic than in the quoll-free sites throughout the study. Furthermore, in a seed (i.e. wheat) removal experiment, Jolly et al. (2020) measured how melomys harvested seeds in the presence or absence of predator scents. In both quoll-invaded and quoll-free sites, melomys density increased seed harvest efficiency. Melomys also removed less seeds in quoll-invaded sites than in quoll-free sites, supporting both the DMII and TMII hypotheses. However, in the quoll-invaded sites only, melomys foraged less on predator-scented seed patches than on unscented ones, trading foraging efficiency for an increased safety against predators, and this effect increased across the years. This last result indicates that predators can indirectly influence seed consumption through the trade-off between foraging and predator avoidance, strongly supporting the TMII hypothesis.
Ideally, the authors would have run a nice before-after, impact-control design, but nature does not always allow for ideal experimental designs. Regardless, the results of such an “experiment in the wild” predation study are still valuable, as they are very rare (Trussell et al. 2006), and they provide crucial information on the direct and indirect interactions along a trophic cascade. Furthermore, the authors have effectively addressed any concerns about potential confounding factors, and thus have a convincing argument that their results represent predator-driven demographic and behavioural changes.
One important question remains from an evolutionary ecology standpoint: do the responses of melomys to the presence of quolls represent phenotypically plastic changes or rapid evolutionary changes caused by novel selection pressures? Classically, TMII are assumed to be mostly caused by phenotypic plasticity (Werner and Peacor 2003), and this might be the case when the presence of the predator is historical. Phenotypic plasticity allows quick and reversible adjustments of the prey population to changes in the predator density. When the predator population declines, such rapid phenotypic changes can be reversed, reducing the cost associated with anti-predator behaviour (e.g., lower foraging efficiency) in the absence of predators. In the case of a novel predator, however, short-term evolutionary responses by the prey may play role in the TMII, as they would allow a phenotypic shift in prey’s traits along the trade-off between foraging efficiency and anti-predator response that will probably more advantageous over the longer term, if the predator does not disappear. The authors state that they could not rule out one or the other of these hypotheses. However, future work estimating the relative importance of phenotypic plasticity and evolutionary changes in the quoll-melomys system would be valuable. Phenotypic selection analysis, for example, by estimating the link between survival and the traits measured, might help test for a fitness advantage to altered behaviour in the presence of a predator. Common garden experiments, comparing the quoll-invaded and the quoll-free melomys populations, might also provide information on any potential evolutionary changes caused by predation. More work could also analyse the potential effects on the seed populations. Not only might the reduction in seed predation have consequences on the landscape in the future, as the authors mention, but it may also mean that the seeds themselves could be subject to novel selection pressures, which may affect their phenology, physiology or life history. Off course, the authors will have to switch from wheat to a more natural situation, and evaluate the effects of changes in the melomys population on the feature of the local vegetation and the ecosystem.
Finally, the authors have not yet found that the observed changes in the traits have translated into a demographic rebound for melomys. Here again, I can see an interesting potential for further studies. Should we really expect an evolutionary rescue (Bell and Gonzalez 2009) in this system? Alternatively, should the changes in behaviour be accompanied by permanent changes in life history, such as a slower pace-of-life (Réale et al. 2010) that could possibly lead to lower melomys density?
This paper provides nice in natura evidence for density- and trait-mediated indirect interactions hypotheses. I hope it will be the first of a long series of work on this interesting quoll-melomys system, and that the authors will be able to provide more information on the eco-evolutionary consequences of a novel predator on a trophic network.
References
-Bell G, Gonzalez A (2009) Evolutionary rescue can prevent extinction following environmental change. Ecology letters, 12(9), 942-948. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01350.x
-Jolly CJ, Smart AS, Moreen J, Webb JK, Gillespie GR, Phillips BL (2020) Trophic cascade driven by behavioural fine-tuning as naïve prey rapidly adjust to a novel predator. bioRxiv, 856997, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/ 10.1101/856997
-Matassa C, Ewanchuk P, Trussell G (2018) Cascading effects of a top predator on intraspecific competition at intermediate and basal trophic levels. Functional Ecology, 32(9), 2241-2252. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13131
-Réale D, Garant D, Humphries MM, Bergeron P, Careau V, Montiglio PO (2010) Personality and the emergence of the pace-of-life syndrome concept at the population level. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 365(1560), 4051-4063. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2010.0208
-Schmitz O, Krivan V, Ovadia O (2004) Trophic cascades: the primacy of trait‐mediated indirect interactions. Ecology Letters 7(2), 153-163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2003.00560.x
-Trussell G, Ewanchuk P, Matassa C (2006). Habitat effects on the relative importance of trait‐ and density‐mediated indirect interactions. Ecology Letters, 9(11), 1245-1252. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00981.x
-Werner EE, Peacor SD (2003) A review of trait‐mediated indirect interactions in ecological communities. Ecology, 84(5), 1083-1100. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2003)084[1083:AROTII]2.0.CO;2
| Trophic cascade driven by behavioural fine-tuning as naïve prey rapidly adjust to a novel predator | Chris J Jolly, Adam S Smart, John Moreen, Jonathan K Webb, Graeme R Gillespie and Ben L Phillips | <p>The arrival of novel predators can trigger trophic cascades driven by shifts in prey numbers. Predators also elicit behavioural change in prey populations, via phenotypic plasticity and/or rapid evolution, and such changes may also contribute t... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Biological invasions, Evolutionary ecology, Experimental ecology, Foraging, Herbivory, Population ecology, Terrestrial ecology, Tropical ecology | Denis Réale | | 2019-11-27 21:39:44 | View |
Why are dominant females not always showing higher reproductive success? A preregistration of a meta-analysis on social mammals
Recommended by Matthieu Paquet based on reviews by Bonaventura Majolo and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Bonaventura Majolo and 1 anonymous reviewer
In social species conflicts among group members typically lead to the formation of dominance hierarchies with dominant individuals outcompeting other groups members and, in some extreme cases, suppressing reproduction of subordinates. It has therefore been typically assumed that dominant individuals have a higher breeding success than subordinates. However, previous work on mammals (mostly primates) revealed high variation, with some populations showing no evidence for a link between female dominance reproductive success, and a meta-analysis on primates suggests that the strength of this relationship is stronger for species with a longer lifespan [1]. Therefore, there is now a need to understand 1) whether dominance and reproductive success are generally associated across social mammals (and beyond) and 2) which factors explains the variation in the strength (and possibly direction) of this relationship.
In their preregistration, Shivani et al. [2] plan to perform a meta-analysis on 86 social mammal species to address these two points. More specifically, they will investigate whether the relationship between female dominance and reproductive success vary according to life history traits (e.g. stronger for species with large litter size), ecological conditions (e.g. stronger when resources are limited) and the social environment (e.g. stronger for cooperative breeders than for plural breeders).
The two reviewers and I were particularly positive and enthusiastic about this preregistration and only had minor comments that were nicely addressed by the authors. We found the background well-grounded in the existing literature and that the predictions were therefore clear and well-motivated. The methods were particularly transparent with a nicely annotated R script and the authors even simulated a dataset with the same structure as the actual data in order to make sure that the coding of the data handling and statistical analyses were appropriate (without being tempted to look at model outputs from the true dataset).
Perhaps one limitation to keep in mind once we will have the chance to look at the outcome of this study if that the dataset may not be fully representative of social species with dominance hierarchies. For example, the current dataset contains only one aquatic mammal (Mirounga angustirostris) as far as I can see, which is likely due to a lack of knowledge on such systems. Furthermore, not only mammals exhibit dominance hierarchies and it will be interesting to see if the results of the proposed study hold for other social taxa (and if not, what may explain their differences).
That being said, the proposed study will already offer a much broader overview of the relationship between dominance and reproductive success in animal societies and a better understanding for its variation. The reviewers and I believe it will make an important contribution to the fields of socio-ecology and evolutionary ecology. I therefore strongly recommend this preregistration and we are particularly looking forward to seeing the outcome of this exciting study.
References
[1] Majolo, B., Lehmann, J., de Bortoli Vizioli, A., & Schino, G. (2012). Fitness‐related benefits of dominance in primates. American journal of physical anthropology, 147(4), 652-660. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22031
[2] Shivani, Huchard, E., Lukas, D. (2020). Preregistration - The effect of dominance rank on female reproductive success in social mammals In principle acceptance by PCI Ecology of the version 1.2 on 07 July 2020. https://github.com/dieterlukas/FemaleDominanceReproductionMetaAnalysis/blob/trunk/PreregistrationMetaAnalysis_RankSuccess.Rmd
| Preregistration - The effect of dominance rank on female reproductive success in social mammals | Shivani, Elise Huchard, Dieter Lukas | <p>Life in social groups, while potentially providing social benefits, inevitably leads to conflict among group members. In many social mammals, such conflicts lead to the formation of dominance hierarchies, where high-ranking individuals consiste... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Meta-analyses, Preregistrations, Social structure, Zoology | Matthieu Paquet | Bonaventura Majolo, Anonymous | 2020-04-06 17:42:37 | View |
Environmental perturbations and transitions between ecological and evolutionary equilibria: an eco-evolutionary feedback framework
Tim Coulson
https://doi.org/10.1101/509067
Stasis and the phenotypic gambit
Recommended by Tom Van Dooren based on reviews by Jacob Johansson, Katja Räsänen and 1 anonymous reviewer
The preprint "Environmental perturbations and transitions between ecological and evolutionary equilibria: an eco-evolutionary feedback framework" by Coulson (2020) presents a general framework for evolutionary ecology, useful to interpret patterns of selection and evolutionary responses to environmental transitions. The paper is written in an accessible and intuitive manner. It reviews important concepts which are at the heart of evolutionary ecology. Together, they serve as a worldview which you can carry with you to interpret patterns in data or observations in nature. I very much appreciate it that Coulson (2020) presents his personal intuition laid bare, the framework he uses for his research and how several strong concepts from theoretical ecology fit in there. Overviews as presented in this paper are important to understand how we as researchers put the pieces together.
A main message of the paper is that resource detection and acquisition traits, broadly called "resource accrual traits" are at the core of evolutionary dynamics. These traits and the processes they are involved in often urge some degree of individual specialization. Not all traits are resource accrual traits all the time. Guppies are cited as an example, which have traits in high predation environments that make foraging easier for them, such as being less conspicuous to predators. In the absence of predators, these same traits might be neutral. Their colour pattern might then contribute much less to the odds of obtaining resources.
"Resource accrual" reminds me of discussions of resource holding potential (Parker 1974), which can be for example the capacity to remain on a bird feeder without being dislodged. However, the idea is much broader and aggression does not need to be important for the acquisition of resources. Evolutionary success is reserved for those steadily obtaining resources. This recalls the pessimization principle of Metz et al. (2008), which applies in a restricted set of situations and where the strategy which persists at the lowest resource levels systematically wins evolutionary contests. If this principle would apply universally, the world then inherently become the worst possible. Resources determine energy budgets and different life history strategies allocate these differently to maximize fitness. The fine grain of environments and the filtration by individual histories generate a lot of variation in outcomes. However, constraint-centered approaches (Kempes et al. 2019, Kooijman 2010) are mentioned but are not at the core of this preprint. Evolution is rather seen as dynamic programming optimization with interactions within and between species. Coulson thus extends life history studies such as for example Tonnabel et al. (2012) with eco-evolutionary feedbacks. Examples used are guppies, algae-rotifer interactions and others. Altogether, this makes for an optimistic paper pushing back the pessimization principle.
Populations are expected to spend most of the time in quasi-equilibrium states where the long run stochastic growth rate is close to zero for all genotypes, alleles or other chosen classes. In the preprint, attention is given to reproductive value calculus, another strong tool in evolutionary dynamics (Grafen 2006, Engen et al. 2009), which tells us how classes within a population contribute to population composition in the distant future. The expected asymptotic fitness of an individual is equated to its expected reproductive value, but this might require particular ways of calculating reproductive values (Coulson 2020). Life history strategies can also be described by per generation measures such as R0 (currently on everyone's radar due to the coronavirus pandemic), generation time etc. Here I might disagree because I believe that this focus in per generation measures can lead to an incomplete characterization of plastic and other strategies involved in strategies such as bet-hedging. A property at quasi-equilibrium states is precise enough to serve as a null hypothesis which can be falsified: all types must in the long run leave equal numbers of descendants. If there is any property in evolutionary ecology which is useful it is this one and it rightfully merits attention.
However, at quasi-equilibrium states, directional selection has been observed, often without the expected evolutionary response. The preprint aims to explain this and puts forward the presence of non-additive gene action as a mechanism. I don't believe that it is the absence of clonal inheritance which matters very much in itself (Van Dooren 2006) unless genes with major effect are present in protected polymorphisms. The preprint remains a bit unclear on how additive gene action is broken, and here I add from the sphere in which I operate. Non-additive gene action can be linked to non-linear genotype-phenotype maps (Van Dooren 2000, Gilchrist and Nijhout 2001) and if these maps are non-linear enough to create constraints on phenotype determination, by means of maximum or minimum phenotypes which cannot be surpassed for any combination of the underlying traits, then they create additional evolutionary quasi-equilibrium states, with directional selection on a phenotype such as body size. I believe Coulson hints at this option (Coulson et al. 2006), but also at a different one: if body size is mostly determined by variation in resource accrual traits, then the resource accrual traits can be under stabilizing selection while body size is not. This requires that all resource accrual traits affect other phenotypic or demographic properties next to body size. In both cases, microevolutionary outcomes cannot be inferred from inspecting body sizes alone, either resource accrual traits need to be included explicitly, or non-linearities, or both when the map between resource accrual and body size is non-linear (Van Dooren 2000).
The discussion of the phenotypic gambit (Grafen 1984) leads to another long-standing issue in evolutionary biology. Can predictions of adaptation be made by inspecting and modelling individual phenotypes alone? I agree that with strongly non-linear genotype-phenotype maps they cannot and for multivariate sets of traits, genetic and phenotypic correlations can be very different (Hadfield et al. 2007). However, has the phenotypic gambit ever claimed to be valid globally or should it rather be used locally for relatively small amounts of variation? Grafen (1984) already contained caveats which are repeated here. As a first approximation, additivity might produce quite correct predictions and thus make the gambit operational in many instances. When important individual traits are omitted, it may just be misspecified. I am interested to see cases where the framework Coulson (2020) proposes is used for very large numbers of phenotypic and genotypic attributes. In the end, these highly dimensional trait distributions might basically collapse to a few major axes of variation due to constraints on resource accrual.
I highly recommend reading this preprint and I am looking forward to the discussion it will generate.
References
[1] Coulson, T. (2020) Environmental perturbations and transitions between ecological and evolutionary equilibria: an eco-evolutionary feedback framework. bioRxiv, 509067, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/509067
[2] Coulson, T., Benton, T. G., Lundberg, P., Dall, S. R. X., and Kendall, B. E. (2006). Putting evolutionary biology back in the ecological theatre: a demographic framework mapping genes to communities. Evolutionary Ecology Research, 8(7), 1155-1171.
[3] Engen, S., Lande, R., Sæther, B. E. and Dobson, F. S. (2009) Reproductive value and the stochastic demography of age-structured populations. The American Naturalist 174: 795-804. doi: 10.1086/647930
[4] Gilchrist, M. A. and Nijhout, H. F. (2001). Nonlinear developmental processes as sources of dominance. Genetics, 159(1), 423-432.
[5] Grafen, A. (1984) Natural selection, kin selection and group selection. In: Behavioural Ecology: An Evolutionary Approach,2nd edn (JR Krebs & NB Davies eds), pp. 62–84. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford.
[6] Grafen, A. (2006). A theory of Fisher's reproductive value. Journal of mathematical biology, 53(1), 15-60. doi: 10.1007/s00285-006-0376-4
[7] Hadfield, J. D., Nutall, A., Osorio, D. and Owens, I. P. F. (2007). Testing the phenotypic gambit: phenotypic, genetic and environmental correlations of colour. Journal of evolutionary biology, 20(2), 549-557. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2006.01262.x
[8] Kempes, C. P., West, G. B., and Koehl, M. (2019). The scales that limit: the physical boundaries of evolution. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 242. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2019.00242
[9] Kooijman, S. A. L. M. (2010) Dynamic Energy Budget theory for metabolic organisation. University Press, third edition.
[10] Metz, J. A. J., Mylius, S.D. and Diekman, O. (2008) When does evolution optimize?. Evolutionary Ecology Research 10: 629-654.
[11] Parker, G. A. (1974). Assessment strategy and the evolution of fighting behaviour. Journal of theoretical Biology, 47(1), 223-243. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90111-8
[12] Tonnabel, J., Van Dooren, T. J. M., Midgley, J., Haccou, P., Mignot, A., Ronce, O., and Olivieri, I. (2012). Optimal resource allocation in a serotinous non‐resprouting plant species under different fire regimes. Journal of Ecology, 100(6), 1464-1474. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.02023.x
[13] Van Dooren, T. J. M. (2000). The evolutionary dynamics of direct phenotypic overdominance: emergence possible, loss probable. Evolution, 54(6), 1899-1914. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2000.tb01236.x
[14] Van Dooren, T. J. M. (2006). Protected polymorphism and evolutionary stability in pleiotropic models with trait‐specific dominance. Evolution, 60(10), 1991-2003. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2006.tb01837.x
| Environmental perturbations and transitions between ecological and evolutionary equilibria: an eco-evolutionary feedback framework | Tim Coulson | <p>I provide a general framework for linking ecology and evolution. I start from the fact that individuals require energy, trace molecules, water, and mates to survive and reproduce, and that phenotypic resource accrual traits determine an individ... | 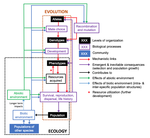 | Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Evolutionary ecology | Tom Van Dooren | | 2019-01-03 10:05:16 | View |
Studying a rare behavior in a polygamous bird: male parental care in great-tailed grackles
Recommended by Marie-Jeanne Holveck based on reviews by Matthieu Paquet and André C Ferreira
The Great-tailed grackle (Quiscalus mexicanus) is a polygamous bird species that is originating from Central America and rapidly expanding its geographic range toward the North, and in which females were long thought to be the sole nest builders and caretakers of the young. In their pre-registration [1], Folsom and collaborators report repeated occurrences of male parental care and develop hypotheses aiming at better understanding the occurrence and the fitness consequences of this very rarely observed male behavior. They propose to assess if male parental care correlates with the circulating levels of several relevant hormones, increases offspring survival, is a local adaptation, and is a mating strategy, in surveying three populations located in Arizona (middle of the geographic range expansion), California (northern edge of the geographic range), and in Central America (core of the range). This study is part of a 5-year bigger project.
Both reviewers and I strongly value Folsom and collaborators’ commitment to program a study, in natural field conditions, of a rare, yet likely evolutionary-important behavior, namely parental care by males of the great-tailed grackle. Yet, we all also recognized that it is a risky endeavor, and as a consequence, we wondered about the authors’ ability to reach a sufficient sample size to statistically test (all) hypotheses and predictions with enough confidence (e.g. risk of type I errors, also known as false positives).
Folsom and collaborators acknowledged these limitations in their pre-registration. (i) They made the exploratory nature of their research work clear to readers. (ii) They adapted their analysis plan in running prior power analyses and in focusing on effect sizes (estimates and confidence intervals). (iii) Last and not least, Folsom and collaborators clearly exposed a priori hypotheses, their associated predictions and alternatives, and ranked the latter based on their plausibility according to knowledge in the current and other study systems. Developing theory about male parental care behavior more generally with regard to a polygamous species that is rapidly expanding its geographic range and that is considered not to provide male parental care is without any doubt an added value to this study.
In summary, while this study will likely be insufficient to fully understand male parental care behavior of great-tailed grackles, it is much needed because it will definitely allow rejecting some predictions (e.g., if this behavior is present in all the studied populations, it would be common across range against expectation; finding only one male providing care to an unrelated offspring would lead to reject the prediction that males only care for their own offspring) and thus it will help laying the foundation of future research directions.
I strongly support the pre-registration system and thank all the contributors for producing a fruitful discussion throughout the review process, which in fine improved the clarity and logic of this pre-registration. Given the positive and encouraging reviews, the detailed and thorough answers to all comments by Folsom and collaborators, and their satisfactory and interesting revisions, I am happy to recommend this pre-registration and I look forward to seeing its outcomes.
References
[1] Folsom MA, MacPherson M, Lukas D, McCune KB, Bergeron L, Bond A, Blackwell A, Rowney C, Logan CJ. 2020. Investigating the rare behavior of male parental care in great-tailed grackles. corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gmalecare.html In principle acceptance by PCI Ecology of the version on 15 June 2020 corinalogan/grackles/blob/master/Files/Preregistrations/gmalecare.Rmd.
| Investigating the rare behavior of male parental care in great-tailed grackles | Folsom MA, MacPherson M, Lukas D, McCune KB, Bergeron L, Bond A, Blackwell A, Rowney C, Logan CJ | This is a PREREGISTRATION submitted for pre-study peer review. Our planned data collection START DATE is May 2020, therefore it would be ideal if the peer review process could be completed before then.
Abstract: Great-tailed grackles (Quiscalus... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Biological invasions, Preregistrations, Zoology | Marie-Jeanne Holveck | | 2019-12-05 17:38:47 | View |
On the efficacy of restoration in stream networks: comments, critiques, and prospective recommendations
David Murray-Stoker
https://doi.org/10.1101/611939
A stronger statistical test of stream restoration experiments
Recommended by Karl Cottenie based on reviews by Eric Harvey and Mariana Perez Rocha
The metacommunity framework acknowledges that local sites are connected to other sites through dispersal, and that these connectivity patterns can influence local dynamics [1]. This framework is slowly moving from a framework that guides fundamental research to being actively applied in for instance a conservation context (e.g. [2]). Swan and Brown [3,4] analyzed the results of a suite of experimental manipulations in headwater and mainstem streams on invertebrate community structure in the context of the metacommunity concept. This was an important contribution to conservation ecology.
However, David Murray-Stoker [5] was not satisfied with their statistical analyses, and recreated, and more importantly, improved their original analyses in the peer-reviewed article. The new analyses are based on a combination of a more consistent site selection, checking the model assumptions, using different estimation procedures, and focusing more on effect size calculations versus statistical significance. This peer-reviewed article is thus the perfect example of the advantages of open research: the original authors making available both the data and their R script files, initially first updating the analyses and results themselves, followed by more in-depth analyses of the original data and question.
This peer reviewed went through a very in-depth process itself, with several rounds of questions and feedback that addressed both the statistical analyses, the interpretation of the results, and the conclusions. It also, however, addressed something that is often harder to provide feedback on, for instance the tone of the argument. I hope that scientists interested in these issues will not only read the final manuscript, but also the different steps of the peer review processes. These are very informative, I think, and provide a more complete picture of mainly the raison for certain decisions.
Not only does this provide the reader interested in stream conservation with the opportunity to make up their own mind on the appropriateness of these decisions, but it could potentially lead to more analyses of this important data set. For instance, maybe a formal meta-analysis that starts with the effect sizes of all the original studies might bring some new insights into this question?
References
[1] Leibold, M. A., Holyoak, M., Mouquet, N. et al. (2004). The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi‐scale community ecology. Ecology letters, 7(7), 601-613. doi: 10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00608.x
[2] Heino, J. (2013). The importance of metacommunity ecology for environmental assessment research in the freshwater realm. Biological Reviews, 88(1), 166-178. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00244.x
[3] Swan, C. M., and Brown, B. L. (2017). Metacommunity theory meets restoration: isolation may mediate how ecological communities respond to stream restoration. Ecological Applications, 27(7), 2209-2219. doi: 10.1002/eap.1602
[4] Swan, C. M., and Brown, B. L. (2018). Erratum for: Metacommunity theory meets restoration: isolation may mediate how ecological communities respond to stream restoration. Ecological Applications 28:1370–1371. doi: 10.1002/eap.1738
[5] Murray-Stoker, D. (2020). On the efficacy of restoration in stream networks: comments, critiques, and prospective recommendations. bioRxiv, 611939, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/611939
| On the efficacy of restoration in stream networks: comments, critiques, and prospective recommendations | David Murray-Stoker | <p>Swan and Brown (2017) recently addressed the effects of restoration on stream communities under the meta-community framework. Using a combination of headwater and mainstem streams, Swan and Brown (2017) evaluated how position within a stream ne... |  | Community ecology, Freshwater ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Karl Cottenie | | 2019-09-21 22:12:57 | View |
Interplay between historical and current features of the cityscape in shaping the genetic structure of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar (Senegal, West Africa)
Claire Stragier, Sylvain Piry, Anne Loiseau, Mamadou Kane, Aliou Sow, Youssoupha Niang, Mamoudou Diallo, Arame Ndiaye, Philippe Gauthier, Marion Borderon, Laurent Granjon, Carine Brouat, Karine Berthier
https://doi.org/10.1101/557066
Urban past predicts contemporary genetic structure in city rats
Recommended by Michelle DiLeo based on reviews by Torsti Schulz, ? and 1 anonymous reviewer
Urban areas are expanding worldwide, and have become a dominant part of the landscape for many species. Urbanization can fragment pre-existing populations of vulnerable species leading to population declines and the loss of connectivity. On the other hand, expansion of urban areas can also facilitate the spread of human commensals including pests. Knowledge of the features of cityscapes that facilitate gene flow and maintain diversity of pests is thus key to their management and eradication.
Cities are complex mosaics of natural and manmade surfaces, and habitat quality is not only influenced by physical aspects of the cityscape but also by socioeconomic factors and human behaviour. Constant development means that cities also change rapidly in time; contemporary urban life reflects only a snapshot of the environmental conditions faced by populations. It thus remains a challenge to identify the features that actually drive ecology and evolution of populations in cities [1]. While several studies have highlighted strong urban clines in genetic structure and adaption [2], few have considered the influence of factors beyond physical aspects of the cityscape or historical processes.
In this paper, Stragier et al. [3] sought to identify the current and past features of the cityscape and socioeconomic factors that shape genetic structure and diversity of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar, Senegal. The authors painstakingly digitized historical maps of Dakar from the time of European settlement in 1862 to present. The authors found that the main spatial genetic cline was best explained by historical cityscape features, with higher apparent gene flow and genetic diversity in areas that were connected earlier to initial European settlements. Beyond the main trend of spatial genetic structure, they found further evidence that current features of the cityscape were important. Specifically, areas with low vegetation and poor housing conditions were found to support large, genetically diverse populations. The authors demonstrate that their results are reproducible using several statistical approaches, including modeling that explicitly accounts for spatial autocorrelation.
The work of Stragier et al. [3] thus highlights that populations of city-dwelling species are the product of both past and present cityscapes. Going forward, urban evolutionary ecologists should consider that despite the potential for rapid evolution in urban landscapes, the signal of a species’ colonization can remain for generations.
References
[1] Rivkin, L. R., Santangelo, J. S., Alberti, M. et al. (2019). A roadmap for urban evolutionary ecology. Evolutionary Applications, 12(3), 384-398. doi: 10.1111/eva.12734
[2] Miles, L. S., Rivkin, L. R., Johnson, M. T., Munshi‐South, J. and Verrelli, B. C. (2019). Gene flow and genetic drift in urban environments. Molecular ecology, 28(18), 4138-4151. doi: 10.1111/mec.15221
[3] Stragier, C., Piry, S., Loiseau, A., Kane, M., Sow, A., Niang, Y., Diallo, M., Ndiaye, A., Gauthier, P., Borderon, M., Granjon, L., Brouat, C. and Berthier, K. (2020). Interplay between historical and current features of the cityscape in shaping the genetic structure of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar (Senegal, West Africa). bioRxiv, 557066, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/557066
| Interplay between historical and current features of the cityscape in shaping the genetic structure of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar (Senegal, West Africa) | Claire Stragier, Sylvain Piry, Anne Loiseau, Mamadou Kane, Aliou Sow, Youssoupha Niang, Mamoudou Diallo, Arame Ndiaye, Philippe Gauthier, Marion Borderon, Laurent Granjon, Carine Brouat, Karine Berthier | <p>Population genetic approaches may be used to investigate dispersal patterns of species living in highly urbanized environment in order to improve management strategies for biodiversity conservation or pest control. However, in such environment,... | 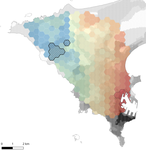 | Biological invasions, Landscape ecology, Molecular ecology | Michelle DiLeo | | 2019-02-22 08:36:13 | View |
A meta-analysis to infer generic predator functional response
Recommended by Samir Simon Suweis based on reviews by Ludek Berec and gyorgy barabas
Species interactions are classically derived from the law of mass action: the probability that, for example, a predation event occurs is proportional to the product of the density of the prey and predator species. In order to describe how predator and prey species populations grow, is then necessary to introduce functional response, describing the intake rate of a consumer as a function of food (e.g. prey) density.
Linear functional responses shapes are typically introduced in the ecological modeling of population dynamics for both predator-prey and mutualistic systems [1,2]. Recently some works have proposed alternatives to the classic approach for mutualistic systems [3,4], both because cooperative interactions also model effect not directly related to mass action [3] and for analytical tractability [4,5].
In this work [6] the authors challenge the classic modeling of functional response also for predator-prey systems. In particular, they use a meta-analysis of several observational studies of predator-prey ecosystems to infer a generic predator functional response, fitting a phenomenological generalization of the mass-action law. Using advanced statistical analysis, they show that the functional response obtained from data is clearly different from the mass-action assumption. In fact, they found that it scales sub-linearly as the square root of the ratio between predator and prey biomass. They further argue that, from a macro-ecological point of view, using such a phenomenological relationship might be more valuable than relying on various mechanistic functional response formulations.
The manuscript thus provides an interesting different perspective on how to approach predator-prey modelling and for this reason, I have recommended the work for PCI Ecology.
References
[1] Volterra, V. (1928). Variations and Fluctuations of the Number of Individuals in Animal Species living together. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 3(1), 3–51. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/3.1.3
[2] Bastolla, U., Fortuna, M. A., Pascual-García, A., Ferrera, A., Luque, B., and Bascompte, J. (2009). The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature, 458(7241), 1018–1020. doi: 10.1038/nature07950
[3] Tu, C., Suweis, S., Grilli, J., Formentin, M., and Maritan, A. (2019). Reconciling cooperation, biodiversity and stability in complex ecological communities. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41614-2
[4] García-Algarra, J., Galeano, J., Pastor, J. M., Iriondo, J. M., and Ramasco, J. J. (2014). Rethinking the logistic approach for population dynamics of mutualistic interactions. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 363, 332–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.08.039
[5] Suweis, S., Simini, F., Banavar, J. R., and Maritan, A. (2013). Emergence of structural and dynamical properties of ecological mutualistic networks. Nature, 500(7463), 449–452. doi: 10.1038/nature12438
[6] Barbier, M., Wojcik, L., and Loreau, M. (2020). A macro-ecological approach to predators’ functional response. BioRxiv, 832220, ver. 4 recommended and peer-reviewed by Peer Community in Ecology. doi: 10.1101/832220
| A macro-ecological approach to predators' functional response | Matthieu Barbier, Laurie Wojcik, Michel Loreau | <p>Predation often deviates from the law of mass action: many micro- and meso-scale experiments have shown that consumption saturates with resource abundance, and decreases due to interference between consumers. But does this observation hold at m... | 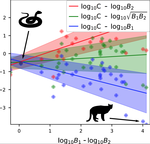 | Community ecology, Food webs, Meta-analyses, Theoretical ecology | Samir Simon Suweis | | 2019-11-08 15:42:16 | View |
Body temperatures, life history, and skeletal morphology in the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus)
Frank Knight, Cristin Connor, Ramji Venkataramanan, Robert J. Asher
https://doi.org/10.17863/CAM.50971
Is vertebral count in mammals influenced by developmental temperature? A study with Dasypus novemcinctus
Recommended by Mar Sobral based on reviews by Darin Croft and ?
Mammals show a very low level of variation in vertebral count, both among and within species, in comparison to other vertebrates [1]. Jordan’s rule for fishes states that the vertebral number among species increases with latitude, due to ambient temperatures during development [2]. Temperature has also been shown to influence vertebral count within species in fish [3], amphibians [4], and birds [5]. However, in mammals the count appears to be constrained, on the one hand, by a possible relationship between the development of the skeleton and the proliferations of cell lines with associated costs (neural malformations, cancer etc., [6]), and on the other by the cervical origin of the diaphragm [7].
Knight et al. [8] investigate the effect of intrauterine temperature variation on skeletal morphology during development, and focus on a particular mammal, Dasypus novemcinctus, or nine-banded armadillo. Armadillos (Xenarthra) and are characterized by relatively low body temperatures and low basal rates of metabolism. Dasypus novemcinctus is the only xenarthran mammal to have naturally expanded its range into the middle latitudes of the U.S., and one of the few mammals that invaded North America from South America. It is one of few placentals that withstand considerable decrease of body temperature without torpor. It presents a resting body temperature that is low and variable for a placental mammal of its size [9] and is the only vertebrate that gives birth to monozygotic quadruplets. Among 42 monotreme, marsupial and placental genera, Dasypus novemcinctus shows the highest variation of thoracolumbar vertebral count [10].
The particularities of Dasypus novemcinctus regarding vertebral count variation and ability to withstand variable temperature qualify it as a target organism for study of the relationship between skeleton morphology and temperature in mammals.
Knight et al. [8] explored variability in vertebral count within Dasypus novemcinctus to understand whether temperature during development determines skeleton morphology. To this end they experimented with 22 armadillos (19 with data) and litters from 12 pregnant females, in two environments, for three years — an impressive effort and experimental setup. Moreover, they used a wide variety of advanced experimental and analytical techniques. For example, they implanted intra-abdominal, long-term temperature recorders, which recorded data every 6 to 120 minutes for up to several months. They analysed body temperature periodicity by approximation of the recordings with Fourier series, and they CT-scanned fetuses.
All 19 individuals (from which data could be gathered) exhibited substantial daily variation in body temperature. Several intriguing results emerged such as the counter-intuitive finding that the mammals’ body temperature fluctuates more indoors than outdoors. Furthermore, three females (out of 12) were found to have offspring with atypical skeletons, and two of these mothers presented an extremely low internal temperature early in pregnancy. Additionally, genetically identical quadruplets differed skeletally among themselves within two litters.
Results are not yet definitive about the relationship of temperature during development and vertebral count in Dasypus novemcinctus. However, Knight et al. [8] demonstrated that nine-banded armadillos survive with high daily internal temperature fluctuations and successfully bring to term offspring which vary in skeletal morphology among and within genetically identical litters despite major temperature extremes.
References
[1] Hautier L, Weisbecker V, Sánchez-Villagra MR, Goswami A, Asher RJ (2010) Skeletal development in sloths and the evolution of mammalian vertebral patterning. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 107, 18903–18908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010335107
[2] Jordan, D.S. (1892) Relations of temperature to vertebrae among fishes. Proceedings of the United States National Museum, 1891, 107-120. doi: 10.5479/si.00963801.14-845.107
[3] Tibblin P, Berggren H, Nordahl O, Larsson P, Forsman A (2016) Causes and consequences of intra-specific variation in vertebral number. Scientific Reports, 6, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/srep26372
[4] Peabody RB, Brodie ED (1975) Effect of temperature, salinity and photoperiod on the number of trunk vertebrae in Ambystoma maculatum. Copeia, 1975, 741–746. doi: 10.2307/1443326
[5] Lindsey CC, Moodie GEE (1967) The effect of incubation temperature on vertebral count in the chicken. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 45, 891–892. doi: 10.1139/z67-099
[6] Galis F, Dooren TJMV, Feuth JD, Metz JAJ, Witkam A, Ruinard S, Steigenga MJ, Wunaendts LCD (2006) Extreme selection in humans against homeotic transformations of cervical vertebrae. Evolution, 60, 2643–2654. doi: 10.1111/j.0014-3820.2006.tb01896.x
[7] Buchholtz EA, Stepien CC (2009) Anatomical transformation in mammals: developmental origin of aberrant cervical anatomy in tree sloths. Evolution and Development, 11, 69–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00303.x
[8] Knight F, Connor C, Venkataramanan R, Asher RJ. (2020). Body temperatures, life history, and skeletal morphology in the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus). PCI-Ecology. doi: 10.17863/CAM.50971
[9] McNab BK (1980) Energetics and the limits to a temperate distribution in armadillos. Journal of Mammalogy, 61, 606–627. doi: 10.2307/1380307
[10] Asher RJ, Lin KH, Kardjilov N, Hautier L (2011) Variability and constraint in the mammalian vertebral column. Journal of Evolutionary Biology, 24, 1080–1090. doi: 10.1111/j.1420-9101.2011.02240.x
| Body temperatures, life history, and skeletal morphology in the nine-banded armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus) | Frank Knight, Cristin Connor, Ramji Venkataramanan, Robert J. Asher | <p>The nine banded armadillo (*Dasypus novemcinctus*) is the only xenarthran mammal to have naturally expanded its range into the middle latitudes of the USA. It is not known to hibernate, but has been associated with unusually labile core body te... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Evolutionary ecology, Life history, Physiology, Zoology | Mar Sobral | | 2019-11-22 22:57:31 | View |
Environmental variables determining the distribution of an avian parasite: the case of the Philornis torquans complex (Diptera: Muscidae) in South America
Pablo F. Cuervo, Alejandro Percara, Lucas Monje, Pablo M. Beldomenico, Martín A. Quiroga
https://doi.org/10.1101/839589
Catching the fly in dystopian times
Recommended by Rodrigo Medel based on reviews by 4 anonymous reviewers
Host-parasite interactions are ubiquitous on Earth. They are present in almost every conceivable ecosystem and often result from a long history of antagonist coevolution [1,2]. Recent studies on climate change have revealed, however, that modification of abiotic variables are often accompanied by shifts in the distributional range of parasites to habitats far beyond their original geographical distribution, creating new interactions in novel habitats with unpredictable consequences for host community structure and organization [3,4]. This situation may be especially critical for endangered host species having small population abundance and restricted distribution range. The infestation of bird species with larvae of the muscid fly genus Philornis is a case in point. At least 250 bird species inhabiting mostly Central and South America are infected by Philornis flies [5,6]. Fly larval development occurs in bird faeces, nesting material, or inside nestlings, affecting the development and nestling survival.
Recent reports indicate significant reduction of bird numbers associated with recent Philornis infection, the most conspicuous being Galapagos finches [7,8]. One way to prevent this potential effect consists in to examine the expected geographical shift of Philornis fly species under future climate change scenarios so that anticipatory conservation practices become implemented for endangered bird species. In this regard, Ecological Niche Modeling (ENM) techniques have been increasingly used as a useful tool to predict disease transmission as well as the species becoming infected under different climate change scenarios [9-11]. The paper of Cuervo et al. [12] is an important advance in this regard. By identifying for the first time the macro-environmental variables influencing the abiotic niche of species of the Philornis torquans complex in southern South America, the authors perform a geographical projection model that permits identification of the areas susceptible to be colonized by Philornis species in Argentina, Brazil, and Chile, including habitats where the parasitic fly is still largely absent at present. Their results are promissory for conservation studies and contribute to the still underdeveloped issue of the way climate change impacts on antagonistic ecological relationships.
References
[1] Thompson JN (1994) The Coevolutionary Process. University of Chicago Press.
[2] Poulin R (2007) Evolutionary Ecology of Parasites: (Second Edition). Princeton University Press. doi: 10.2307/j.ctt7sn0x
[3] Pickles RSA, Thornton D, Feldman R, Marques A, Murray DL (2013) Predicting shifts in parasite distribution with climate change: a multitrophic level approach. Global Change Biology, 19, 2645–2654. doi: 10.1111/gcb.12255
[4] Marcogliese DJ (2016) The distribution and abundance of parasites in aquatic ecosystems in a changing climate: More than just temperature. Integrative and Comparative Biology, 56, 611–619. doi: 10.1093/icb/icw036
[5] Dudaniec RY, Kleindorfer S (2006) Effects of the parasitic flies of the genus Philornis (Diptera: Muscidae) on birds. Emu - Austral Ornithology, 106, 13–20. doi: 10.1071/MU04040
[6] Antoniazzi LR, Manzoli DE, Rohrmann D, Saravia MJ, Silvestri L, Beldomenico PM (2011) Climate variability affects the impact of parasitic flies on Argentinean forest birds. Journal of Zoology, 283, 126–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7998.2010.00753.x
[7] Fessl B, Sinclair BJ, Kleindorfer S (2006) The life-cycle of Philornis downsi (Diptera: Muscidae) parasitizing Darwin’s finches and its impacts on nestling survival. Parasitology, 133, 739–747. doi: 10.1017/S0031182006001089
[8] Kleindorfer S, Peters KJ, Custance G, Dudaniec RY, O’Connor JA (2014) Changes in Philornis infestation behavior threaten Darwin’s finch survival. Current Zoology, 60, 542–550. doi: 10.1093/czoolo/60.4.542
[9] Johnson EE, Escobar LE, Zambrana-Torrelio C (2019) An ecological framework for modeling the geography of disease transmission. Trends in Ecology and Evolution, 34, 655–668. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2019.03.004
[10] Carvalho BM, Rangel EF, Ready PD, Vale MM (2015) Ecological niche modelling predicts southward expansion of Lutzomyia (Nyssomyia) flaviscutellata (Diptera: Psychodidae: Phlebotominae), vector of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis in South America, under climate change. PLOS ONE, 10, e0143282. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143282
[11] Garrido R, Bacigalupo A, Peña-Gómez F, Bustamante RO, Cattan PE, Gorla DE, Botto-Mahan C (2019) Potential impact of climate change on the geographical distribution of two wild vectors of Chagas disease in Chile: Mepraia spinolai and Mepraia gajardoi. Parasites and Vectors, 12, 478. doi: 10.1186/s13071-019-3744-9
[12] Cuervo PF, Percara A, Monje L, Beldomenico PM, Quiroga MA (2020) Environmental variables determining the distribution of an avian parasite: the case of the Philornis torquans complex (Diptera: Muscidae) in South America. bioRxiv, 839589, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/839589
| Environmental variables determining the distribution of an avian parasite: the case of the Philornis torquans complex (Diptera: Muscidae) in South America | Pablo F. Cuervo, Alejandro Percara, Lucas Monje, Pablo M. Beldomenico, Martín A. Quiroga | <p>*Philornis* flies are the major cause of myasis in altricial nestlings of neotropical birds. Its impact ranges from subtle to lethal, being of major concern in endangered bird species with geographically-restricted, fragmented and small-sized p... | 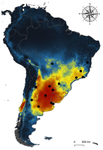 | Biogeography, Macroecology, Parasitology, Species distributions | Rodrigo Medel | | 2019-11-26 21:31:33 | View |





 based on reviews by Bonaventura Majolo and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Bonaventura Majolo and 1 anonymous reviewer

























