Direct submissions to PCI Ecology from bioRxiv.org are possible using the B2J service
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
26 May 2025
Behavioral flexibility is related to foraging, but not social or habitat use behaviors, in a species that is rapidly expanding its rangeLogan CJ, Lukas D, Geng X, Hardy K, LeGrande C, Marfori Z, MacPherson M, Rowney C, Smith C, McCune KB https://doi.org/10.32942/X2T036The role of behavioral flexibility in a rapid expanding birdRecommended by Esther Sebastián González and Julia Astegiano and Julia Astegiano based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
Behavioral flexibility (i.e., the ability of some animal species to adapt their actions to new conditions) is a feature that may be critical for the local persistence and, therefore, the geographic distribution of many animal species in our fast-changing world. However, most studies have measured it using different aspects of foraging, social or habitat use behavior as proxies, lacking an empirical demonstration of the relationship between behavioral flexibility and these variables (e.g., Sol et al. 2002). In this study, Corina Logan and co-authors (Logan et al. 2025) undertake a set of well-described experiments that start using two methods (i.e., reversal learning of a color preference and a multiaccess box study weather behavioral flexibility) to measure the behavioral flexibility of great-tailed grackles, a species that is rapidly expanding its geographic range. The grackles are then released to the wild and their foraging, social or habitat use behaviors are measured and compared to those of wild unmanipulated individuals.
| Behavioral flexibility is related to foraging, but not social or habitat use behaviors, in a species that is rapidly expanding its range | Logan CJ, Lukas D, Geng X, Hardy K, LeGrande C, Marfori Z, MacPherson M, Rowney C, Smith C, McCune KB | <p>The ability of other species to adapt to human modified environments is increasingly crucial because of the rapid expansion of this landscape type. Behavioral flexibility, the ability to change behavior in the face of a changing environment by ... | Behaviour & Ethology, Preregistrations, Zoology | Esther Sebastián González | 2024-05-27 10:12:15 | View | ||
20 May 2025
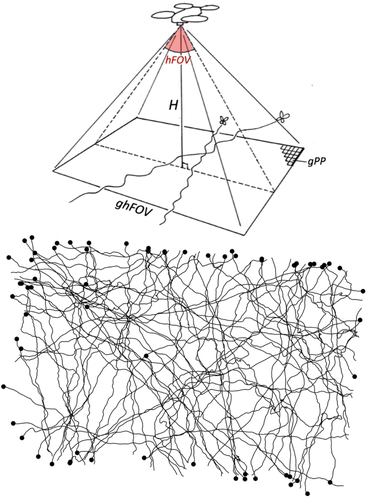
Tracking butterfly flight in the field from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV): a methodological proof of principle.Emmanuel de Margerie, Kyra Monmasson https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.17.603869Breaking barriers in butterfly tracking: how drone technology and image analysis could boost movement ecology of butterfliesRecommended by Nicolas Schtickzelle based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewers
Understanding how animals move within and across landscapes is fundamental to behavioural ecology, conservation biology, and movement ecology. Tracking movement provides insights into migration and dispersal patterns, habitat preferences, intra- and interspecific interactions, etc. For long, movement recording was limited to indirect methods, such as Capture-Mark-Recapture. Despite being at the basis of an incredible amount of knowledge and developments in ecology, these methods do not inform on the movement path itself, just its beginning and end. Tracking individuals during their movement was really needed. Over the years, researchers have developed a range of tracking methodologies, with technological innovations continually improving precision and efficiency (Trappes, 2023). While tracking large terrestrial and marine animals and birds is now well-established using GPS telemetry and biologging, monitoring small flying insects remains a significant challenge due to their size, erratic flight patterns, and sensitivity to environmental disturbances. It is especially the case for butterflies due to their lightweight bodies and relative low flight power. Given the role butterflies play as model organisms in diverse areas of ecology, research to allow tracking their movement path is of prime interest. I remember the many hours I spent, in a time (early 2000s) GPS technology was still quite imprecise, following butterflies for a distance, placing sticks at turning points and reconstructing afterwards the movement path by triangulating the distances of sticks to know location marks (Schtickzelle et al., 2007). It was quite effective but prohibitive in terms of resources. Later came GPS devices precise enough for an individual to run in the footsteps of a butterfly to record its path. Still, methods have been highly desirable that could track butterflies with some level of automation and from a distance. Experiments were performed with harmonic radar (attaching a passive transponder that reflects radar signals; Cant et al., 2005) but were never largely adopted given they required acquiring and positioning costly and heavy equipment and maintaining at all time a direct line of sight with the tracked butterfly. Here comes this pioneering study by de Margerie and Monmasson (Margerie & Monmasson, 2025) who introduce an innovative approach using a consumer-level commercial drone to track butterfly flight, offering a promising solution for long-duration, high-resolution flight trajectory analysis in natural habitats. Their study is a proof of principle that a drone, hovering in a fixed position, can be used as a flying platform to capture high-resolution vertical imagery to precisely record butterfly flight movements. Images are then analysed to reconstruct the flight path, a point on which they developed innovative approaches in the study. The study therefore represents a significant leap forward in butterfly flight tracking methodology, with technology that many labs could acquire and operate. Further research is needed to alleviate some of the current limitations before large-scale adoption to track butterfly movements in the field is within reach: e.g. the need for a very high contrast between the butterfly and the vegetation above which it flies (here white Pieris butterflies over a relatively homogeneous green crop field were filmed), the limits in spatiotemporal scale due to the fixed drone position and its short battery life, and some difficulties in image processing to reconstruct movement paths, in particular when several individuals would cross paths. Considering the fast progress in both the drone technology and image analysis techniques, such progress could however come faster than we might anticipate. References Cant E. T., Smith A. D., Reynolds D. R. & Osborne J. L. (2005). Tracking butterfly flight paths across the landscape with harmonic radar. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B 272, 785–790. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2004.3002 de Margerie E. & Monmasson K. (2025) Tracking butterfly flight in the field from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV): a methodological proof of principle. bioRxiv, ver.5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.17.603869 Schtickzelle N., Joiris A., Van Dyck H., & Baguette M. (2007). Quantitative analysis of changes in movement behaviour within and outside habitat in a specialist butterfly. BMC Evolutionary Biology 7, 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-7-4 Trappes R. (2023). How tracking technology is transforming animal ecology: Epistemic values, interdisciplinarity, and technology-driven scientific change. Synthese 201, 128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11229-023-04122-5
| Tracking butterfly flight in the field from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV): a methodological proof of principle. | Emmanuel de Margerie, Kyra Monmasson | <p>Tracking and understanding the movements of animals in the wild is a fast-growing area of research, known as movement ecology. However, tracking small animals such as flying insects, which cannot easily carry an electronic tag, remains challeng... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Dispersal & Migration | Nicolas Schtickzelle | 2025-01-06 10:29:10 | View | |
16 May 2025
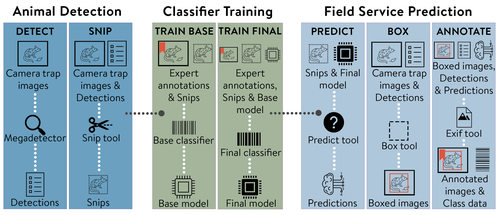
MEWC: A user-friendly AI workflow for customised wildlife-image classificationBarry W. Brook, Jessie C. Buettel, Peter van Lunteren, Prakash P. Rajmohan, R. Zach Aandahl https://doi.org/10.32942/X2ZW3DDemocratising AI for Ecology: MEWC Delivers Custom Wildlife Classification to AllRecommended by Cédric Sueur based on reviews by Timm Haucke and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Timm Haucke and 1 anonymous reviewer
Although artificial intelligence (AI) offers a powerful solution to the bottleneck in processing camera-trap imagery, ecological researchers have long struggled with the practical application of such tools. The complexity of development, training, and deploying deep learning models remains a significant barrier for many conservationists, ecologists, and citizen scientists who lack formal training in computer science. While platforms like Wildlife Insights (Ahumada et al. 2020), MegaDetector (Beery et al. 2019), and tools such as ClassifyMe (Falzon et al. 2020) have laid critical groundwork in AI-assisted wildlife monitoring, these solutions either remain opaque, lack customisability, or are often locked behind commercial or infrastructural limitations. Others, like Sherlock (Penn et al., 2024), while powerful, are not always deployable without significant local expertise. A notable example of a more open and collaborative approach is the DeepFaune initiative, which provides a free, high-performance tool for the automatic classification of European wildlife in camera-trap images, highlighting the growing importance of locally relevant, user-friendly AI solutions developed through broad partnerships (Rigoudy et al. 2022). It is in this context that Brook et al. (2025) makes a compelling and timely contribution. The authors present an elegant, open-source AI pipeline—MEWC (Mega-Efficient Wildlife Classifier)—that bridges the gap between high-performance image classification and usability by non-specialists. Combining deep learning advances with user-friendly software engineering, MEWC enables users to detect, classify, and manage wildlife imagery without advanced coding skills or reliance on high-cost third-party infrastructures. What makes MEWC particularly impactful is its modular and accessible architecture. Built on Docker containers, the system can run seamlessly across different operating systems, cloud services, and local machines. From image detection using MegaDetector to classifier training via EfficientNet or Vision Transformers, the pipeline maintains a careful balance between technical flexibility and operational simplicity. This design empowers ecologists to train their own species-specific classifiers and maintain full control over their data—an essential feature given the increasing scrutiny around data sovereignty and privacy. The practical implications are impressive. The case study provided—focused on Tasmanian wildlife—demonstrates not only high accuracy (up to 99.6%) but also remarkable scalability, with models trainable even on mid-range desktops. Integration with community tools like Camelot (Hendry and Mann 2018)and AddaxAI (Lunteren 2023) further enhances its utility, allowing rapid expert validation and facilitating downstream analyses. Yet the article does not shy away from discussing the limitations. As with any supervised system, MEWC’s performance is only as good as the training data provided. Class imbalances, rare species, or subtle morphological traits can challenge even the best classifiers. Moreover, the authors caution that pre-trained models may not generalise well across regions with different fauna, requiring careful curation and expert tagging for local deployments. One particularly exciting future direction briefly mentioned—and worth highlighting—is MEWC’s potential application to behavioural and cognitive ecology (Sueur et al. 2013; Battesti et al. 2015; Grampp et al. 2019). Studies in these domains underscore the need for scalable tools to quantify social dynamics in real time. By assisting with individual identification and the detection of postures or spatial configurations, MEWC could significantly enhance the throughput, reproducibility, and objectivity of such research. This opens the door to even richer applications. Behavioural ecologists might use MEWC for fine-grained detection tasks such as individual grooming interactions, kin proximity analysis, or identification of tool-use sequences in wild primates. Similarly, for within-species classification (e.g. sex, reproductive state, or disease symptoms), MEWC's modular backbone and compatibility with transfer learning architectures like EfficientNet or ViT make it a suitable candidate for expansion (Ferreira et al. 2020; Clapham et al. 2022). In conclusion (Brook et al. 2025) have delivered more than a tool—they've designed an ecosystem. MEWC lowers the technical barrier to AI in ecology, promotes open science, and enables tailored workflows for a wide variety of conservation, research, and educational contexts. For anyone interested in democratising ecological AI and reclaiming control over wildlife-monitoring data, this article and its associated software are essential resources. References Ahumada JA, Fegraus E, Birch T, et al (2020) Wildlife Insights: A Platform to Maximize the Potential of Camera Trap and Other Passive Sensor Wildlife Data for the Planet. Environmental Conservation 47:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0376892919000298 Battesti M, Pasquaretta C, Moreno C, et al (2015) Ecology of information: social transmission dynamics within groups of non-social insects. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences 282:20142480. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.2480 Beery S, Morris D, Yang S, et al (2019) Efficient pipeline for automating species ID in new camera trap projects. Biodiversity Information Science and Standards 3:e37222. https://doi.org/10.3897/biss.3.37222 Barry W. Brook, Jessie C. Buettel, Peter van Lunteren, Prakash P. Rajmohan, R. Zach Aandahl (2025) MEWC: A user-friendly AI workflow for customised wildlife-image classification. EcoEvoRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2ZW3D Clapham M, Miller E, Nguyen M, Van Horn RC (2022) Multispecies facial detection for individual identification of wildlife: a case study across ursids. Mamm Biol 102:921–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42991-021-00168-5 Falzon G, Lawson C, Cheung K-W, et al (2020) ClassifyMe: A Field-Scouting Software for the Identification of Wildlife in Camera Trap Images. Animals 10:58. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10010058 Ferreira AC, Silva LR, Renna F, et al (2020) Deep learning-based methods for individual recognition in small birds. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 11:1072–1085. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13436 Grampp M, Sueur C, van de Waal E, Botting J (2019) Social attention biases in juvenile wild vervet monkeys: implications for socialisation and social learning processes. Primates 60:261–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10329-019-00721-4 Hendry H, Mann C (2018) Camelot—intuitive software for camera-trap data management. Oryx 52:15–15. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0030605317001818 Lunteren P van (2023) AddaxAI: A no-code platform to train and deploy custom YOLOv5 object detection models. Journal of Open Source Software 8:5581. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05581 Rigoudy, N, Dussert, G, Benyoub, A et al (2023) The DeepFaune initiative: a collaborative effort towards the automatic identification of European fauna in camera trap images. Eur J Wildl Res 69, 113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-023-01742-7 Sueur C, MacIntosh AJJ, Jacobs AT, et al (2013) Predicting leadership using nutrient requirements and dominance rank of group members. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 67:457–470. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-012-1466-5 | MEWC: A user-friendly AI workflow for customised wildlife-image classification | Barry W. Brook, Jessie C. Buettel, Peter van Lunteren, Prakash P. Rajmohan, R. Zach Aandahl | <p>Monitoring wildlife is crucial for making informed conservation and land-management decisions. Remotely triggered cameras are widely used for this purpose, but the resulting 'big data' are laborious to process. Although artificial intelligence ... |  | Biodiversity, Community ecology, Conservation biology, Statistical ecology, Zoology | Cédric Sueur | 2025-02-21 02:16:08 | View | |
16 May 2025
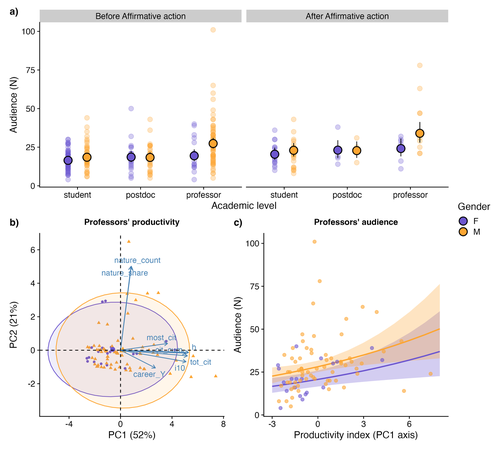
Is the audience gender-blind? Smaller attendance in female talks highlights imbalanced visibility in academiaJúlia Rodrigues Barreto, Isabella Romitelli, Pamela Cristina Santana, Ana Paula Aprígio Assis, Renata Pardini, Melina de Souza Leite https://doi.org/10.32942/X25607Gender matters: smaller audiences for women in academiaRecommended by Natalia Mariel Schroeder based on reviews by Silvia Beatriz Lomascolo and Letícia dos Anjos based on reviews by Silvia Beatriz Lomascolo and Letícia dos Anjos
The current lack of social diversity - that is, gender, race and ethnicity - in academia reinforces a historical pattern of exclusion, wherein the knowledge, perspectives and advances of certain groups dominate the narrative, set rhythms and agenda, while the contributions of others are minimised or overlooked. The underrepresentation of and discrimination against women in academia is a well-documented and persistent issue. Despite policies designed to increase female representation and mitigate the structural processes that lead women to abandon their academic careers (Shaw & Stanton, 2012), women scientists continue to face inequalities in authorship, publications, funding, salaries, recognition and decision-making spaces (Astegiano et al., 2019, Woolston, 2019; Fox et a. 2023; Fontanarrosa et al. 2024; Zandonà, 2022; among others). Making these inequalities visible and fostering open discussion is a critical first step toward dismantling them. In this sense, the study by Rodrigues Barreto et al. (2025) makes an important contribution. The authors examine gender bias in seminar series within the field of Ecology, Evolution and Conservation Biology at the University of São Paulo (Brazil), using audience size as an indirect measure of speaker recognition. The most interesting and novel finding of this work is that talks given by women -especially by female professors- attract smaller audiences than those given by men counterparts, despite the women having comparable levels of academic productivity, similar career trajectories, and presenting on equivalent topics to those of their male colleagues. These results suggest that seminar culture is not gender-blind (Dupas et al., 2021) and provide a new layer of evidence on how gender-based stereotypes continue to influence the visibility and recognition of women in science. The authors also investigated whether the implementation of affirmative actions (i.e., open calls for volunteer speakers that prioritised women) improved both the representation of female speakers and the size of their audiences. As expected, these actions did succeed in increasing the representation of women among presenters, especially at senior academic levels; however, they did not lead to a proportional rise in audience size. While the time series and number of talks considered before the implementation of affirmative actions were considerably higher than those after this policy, the comparison remains relevant given the importance and timeliness of the topic. The authors found that women give fewer talks than men. However, as they discuss, their results do not allow them to distinguish whether this inequality is due to gender bias or to a structural gender imbalance. Through a supplementary analysis of a subset of data from the University of São Paulo community, they find some evidence that the underrepresentation of women in the academic population itself may partly explain the gender gap in the seminar series. In any case, these findings, along with similar results from other studies (e.g. Greska, 2023) raise valuable questions: Will simply increasing the number of women in academia be enough to close the recognition gap between men and women scholars? What role might affirmative actions play in attracting a wider audience or enhancing the visibility and recognition of women's work? What kinds of initiatives could change the way we acknowledge women researchers’ contributions? What could reconfigure that “recognition landscape” from a feminist perspective, i.e., one less competitive, less hierarchical, more communitarian and less individual-centered? As the authors acknowledge, the study has limitations (e.g., its focus on a single institution, a short timeframe to assess the impact of affirmative actions), but it provides valuable evidence to initiate broader approaches that include other disciplines, institutions, experimental approaches, and intersectional perspectives. References Astegiano J, Sebastián-González E, Castanho C de T (2019) Unravelling the gender 465 productivity gap in science: a meta-analytical review. Royal Society Open Science 6: 466 181566. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.181566 Dupas P, Modestino AS, Niederle M, Wolfers J, Collective TSD (2021) Gender and the Dynamics of Economics Seminars. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research. http://www.nber.org/papers/w28494.pdf Fontanarrosa, G., Zarbá, L., Aschero, V., Dos Santos, D. A., Montellano, M. G. N. et al. (2024). Over twenty years of publications in Ecology: Over-contribution of women reveals a new dimension of gender bias. PLoS ONE 19(9): e0307813. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0307813 Fox CW, Meyer J, Aimé E (2023) Double-blind peer review affects reviewer ratings and 509 editor decisions at an ecology journal. Functional Ecology 37: 1144–1157. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.14259 Greska L (2023) Women in Academia: Why and where does the pipeline leak, and how can we fix it? MIT Science Policy Review 4: 102–109. https://doi.org/10.38105/spr.xmvdiojee1 Rodrigues Barreto J, Romitelli I, Santana PC, Aprígio Assis A.N., Pardini R, de Souza Leite M. (2025) Is the audience gender-blind? Smaller attendance in female talks highlights imbalanced visibility in academia. EcoEvoRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.32942/X25607 Shaw AK, Stanton DE (2012) Leaks in the pipeline: separating demographic inertia from ongoing gender differences in academia. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 279: 3736–3741. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2012.0822 Woolston C (2019) Scientists’ salary data highlight US$18,000 gender pay gap. Nature 565: 597 527–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-00220-y Zandonà E (2022) Female ecologists are falling from the academic ladder: A call for action. 602 Perspectives in Ecology and Conservation 20: 294–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pecon.2022.04.001 | Is the audience gender-blind? Smaller attendance in female talks highlights imbalanced visibility in academia | Júlia Rodrigues Barreto, Isabella Romitelli, Pamela Cristina Santana, Ana Paula Aprígio Assis, Renata Pardini, Melina de Souza Leite | <p>Although diverse perspectives are fundamental for fostering and advancing science, power relations have limited the development, propagation of ideas, and recognition of political minority groups in academia. Gender bias is one of the most well... |  | Biodiversity, Conservation biology, Evolutionary ecology, Tropical ecology | Natalia Mariel Schroeder | 2024-05-30 23:00:46 | View | |
02 May 2025
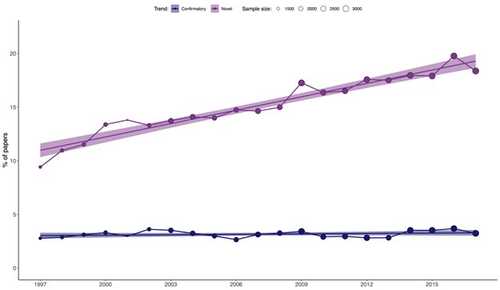
On the quest for novelty in ecologyGianluigi Ottaviani, Alejandro Martinez, Matteo Petit Bon, Stefano Mammola https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.27.530333From Paradigm to Publication: What Does the Pursuit of Novelty Reveal in Ecology?Recommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Francois Massol, Matthias Grenié and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Francois Massol, Matthias Grenié and 1 anonymous reviewer
In this study, Ottaviani et al. (2025) examined the variation in the use of terms related to "novelty" in 52,236 abstracts published between 1997 and 2017 across 17 ecological journals. They also analyzed the change in the frequency of terms related to "confirmatory" results. Their findings revealed a clear and consistent increase in the use of "novelty" terms, while the frequency of "confirmatory" terms remained relatively stable. This trend was observed across all the ecological journals, with the exception of Austral Ecology. Furthermore, the greater use of "novelty" terms was correlated with higher citation counts and publication in journals with higher impact factors. These findings should prompt further reflection on our research practices and may be connected to ongoing discussions in the philosophy of science. Thomas S. Kuhn's seminal work, The Structure of Scientific Revolutions (1962), challenged traditional views of scientific progress. Central to Kuhn's argument is the idea that science progresses through periods of adherence to a dominant "paradigm"—a framework that provides scientists with puzzles to solve and the tools to solve them. A scientific crisis arises when the paradigm fails to address emerging anomalies, leading to the replacement of the old paradigm with a new one, a process Kuhn calls a "scientific revolution." Kuhn's perspective stands in stark contrast to previous views, which held that science progresses through the steady accumulation of truths or the gradual refinement of theories, often guided by the scientific method. One might wonder if the growing emphasis on "novelty" in ecological research mirrors the idea that theories are gradually refined until an exceptional discovery sparks a paradigm shift. In ecology, such a shift could be seen in the transition from niche-based theories of biodiversity dynamics (1960s-2000) to the radical neutral theory (Hubbell, 2001), which posits that diverse ecosystems can exist without niche differences. This paradigm was initially met with fierce opposition but eventually led to more integrative theories, recognizing the combined influence of both niche-based and neutral processes (Gravel et al., 2006, among others). What, then, is the current paradigm in ecology? Kuhn's theory of scientific progress suggests alternating periods of "normal" and "revolutionary" science. Normal science is characterized by cumulative puzzle-solving within established frameworks, while revolutionary science involves major shifts that can invalidate previous knowledge, a phenomenon Kuhn terms "Kuhn-loss." Kuhn rejected both the traditional and Popperian views on scientific revolutions. He argued that normal science depends on a shared commitment to certain beliefs, values, methods, and even metaphysical assumptions, which he referred to as a "disciplinary matrix" or "paradigm." This collective commitment is essential for scientific progress and must be instilled during the training of scientists. Kuhn's emphasis on the conservative nature of normal science contrasts with the heroic idea of continuous innovation and Popper's view of scientists constantly seeking to falsify theories. However, contemporary ecological research often follows the hypothetico-deductive approach championed by Popper. In light of these contrasting views, one might ask: What is the status of "novelty" in modern ecology? Is it contributing to the gradual solving of scientific puzzles, or is it focused on refuting hypotheses? Should "novelty" and "confirmatory" research be seen as opposites, or should both contribute to the advancement of science? Finally, is the increasing use of "novelty" terms a precursor to a scientific revolution, as Kuhn defined it, or merely a semantic trend driven by editorial policies aimed at attracting readers rather than contributing to real scientific progress? In conclusion, Ottaviani's study provides compelling evidence of the growing use of "novelty" terms in ecological journals, but it remains unclear whether this trend signals the onset of a Kuhnian "scientific revolution." This work should spark further discussion on the nature of current research practices, which may either facilitate or hinder the emergence of new paradigms. References Gravel, D., Canham, C. D., Beaudet, M., & Messier, C. (2006). Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecology letters, 9(4), 399-409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x Hubbell, S. P. (2001). The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography, vol.1, Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. Kuhn, T. S. (1962). The structure of scientific revolutions. International Encyclopedia of Unified Science, vol.2, 1962. Ottaviani, G., Martinez, A., Petit Bon, M., Mammola, S. (2025). On the quest for novelty in ecology. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.27.530333 | On the quest for novelty in ecology | Gianluigi Ottaviani, Alejandro Martinez, Matteo Petit Bon, Stefano Mammola | <p>The volume of scientific publications continues to grow, making it increasingly challenging for scholars to publish papers that capture readers' attention. While making a truly significant discovery is one way to attract readership, another app... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Human impact, Theoretical ecology | François Munoz | 2024-09-20 10:37:05 | View | |
24 Apr 2025
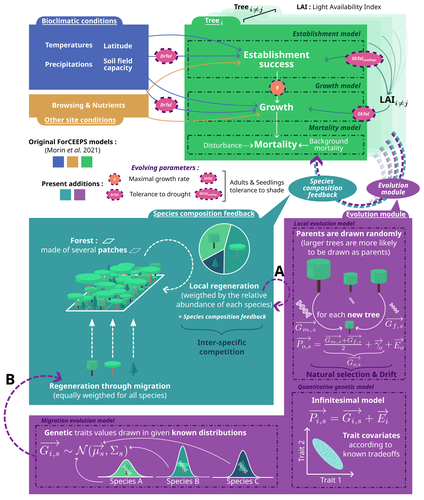
Evolutionary rescue in a mixed beech-fir forest: insights from a quantitative-genetics approach in a process-based modelLouis Devresse, Freya Way, Tanguy Postic, François de Coligny, Xavier Morin https://hal.science/hal-04575070Integrating evolution and ecology in forests: insights from a multi species demogenetic modelRecommended by Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio based on reviews by Silvio Shueler and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Silvio Shueler and 3 anonymous reviewers
The study of eco-evolutionary dynamics, i.e. of the inter-twinning between ecological and evolutionary processes when they occur at comparable time scales, is of growing interest in the current context of global change (Carroll, Hendry, Reznick, & Fox, 2007; Govaert et al., 2019). Demo-genetic agent-based models (DG-ABMs) have gained popularity to address this issue because of their abilities to consider feedback loops between ecological and evolutionary processes and to track populations of interacting individuals with adaptive traits variations (Berzaghi et al., 2019; Lamarins et al., 2022). This type of individual- and process-based simulation modelling where interindividual variation in fitness and hence opportunities for selection emerge from demography, which in turn affects the genetic composition of the population over successive generations (feedback loop), is only beginning to be applied to forest trees (Oddou-Muratorio, Hendrik, & Lefèvre, 2020). Examples include studies investigating the dispersal capacity of transgenes in forest landscapes using spatially explicit DG-ABMs with different demographic rates for transgenic and wild-type trees (DiFazio, Slavov, Burczyk, Leonardi, & Strauss, 2004; Kuparinen & Schurr, 2007), the effect of assortative mating and selection on genetic and plastic differentiation along environmental gradients (Soularue et al., 2023) or the interactions and feedback between tree thinning, genetic evolution, and forest stand dynamics, eventually in the context of drought-induced disturbances (Fririon, Davi, Oddou‐Muratorio, Ligot, & Lefèvre, 2024; Godineau et al., 2023). In this study, Devresse et al. (2025) extend the current DG-ABM framework for forest trees by incorporating interspecific interactions within diverse, uneven-aged forests. To this end, they adapted an existing multi-species, process-based forest dynamics model—ForCEEPS (Morin et al., 2021)—enabling the evolution of selected tree functional traits across generations. Their work focuses on three quantitative traits: drought tolerance, shade tolerance, and maximal growth rate. Using this enhanced DG-ABM, the authors investigate the conditions under which evolutionary rescue might occur in a mixed beech-fir forest facing climate change. Their results demonstrate that greater trait variability and higher heritability can mitigate short-term (century-scale) forest cover loss under climate warming. The study also shows that assisted gene flow facilitates species adaptation to climate change, while the introduction of pre-adapted species (assisted migration) may enhance post-disturbance recovery but simultaneously constrain the evolutionary rescue of local species. This work represents a major interdisciplinary advancement in forest ecology and nicely illustrates how integrating evolutionary processes into ecology-focused models can offer novel insights into forest dynamics. The implementation of genetic variability and inheritance via the infinitesimal model of quantitative genetics, along with its limitations, is described in detail, and the various research questions explored using the coupled DG‑ABM are presented as proof of concept for this successful integration. Beyond its methodological contribution, the study highlights the importance of more integrated approaches to understanding forest responses to climate change—approaches that account for both within- and between-species diversity and that promote nature-based solutions. It also underscores the urgent need for experimental studies exploring the genetic variation and architecture of adaptive traits in forest species to better anticipate and support their adaptive potential in a rapidly changing environment.
References Berzaghi, F., Wright, I. J., Kramer, K., Oddou-Muratorio, S., Bohn, F. J., Reyer, C. P. O., … Hartig, F. (2019). Towards a new generation of trait-flexible vegetation models. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 35(3), 191–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2019.11.006 Carroll, S. P., Hendry, A. P., Reznick, D. N., & Fox, C. W. (2007). Evolution on ecological time-scales. Functional Ecology, 21(3), 387–393. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2007.01289.x Devresse, L., Way, F., Postic, T., de Coligny, F. & Morin, X. (2025) Evolutionary rescue in a mixed beech-fir forest: insights from a quantitative-genetics approach in a process-based model. HAL, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://hal.science/hal-04575070 DiFazio, S. P., Slavov, G. T., Burczyk, J., Leonardi, S., & Strauss, S. H. (2004). Gene flow from tree plantations and implications for transgenic risk assessment. In Plantation Forest Biotechnology for the 21st Century (pp. 405–422). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2009.10.017 Fririon, V., Davi, H., Oddou‐Muratorio, S., Ligot, G., & Lefèvre, F. (2024). Can Thinning Foster Forest Genetic Adaptation to Drought? A Demo‐Genetic Modelling Approach With Disturbance Regimes. Evolutionary Applications, 17(12). https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.70051 Godineau, C., Fririon, V., Beudez, N., de Coligny, F., Courbet, F., Ligot, G., … Lefèvre, F. (2023). A demo-genetic model shows how silviculture reduces natural density-dependent selection in tree populations. Evolutionary Applications, (March), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.13606 Govaert, L., Fronhofer, E. A., Lion, S., Eizaguirre, C., Bonte, D., Egas, M., … Matthews, B. (2019). Eco-evolutionary feedbacks—Theoretical models and perspectives. Functional Ecology, 33(1), 13–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13241 Kuparinen, A., & Schurr, F. M. (2007). A flexible modelling framework linking the spatio-temporal dynamics of plant genotypes and populations: Application to gene flow from transgenic forests. Ecological Modelling, 202(3–4), 476–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.11.015 Lamarins, A., Fririon, V., Folio, D., Vernier, C., Daupagne, L., Labonne, J., … Oddou-Muratorio, S. (2022). Importance of interindividual interactions in eco-evolutionary population dynamics: The rise of demo-genetic agent-based models. Evolutionary Applications, 15(12), 1988–2001. https://doi.org/10.1111/eva.13508 Morin, X., Bugmann, H., de Coligny, F., Martin-StPaul, N., Cailleret, M., Limousin, J. M., … Guillemot, J. (2021). Beyond forest succession: A gap model to study ecosystem functioning and tree community composition under climate change. Functional Ecology, 35(4), 955–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13760 Oddou-Muratorio, S., Hendrik, D., & Lefèvre, F. (2020). Integrating evolutionary, demographic and ecophysiological processes to predict the adaptive dynamics of forest tree populations under global change. Tree Genetics & Genomes, 16(5), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-020-01451-1 Soularue, J. P., Firmat, C., Caignard, T., Thöni, A., Arnoux, L., Delzon, S., … Kremer, A. (2023). Antagonistic Effects of Assortative Mating on the Evolution of Phenotypic Plasticity along Environmental Gradients. American Naturalist, 202(1), 18–39. https://doi.org/10.1086/724579 | Evolutionary rescue in a mixed beech-fir forest: insights from a quantitative-genetics approach in a process-based model | Louis Devresse, Freya Way, Tanguy Postic, François de Coligny, Xavier Morin | <p>Questions have been raised about the ability of long-lived organisms, such as trees, to adapt to rapid climate change, and to what extent forest management actions influence the evolutionary responses of tree species. Given the life history of ... |  | Community ecology, Competition, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Ecosystem functioning, Evolutionary ecology, Theoretical ecology | Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio | 2024-05-17 19:33:41 | View | |
14 Apr 2025
Behavioral flexibility is related to exploration, but not boldness, persistence or motor diversityKelsey B. McCune, Dieter Lukas, Maggie MacPherson, Corina J. Logan https://doi.org/10.32942/X2H33FExploring exploration and behavioral flexibility in grackles: how to handle issues of "jingle-jangle" and repeatabilityRecommended by Jeremy Van Cleve based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Animal behavior, like other kinds of phenotypic plasticity, is crucial for survival and reproduction in environments that vary over space and time. Behaviors themselves may need to be flexible when the distributions of environmental conditions themselves change; for example, short-term weather patterns and long-term climate conditions are changing due to human activity, and behavioral flexibility will likely be key to some population persisting during these changes and others going extinct. Thus, measuring this flexibility is key to understanding which species may be resilient to climate change. Measuring behavioral flexibility is tricky as different studies may define and measure it differently and yet other studies may measure similar kinds of flexibility yet call them different things. This so-called "jingle-jangle" issue suggests that studies can more robustly measure a behavioral trait when they use multiple behavioral tests. An additional issue is that measuring behavioral traits that vary between individuals due to genetic or development effects, often referred to as "personality" traits, requires that those trait differences be repeatable across time and between individuals. With these issues in mind, McCune et al. (2019) presented a preregistration for experiments using a population of great-tailed grackles to investigate how behavioral flexibility relates to other important traits that are known to vary across individuals including exploratory behavior, boldness, and persistence and motor diversity in accessing a new food source. Behavioral flexibility is measured by the rate of learning a color associated with reward after first learning an association with a different color. That preregistration was recommended by PCI Ecology (Van Cleve, 2019). Now, McCune et al. (2025) present results from this study and find that only exploration of a novel environment and persistence were statistically repeatable behaviors. Both behaviors were not significantly correlated with behavioral flexibility. However, grackles that were trained to perform better in the color reversal learning task were more exploratory. This association between behavioral flexibility and exploratory tendencies may have evolved in grackles to help them survive in new environments, which they have proven very capable of doing as they have expanded their range in North American over the last 140 years (Wehtje, 2003). There are a few key features of McCune et al. (2025) to merit recommendation. First, the authors are intent on demonstrating careful behavioral research practices including, as evidenced above, preregistering their hypotheses and predictions and making available both the preregistered and final analysis code. Second, the study demonstrates a thorough attempt to address two aspects that bedevil behavioral research, namely the "jingle-jangle" issue and repeatability of traits across individuals. Even after measuring multiple features of boldness, exploratory, persistence, McCune et al. (2025) find that only a subset of the measured behaviors are repeatable and only a subset of those are associated with behavioral flexibility. This suggests that only thorough studies like McCune et al. (2025) can start to probe difficult to measure behavioral associations that may be key to understanding how species will respond to our changing world. References McCune K, Lukas D, MacPherson M, Logan CJ (2025) Behavioral flexibility is related to exploration, but not boldness, persistence or motor diversity. EcoEvoRxiv, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.32942/X2H33F Van Cleve, J. (2019) Probing behaviors correlated with behavioral flexibility. PCI Ecology, 100020. https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100020 McCune K, Rowney C, Bergeron L, Logan CJ. (2019) Is behavioral flexibility linked with exploration, but not boldness, persistence, or motor diversity? (http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_exploration.html) In principle acceptance by PCI Ecology of the version on 27 Mar 2019 Wehtje, W. (2003) The range expansion of the great-tailed grackle (Quiscalus mexicanus Gmelin) in North America since 1880. Journal of Biogeography 30:1593–1607 https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2003.00970.x. | Behavioral flexibility is related to exploration, but not boldness, persistence or motor diversity | Kelsey B. McCune, Dieter Lukas, Maggie MacPherson, Corina J. Logan | <p><strong><em>This is REVISION 1 for the post-study manuscript of the preregistration that was pre-study peer reviewed and received an In Principle Recommendation on 27 March 2019 by Jeremy Van Cleve.</em></strong><br>Behavioral flexibility, the ... | Behaviour & Ethology, Biological invasions | Jeremy Van Cleve | 2024-11-11 15:29:20 | View | ||
09 Apr 2025
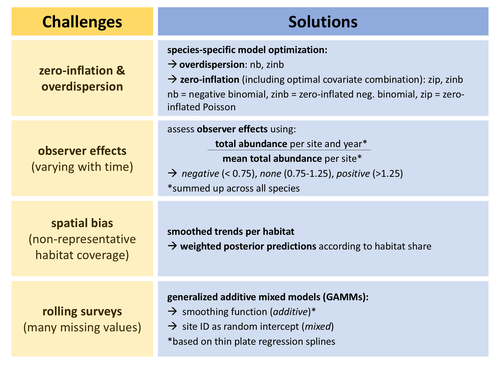
Bird population trend analyses for a monitoring scheme with a highly structured sampling designMirjam R. Rieger, Christoph Grueneberg, Michael Oberhaus, Sven Trautmann, Madalin Parepa, Nils Anthes https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.30.601382Discarding data or dealing with bias?Recommended by Matthieu Paquet based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Obtaining accurate estimates of population trends is crucial to assess populations’ status and make more informed decisions, notably for conservation measures. However, analyzing data we have at hand, including data from systematic monitoring programs, typically induces some bias one way or another (Buckland and Johnston 2017). For example, sampling can be biased towards some types of environments (sometimes historically, before being realized and corrected), and observer identity and experience can vary through time (e.g., an increase in observed experience, if ignored, would cause bias towards positive trends). One way to deal with such biases can be to discard some data, for example, from some overrepresented habitats or from first years surveys to minimize observer bias. However, this may lead to sample sizes becoming too small to detect any trends of interest, especially for surveys with already small temporal resolution (e.g., if time series are too short or with too many missing years). In this study, Rieger et al. (2025) analyzed data from bird surveys from the Ecological Area Sampling in the German federal state North Rhine-Westphalia in order to assess population trends. This survey uses a ‘rolling’ design, meaning that each site is only visited one year within a multi-year rotation (here six), but this allows to cover a high number of sites. To deal with spatial bias, they analyzed trends per natural region. To control for observer effects, they used a correction factor as an explanatory variable (based on the ratio between the total abundance of all species per site per survey year and the mean total abundance on the same site across all survey years). To deal with the fact that count data for some species but not others may be zero inflated and/or over dispersed, they performed species-specific optimization regarding data distribution (and also regarding inclusion of continuous and categorical covariates). Finally, they deal with the many missing values per year per site (due to the rolling design) by using generalized additive mixed models with site identity as a random intercept. Importantly, the authors assess how accounting for these biases affects estimates (quite strongly so for some species) and study the consistency of the results with trends estimated from the German Common Bird Monitoring scheme using the software TRIM (Pannekoek and van Strien 2001). I appreciated their cautious interpretation of their results and of the generalizability of their approach to other datasets. I also recommend that the readers read the review history of the preprint (and I take the opportunity to thank the reviewers and the authors again for the very constructive exchange). References Buckland, S., and A. Johnston. 2017. Monitoring the biodiversity of regions: Key principles and possible pitfalls. Biological Conservation 214: 23-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2017.07.034 Pannekoek, J., van Strienand, A. J. 2001. TRIM 3 manual (Trends & Indices for Monitoring Data). CBS Statistics Netherlands, Voorburg, The Netherlands. Rieger, M. R., Grüneberg, C., Oberhaus, M., Trautmann, S., Parepa, M., Anthes, N., 2025. Bird population trend analyses for a monitoring scheme with a highly structured sampling design. BioRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.30.601382 | Bird population trend analyses for a monitoring scheme with a highly structured sampling design | Mirjam R. Rieger, Christoph Grueneberg, Michael Oberhaus, Sven Trautmann, Madalin Parepa, Nils Anthes | <p>Population trends derived from systematic monitoring programmes are essential to identify species of conservation concern and to evaluate conservation measures. However, monitoring data pose several challenges for statistical analysis, includin... |  | Biodiversity, Statistical ecology | Matthieu Paquet | 2024-07-04 15:08:03 | View | |
09 Apr 2025
Habitat structural complexity increases age-class coexistence and population growth rate through relaxed cannibalism in a freshwater fishEric Edeline, Yoann Bennevault, David Rozen-Rechels https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.18.549540Habitat complexity reduces cannibalism, enhancing population-level diversity and productivity in a freshwater fishRecommended by Matthew Bracken based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Joacim Näslund and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Joacim Näslund and 2 anonymous reviewers
Habitat complexity is an important mediator of processes spanning levels of biological organization from organisms to ecosystems (Shumway et al. 2007, Soukup et al. 2022). This complexity, which can be biogenic (e.g., foundation species; Bracken et al. 2007, Ellison 2019) or abiotic (e.g., substrate rugosity; Kovalenko et al. 2012), shapes processes ranging from individual foraging behavior (Michel and Adams 2009) to species’ interactions to food-web structure and biogeochemical rates (Langellotto and Denno 2006, Larsen et al. 2021, Soukup et al. 2022). For example, in the presence of simulated aquatic vegetation, predatory diving beetle larvae shift from active foraging to sit-and-wait predation, reducing activity and prey encounter rates (Michel and Adams 2009).
In this contribution, Edeline et al. (2023) present a detailed perspective on the role of habitat complexity in shaping populations of a freshwater fish (medaka, Oryzias latipes, Adrianichthyidae), including survival, age-class diversity, population growth rate, and density-dependence in the stock-recruitment relationship associated with changes in carrying capacity. Importantly, changes in these population demographic attributes and rates were associated with the role of habitat complexity in mitigating cannibalism – consumption of juvenile O. latipes by conspecific adults. Whereas this is not unexpected – Langelotto and Denno (2006) showed that habitat complexity reduces cannibalism in wolf spiders – the careful work of Edeline et al. (2023) to link changes in habitat complexity to multiple population-level attributes provides a uniquely detailed description of the role of submerged aquatic vegetation in mediating population diversity (e.g., higher age-class diversity) and productivity (e.g., population growth rate).
In many ways, this work by Edeline et al. (2023) provides population-level parallels to perspectives on the role of habitat complexity in determining community-level diversity and productivity. Structurally complex habitats, such as those provided by foundation species (Bracken et al. 2007, Ellison 2019) and substrate heterogeneity (Fairchild et al. 2024), are associated with higher species diversity and abundance at the community level. Edeline et al. (2023) extend these perspectives to the population level, highlighting the importance of habitat complexity across levels of biological organization. Their work highlights within-population diversity and interactions, including cannibalism and competition, illustrating often-neglected aspects of food-web complexity (Polis and Strong 1996). References Matthew E. S. Bracken, Barry E. Bracken, Laura Rogers-Bennett (2007) Species diversity and foundation species: potential indicators of fisheries yields and marine ecosystem functioning. California Cooperative Oceanic Fisheries Investigations Reports 48: 82-91. https://calcofi.org/downloads/publications/calcofireports/v48/Vol_48_Bracken.pdf Eric Edeline, Yoann Bennevault, David Rozen-Rechels (2023) Habitat structural complexity increases age-class coexistence and population growth rate through relaxed cannibalism in a freshwater fish. bioRxiv, ver.4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.07.18.549540v4 Aaron M. Ellison (2019) Foundation species, non-trophic interactions, and the value of being common. iScience 13: 254-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.020 Tom P. Fairchild, Bettina Walter, Joshua J. Mutter, John N. Griffin. (2024) Topographic heterogeneity triggers complementary cascades that enhance ecosystem multifunctionality. Ecology 105: e4434. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.4434 Katya E. Kovalenko, Sidinei M. Thomaz, Danielle M. Warfe (2012) Habitat complexity: approaches and future directions. Hydrobiologia 685: 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-011-0974-z Gail A. Langellotto, Robert F. Denno. (2006) Refuge from cannibalism in complex-structured habitats: implications for the accumulation of invertebrate predators. Ecological Entomology 31: 575-81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2311.2006.00816.x Annegret Larsen, Joshua R. Larsen, Stuart N. Lane (2021) Dam builders and their works: beaver influences on the structure and Function of river corridor hydrology, geomorphology, biogeochemistry and ecosystems. Earth-Science Reviews 218: 103623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2021.103623 Matt J. Michel, Melinda M. Adams. (2009) Differential effects of structural complexity on predator foraging behavior. Behavioral Ecology: 313-17. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arp005 Gary A. Polis, Donald R. Strong (1996) Food web complexity and community dynamics. American Naturalist 147: 813-46. https://doi.org/10.1086/285880 Caroly A. Shumway, Hans A. Hofmann, Adam P. Dobberfuhl (2007) Quantifying habitat complexity in aquatic ecosystems. Freshwater Biology 52: 1065-76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01754.x. Pavel R. Soukup, Joacim Näslund, Johan Höjesjö, David S. Boukal (2022) From individuals to communities: habitat complexity affects all levels of organization in aquatic environments. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Water 9: e1575. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1575 | Habitat structural complexity increases age-class coexistence and population growth rate through relaxed cannibalism in a freshwater fish | Eric Edeline, Yoann Bennevault, David Rozen-Rechels | <p>Structurally-complex habitats harbour more taxonomically-diverse and more productive communities, a phenomenon generally ascribed to habitat complexity relaxing the strength of inter-specific predation and competition. Here, we extend this clas... | Allometry, Experimental ecology, Population ecology | Matthew Bracken | 2023-12-11 15:36:32 | View | ||
06 Apr 2025

Scales of marine endemism in oceanic islands and the Provincial-Island endemismHudson T. Pinheiro, Luiz A. Rocha, Juan P. Quimbayo https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.12.603346Provincial-island endemism adds to our understanding of the geographical distribution of speciesRecommended by Werner Ulrich based on reviews by Paulo Borges and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Paulo Borges and 1 anonymous reviewer
Many ecological, evolutionary, biogeographic studies on animals and plants have focused on endemism (e.g. (Crisp et al., 2001; Kier et al., 2009; Matthews et al., 2024, 2022; Qian et al., 2024). Ecological hotspots were first defined on endemic species (Myers et al., 2000). Nevertheless, despite the fact that the concept of endemism is crucial in biogeography and also in palaeontology there is still no stringent definition of endemism and very different concepts of endemism are used. It is another example of a concept that tries to define the undefinable (Darwin, 1859). ‘Definitions’ are either based on geographic and genetic isolation (Myers et al., 2000; Qian et al., 2024) or founded in geometric approaches that define restricted range sizes (Kinzig and Harte, 2000). Often, an ad hoc concept is used to cover taxon specificity and the habitats studied. Pinheiro et al. (2025) focus on species restricted to oceanic islands and rightly remark that these work as cradles for species origination and also as museums that contribute to lineages persistence. However, they also notice that in the case of islands any definition of endemism from species occurring only on single islands would be too narrow. Rather, endemism shows a spatial scaling with an increasing number of species occurring of multiple islands. In this respect they introduce the concept of provincial-island endemism and study the importance of single and multiple-island endemic species to island biodiversity Pinheiro et al. (2025) use data from 7,289 fish species associated with reef environments of 87 oceanic islands and 189 coastal reefs around the world. A strong negative correlation appeared between the number of endemic species and the number of islands they occur. This relationship directly translates into our assessment of whether an archipelago is rich or poor in endemics. Pinheiro et al. (2025) explicitly demonstrate this with the examples of the Hawaiian Islands and Rapa Nui. They conclude that biogeographers need to clarify whether they deal with single-island or multiple island endemics. We can adapt this distinction to terrestrial and freshwater habitats and differentiate between single and multiple restricted areas and water bodies, for instance rivers, lakes, alpine valleys, mountains, or deserts. Of course, the idea that endemism patterns are scale dependent is not new. Daru et al. (2020), Graham et al. (2018), or Keil et al. (2015) already noticed the importance of spatial scale and Townsend Peterson and Watson (1998) introduced the partly equivalent concepts of weighted spatial and phylogenetic endemism that also contain the scaling component. Pinheiro et al. (2025) add to this by providing a sound analysis of the strength of the scaling component. They argue that fish endangerment categories and fishery limits might change when considering multiple island endemics. References Crisp, M.D., Laffan, S., Linder, H.P., Monro, A., 2001. Endemism in the Australian flora. J. Biogeogr. 28, 183–198. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2699.2001.00524.x Daru, B.H., Farooq, H., Antonelli, A., Faurby, S., 2020. Endemism patterns are scale dependent. Nat. Commun. 11, 2115. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15921-6 Darwin, C., 1859. On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favoured races in the struggle for life. John Murray, London. Graham, C.H., Storch, D., Machac, A., 2018. Phylogenetic scale in ecology and evolution. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 27, 175–187. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12686 Keil, P., Storch, D., Jetz, W., 2015. On the decline of biodiversity due to area loss. Nat. Commun. 6, 8837. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9837 Kier, G., Kreft, H., Lee, T.M., Jetz, W., Ibisch, P.L., Nowicki, C., Mutke, J., Barthlott, W., 2009. A global assessment of endemism and species richness across island and mainland regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106, 9322–9327. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0810306106 Kinzig, A.P., Harte, J., 2000. Implications of Endemics–Area Relationships for Estimates of Species Extinctions. Ecology 81, 3305–3311. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2000)081[3305:IOEARF]2.0.CO;2 Matthews, T.J., Triantis, K.A., Wayman, J.P., Martin, T.E., Hume, J.P., Cardoso, P., Faurby, S., Mendenhall, C.D., Dufour, P., Rigal, F., Cooke, R., Whittaker, R.J., Pigot, A.L., Thébaud, C., Jørgensen, M.W., Benavides, E., Soares, F.C., Ulrich, W., Kubota, Y., Sadler, J.P., Tobias, J.A., Sayol, F., 2024. The global loss of avian functional and phylogenetic diversity from anthropogenic extinctions. Science 386, 55–60. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adk7898 Matthews, T.J., Wayman, J.P., Cardoso, P., Sayol, F., Hume, J.P., Ulrich, W., Tobias, J.A., Soares, F.C., Thébaud, C., Martin, T.E., Triantis, K.A., 2022. Threatened and extinct island endemic birds of the world: Distribution, threats and functional diversity. J. Biogeogr. 49, 1920–1940. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.14474 Myers, N., Mittermeier, R.A., Mittermeier, C.G., da Fonseca, G.A.B., Kent, J., 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403, 853–858. https://doi.org/10.1038/35002501 Pinheiro, H.T., Rocha, L.A., Quimbayo, J.P 2025. Scales of marine endemism in oceanic islands and the Provincial-Island endemism. bioRxiv, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.07.12.603346 Qian, H., Mishler, B.D., Zhang, J., Qian, S., 2024. Global patterns and ecological drivers of taxonomic and phylogenetic endemism in angiosperm genera. Plant Divers. 46, 149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2023.11.004 Townsend Peterson, A., Watson, D.M., 1998. Problems with areal definitions of endemism: the effects of spatial scaling. Divers. Distrib. 4, 189–194. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1472-4642.1998.00021.x | Scales of marine endemism in oceanic islands and the Provincial-Island endemism | Hudson T. Pinheiro, Luiz A. Rocha, Juan P. Quimbayo | <p>Oceanic islands are remote environments commonly harboring endemic species, which often are unique lineages originated and maintained by a variety of ecological, biogeographical and evolutionary processes. Endemic species are found mostly in a ... |  | Biodiversity, Biogeography, Macroecology, Species distributions | Werner Ulrich | 2024-07-13 02:55:05 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Vasilis Dakos (Representative)
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










