
SUWEIS Samir Simon
- Laboratory of Interdisciplinary Physics (LIPh), Physics and Astronomy Department, University of Padova, Padova, Italy
- Biodiversity, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Interaction networks, Macroecology, Theoretical ecology
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
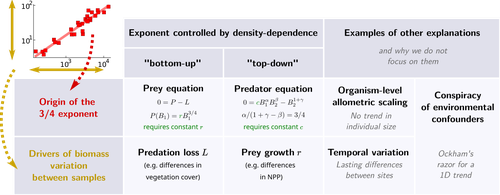
General mechanisms for a top-down origin of the predator-prey power law
Rethinking Biomass Scaling in Predators-Preys ecosystems
Recommended by Samir Simon Suweis based on reviews by Samraat Pawar and 1 anonymous reviewerThe study titled “General mechanisms for a top-down origin of the predator-prey power law” provides a fresh perspective on the classic predator-prey biomass relationship often observed in ecological communities. Traditionally, predator-prey dynamics have been examined through a bottom-up lens, where prey biomass and energy availability dictate predator populations. However, this study, which instead explores the possibility of a top-down origin for predator-prey power laws, offers a new dimension to our understanding of ecosystem regulation and raises questions about how predator-driven interactions might influence biomass scaling laws independently of prey abundance.
Ecologists have long noted that ecosystems often exhibit sublinear scaling between predator and prey biomasses. This pattern implies that predator biomass does not increase proportionally with prey biomass but at a slower rate, leading to a power-law relationship. Traditional explanations, such as those discussed by Peters (1983) and McGill (2006), have linked this to bottom-up processes, suggesting that increases in prey availability support, but do not fully translate to, larger predator populations due to energy losses in the trophic cascade. However, these explanations assume prey abundance as the principal driver. This new work raises an intriguing question: could density-dependent predator interactions, such as competition and interference, be equally or more important in creating this observed power law?
The authors hypothesized that density-dependent predator interactions might independently control predator biomass, even when prey is abundant. To test this, they combined predator and prey biomass dynamics equation based on a modified Lotka-Volterra model with agent-based models (ABMs) on a spatial grid, simulating predator-prey populations under varying environmental gradients and density-dependent conditions. These models allowed them to incorporate predator-specific factors, such as intraspecific competition (predator self-regulation) and predation interference, offering a quantitative framework to observe whether these top-down dynamics could indeed explain the observed biomass scaling independently of prey population changes.
Their results show that density-dependent predator dynamics, particularly at high predator densities, can yield sublinear scaling in predator-prey biomass relationships. This aligns well with empirical data, such as African mammalian ecosystems where predators seem to self-regulate under high prey availability by competing amongst themselves rather than expanding in direct proportion to prey biomass. Such findings support a shift from bottom-up perspectives to a model where top-down processes drive population regulation and biomass scaling.
I think that the work by Mazzarisi and collaborators (2024) offers a thought-provoking twist on predator-prey dynamics and suggests that our traditional frameworks may benefit from a broader, more predator-centered focus.
References
1. Onofrio Mazzarisi, Matthieu Barbier, Matteo Smerlak (2024) General mechanisms for a top-down origin of the predator-prey power law. bioRxiv, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.04.04.588057
2. Peters, R. H. (1986). The ecological implications of body size (Vol. 2). Cambridge university press.
3. McGill, B. J. (2006). “A renaissance in the study of abundance.” Science, 314(5801), 770-772. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1134920
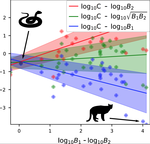
A macro-ecological approach to predators' functional response
A meta-analysis to infer generic predator functional response
Recommended by Samir Simon Suweis based on reviews by Ludek Berec and gyorgy barabasSpecies interactions are classically derived from the law of mass action: the probability that, for example, a predation event occurs is proportional to the product of the density of the prey and predator species. In order to describe how predator and prey species populations grow, is then necessary to introduce functional response, describing the intake rate of a consumer as a function of food (e.g. prey) density.
Linear functional responses shapes are typically introduced in the ecological modeling of population dynamics for both predator-prey and mutualistic systems [1,2]. Recently some works have proposed alternatives to the classic approach for mutualistic systems [3,4], both because cooperative interactions also model effect not directly related to mass action [3] and for analytical tractability [4,5].
In this work [6] the authors challenge the classic modeling of functional response also for predator-prey systems. In particular, they use a meta-analysis of several observational studies of predator-prey ecosystems to infer a generic predator functional response, fitting a phenomenological generalization of the mass-action law. Using advanced statistical analysis, they show that the functional response obtained from data is clearly different from the mass-action assumption. In fact, they found that it scales sub-linearly as the square root of the ratio between predator and prey biomass. They further argue that, from a macro-ecological point of view, using such a phenomenological relationship might be more valuable than relying on various mechanistic functional response formulations.
The manuscript thus provides an interesting different perspective on how to approach predator-prey modelling and for this reason, I have recommended the work for PCI Ecology.
References
[1] Volterra, V. (1928). Variations and Fluctuations of the Number of Individuals in Animal Species living together. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 3(1), 3–51. doi: 10.1093/icesjms/3.1.3
[2] Bastolla, U., Fortuna, M. A., Pascual-García, A., Ferrera, A., Luque, B., and Bascompte, J. (2009). The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature, 458(7241), 1018–1020. doi: 10.1038/nature07950
[3] Tu, C., Suweis, S., Grilli, J., Formentin, M., and Maritan, A. (2019). Reconciling cooperation, biodiversity and stability in complex ecological communities. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41614-2
[4] García-Algarra, J., Galeano, J., Pastor, J. M., Iriondo, J. M., and Ramasco, J. J. (2014). Rethinking the logistic approach for population dynamics of mutualistic interactions. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 363, 332–343. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.08.039
[5] Suweis, S., Simini, F., Banavar, J. R., and Maritan, A. (2013). Emergence of structural and dynamical properties of ecological mutualistic networks. Nature, 500(7463), 449–452. doi: 10.1038/nature12438
[6] Barbier, M., Wojcik, L., and Loreau, M. (2020). A macro-ecological approach to predators’ functional response. BioRxiv, 832220, ver. 4 recommended and peer-reviewed by Peer Community in Ecology. doi: 10.1101/832220