Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields▼ | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 Feb 2020

Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical treeSébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret https://doi.org/10.1101/351197Growth trajectories, better than organ-level functional traits, reveal intraspecific response to environmental variationRecommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz
Functional traits are “morpho-physio-phenological traits which impact fitness indirectly via their effects on growth, reproduction and survival” [1]. Most functional traits are defined at organ level, e.g. for leaves, roots and stems, and reflect key aspects of resource acquisition and resource use by organisms for their development and reproduction [2]. More rarely, some functional traits can be related to spatial development, such as vegetative height and lateral spread in plants. References [1] Violle, C., Navas, M. L., Vile, D., Kazakou, E., Fortunel, C., Hummel, I., & Garnier, E. (2007). Let the concept of trait be functional!. Oikos, 116(5), 882-892. doi: 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15559.x | Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree | Sébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret | <p style="text-align: justify;">1- Trait-environment relationships have been described at the community level across tree species. However, whether interspecific trait-environment relationships are consistent at the intraspecific level is yet unkn... |  | Botany, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Habitat selection, Ontogeny, Tropical ecology | François Munoz | 2018-06-21 17:13:17 | View | |
07 Aug 2023
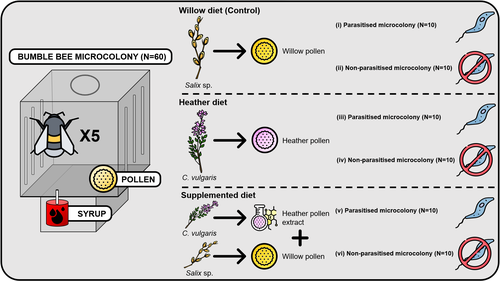
Heather pollen is not necessarily a healthy diet for bumble beesClément Tourbez, Irène Semay, Apolline Michel, Denis Michez, Pascal Gerbaux, Antoine Gekière, Maryse Vanderplanck https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8192036The importance of understanding bee nutritionRecommended by Ignasi Bartomeus based on reviews by Cristina Botías and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Cristina Botías and 1 anonymous reviewer
Contrasting with the great alarm on bee declines, it is astonishing how little basic biology we know about bees, including on abundant and widespread species that are becoming model species. Plant-pollinator relationships are one of the cornerstones of bee ecology, and researchers are increasingly documenting bees' diets. However, we rarely know which effects feeding on different flowers has on bees' health. This paper (Tourbez et al. 2023) uses an elegant experimental setting to test the effect of heather pollen on bumblebees' (Bombus terrestris) reproductive success. This is a timely question as heather is frequently used by bumblebees, and its nectar has been reported to reduce parasite infections. In fact, it has been suggested that bumblebees can medicate themselves when infected (Richardson et al. 2014), and the pollen of some Asteraceae has been shown to help them fight parasites (Gekière et al. 2022). The starting hypothesis is that heather pollen contains flavonoids that might have a similar effect. Unfortunately, Tourbez and collaborators do not support this hypothesis, showing a negative effect of heather pollen, in particular its flavonoids, in bumblebees offspring, and an increase in parasite loads when fed on flavonoids. This is important because it challenges the idea that many pollen and nectar chemical compounds might have a medicinal use, and force us to critically analyze the effect of chemical compounds in each particular case. The results open several questions, such as why bumblebees collect heather pollen, or in which concentrations or pollen mixes it is deleterious. A limitation of the study is that it uses micro-colonies, and extrapolating this to real-world conditions is always complex. Understanding bee declines require a holistic approach starting with bee physiology and scaling up to multispecies population dynamics. References Gekière, A., Semay, I., Gérard, M., Michez, D., Gerbaux, P., & Vanderplanck, M. 2022. Poison or Potion: Effects of Sunflower Phenolamides on Bumble Bees and Their Gut Parasite. Biology, 11(4), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11040545 Richardson, L.L., Adler, L.S., Leonard, A.S., Andicoechea, J., Regan, K.H., Anthony, W.E., Manson, J.S., & Irwin, R.E. 2015. Secondary metabolites in floral nectar reduce parasite infections in bumblebees. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences 282 (1803), 20142471. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2014.2471 Tourbez, C., Semay, I., Michel, A., Michez, D., Gerbaux, P., Gekière A. & Vanderplanck, M. 2023. Heather pollen is not necessarily a healthy diet for bumble bees. Zenodo, ver 3, reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8192036 | Heather pollen is not necessarily a healthy diet for bumble bees | Clément Tourbez, Irène Semay, Apolline Michel, Denis Michez, Pascal Gerbaux, Antoine Gekière, Maryse Vanderplanck | <p>There is evidence that specialised metabolites of flowering plants occur in both vegetative parts and floral resources (i.e., pollen and nectar), exposing pollinators to their biological activities. While such metabolites may be toxic to bees, ... |  | Botany, Chemical ecology, Host-parasite interactions, Pollination, Zoology | Ignasi Bartomeus | 2023-04-10 21:22:34 | View | |
11 May 2020
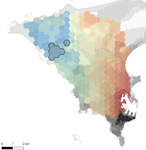
Interplay between historical and current features of the cityscape in shaping the genetic structure of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar (Senegal, West Africa)Claire Stragier, Sylvain Piry, Anne Loiseau, Mamadou Kane, Aliou Sow, Youssoupha Niang, Mamoudou Diallo, Arame Ndiaye, Philippe Gauthier, Marion Borderon, Laurent Granjon, Carine Brouat, Karine Berthier https://doi.org/10.1101/557066Urban past predicts contemporary genetic structure in city ratsRecommended by Michelle DiLeo based on reviews by Torsti Schulz, ? and 1 anonymous reviewerUrban areas are expanding worldwide, and have become a dominant part of the landscape for many species. Urbanization can fragment pre-existing populations of vulnerable species leading to population declines and the loss of connectivity. On the other hand, expansion of urban areas can also facilitate the spread of human commensals including pests. Knowledge of the features of cityscapes that facilitate gene flow and maintain diversity of pests is thus key to their management and eradication. References [1] Rivkin, L. R., Santangelo, J. S., Alberti, M. et al. (2019). A roadmap for urban evolutionary ecology. Evolutionary Applications, 12(3), 384-398. doi: 10.1111/eva.12734 | Interplay between historical and current features of the cityscape in shaping the genetic structure of the house mouse (Mus musculus domesticus) in Dakar (Senegal, West Africa) | Claire Stragier, Sylvain Piry, Anne Loiseau, Mamadou Kane, Aliou Sow, Youssoupha Niang, Mamoudou Diallo, Arame Ndiaye, Philippe Gauthier, Marion Borderon, Laurent Granjon, Carine Brouat, Karine Berthier | <p>Population genetic approaches may be used to investigate dispersal patterns of species living in highly urbanized environment in order to improve management strategies for biodiversity conservation or pest control. However, in such environment,... |  | Biological invasions, Landscape ecology, Molecular ecology | Michelle DiLeo | 2019-02-22 08:36:13 | View | |
20 Feb 2019
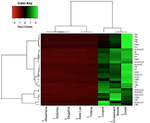
Differential immune gene expression associated with contemporary range expansion of two invasive rodents in SenegalNathalie Charbonnel, Maxime Galan, Caroline Tatard, Anne Loiseau, Christophe Diagne, Ambroise Dalecky, Hugues Parrinello, Stephanie Rialle, Dany Severac and Carine Brouat https://doi.org/10.1101/442160Are all the roads leading to Rome?Recommended by Simon Blanchet based on reviews by Nadia Aubin-Horth and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying the factors which favour the establishment and spread of non-native species in novel environments is one of the keys to predict - and hence prevent or control - biological invasions. This includes biological factors (i.e. factors associated with the invasive species themselves), and one of the prevailing hypotheses is that some species traits may explain their impressive success to establish and spread in novel environments [1]. In animals, most research studies have focused on traits associated with fecundity, age at maturity, level of affiliation to humans or dispersal ability for instance. The “composite picture” of the perfect (i.e. successful) invader that has gradually emerged is a small-bodied animal strongly affiliated to human activities with high fecundity, high dispersal ability and a super high level of plasticity. Of course, the story is not that simple, and actually a perfect invader sometimes – if not often- takes another form… Carrying on to identify what makes a species a successful invader or not is hence still an important research axis with major implications. References [1] Jeschke, J. M., & Strayer, D. L. (2006). Determinants of vertebrate invasion success in Europe and North America. Global Change Biology, 12(9), 1608-1619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01213.x | Differential immune gene expression associated with contemporary range expansion of two invasive rodents in Senegal | Nathalie Charbonnel, Maxime Galan, Caroline Tatard, Anne Loiseau, Christophe Diagne, Ambroise Dalecky, Hugues Parrinello, Stephanie Rialle, Dany Severac and Carine Brouat | <p>Background: Biological invasions are major anthropogenic changes associated with threats to biodiversity and health. What determines the successful establishment of introduced populations still remains unsolved. Here we explore the appealing as... |  | Biological invasions, Eco-immunology & Immunity, Population ecology | Simon Blanchet | 2018-10-14 12:21:52 | View | |
20 Sep 2018
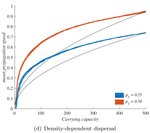
When higher carrying capacities lead to faster propagationMarjorie Haond, Thibaut Morel-Journel, Eric Lombaert, Elodie Vercken, Ludovic Mailleret & Lionel Roques https://doi.org/10.1101/307322When the dispersal of the many outruns the dispersal of the fewRecommended by Matthieu Barbier based on reviews by Yuval Zelnik and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Yuval Zelnik and 1 anonymous reviewer
Are biological invasions driven by a few pioneers, running ahead of their conspecifics? Or are these pioneers constantly being caught up by, and folded into, the larger flux of propagules from the established populations behind them? References [1] Levins, R., & Culver, D. (1971). Regional Coexistence of Species and Competition between Rare Species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 68(6), 1246–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1246 | When higher carrying capacities lead to faster propagation | Marjorie Haond, Thibaut Morel-Journel, Eric Lombaert, Elodie Vercken, Ludovic Mailleret & Lionel Roques | <p>This preprint has been reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Ecology (https://dx.doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100004). Finding general patterns in the expansion of natural populations is a major challenge in ecology and invasion biology... |  | Biological invasions, Colonization, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Matthieu Barbier | Yuval Zelnik | 2018-04-25 10:18:48 | View |
16 Jun 2023
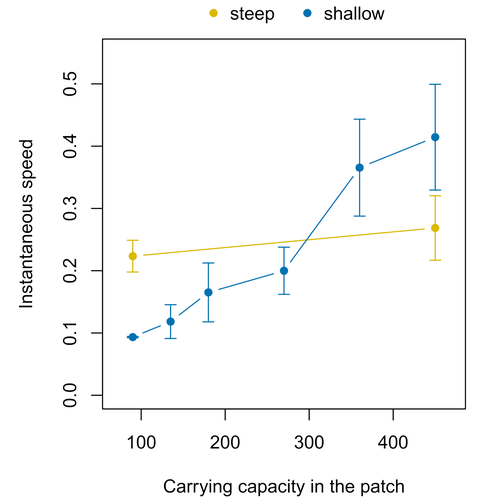
Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansionThibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255Combining stochastic models and experiments to understand dispersal in heterogeneous environmentsRecommended by Joaquín Hortal based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersDispersal is a key element of the natural dynamics of meta-communities, and plays a central role in the success of populations colonizing new landscapes. Understanding how demographic processes may affect the speed at which alien species spread through environmentally-heterogeneous habitat fragments is therefore of key importance to manage biological invasions. This requires studying together the complex interplay of dispersal and population processes, two inextricably related phenomena that can produce many possible outcomes. Stochastic models offer an opportunity to describe this kind of process in a meaningful way, but to ensure that they are realistic (sensu Levins 1966) it is also necessary to combine model simulations with empirical data (Snäll et al. 2007). Morel-Journel et al. (2023) put together stochastic models and experimental data to study how population density may affect the speed at which alien species spread through a heterogeneous landscape. They do it by focusing on what they call ‘colonisation debt’, which is merely the impact that population density at the invasion front may have on the speed at which the species colonizes patches of different carrying capacities. They investigate this issue through two largely independent approaches. First, a stochastic model of dispersal throughout the patches of a linear, 1-dimensional landscape, which accounts for different degrees of density-dependent growth. And second, a microcosm experiment of a parasitoid wasp colonizing patches with different numbers of host eggs. In both cases, they compare the velocity of colonization of patches with lower or higher carrying capacity than the previous one (i.e. what they call upward or downward gradients). Their results show that density-dependent processes influence the speed at which new fragments are colonized is significantly reduced by positive density dependence. When either population growth or dispersal rate depend on density, colonisation debt limits the speed of invasion, which turns out to be dependent on the strength and direction of the gradient between the conditions of the invasion front, and the newly colonized patches. Although this result may be quite important to understand the meta-population dynamics of dispersing species, it is important to note that in their study the environmental differences between patches do not take into account eventual shifts in the scenopoetic conditions (i.e. the values of the environmental parameters to which species niches’ respond to; Hutchinson 1978, see also Soberón 2007). Rather, differences arise from variations in the carrying capacity of the patches that are consecutively invaded, both in the in silico and microcosm experiments. That is, they account for potential differences in the size or quality of the invaded fragments, but not on the costs of colonizing fragments with different environmental conditions, which may also determine invasion speed through niche-driven processes. This aspect can be of particular importance in biological invasions or under climate change-driven range shifts, when adaptation to new environments is often required (Sakai et al. 2001; Whitney & Gabler 2008; Hill et al. 2011). The expansion of geographical distribution ranges is the result of complex eco-evolutionary processes where meta-community dynamics and niche shifts interact in a novel physical space and/or environment (see, e.g., Mestre et al. 2020). Here, the invasibility of native communities is determined by niche variations and how similar are the traits of alien and native species (Hui et al. 2023). Within this context, density-dependent processes will build upon and heterogeneous matrix of native communities and environments (Tischendorf et al. 2005), to eventually determine invasion success. What the results of Morel-Journel et al. (2023) show is that, when the invader shows density dependence, the invasion process can be slowed down by variations in the carrying capacity of patches along the dispersal front. This can be particularly useful to manage biological invasions; ongoing invasions can be at least partially controlled by manipulating the size or quality of the patches that are most adequate to the invader, controlling host populations to reduce carrying capacity. But further, landscape manipulation of such kind could be used in a preventive way, to account in advance for the effects of the introduction of alien species for agricultural exploitation or biological control, thereby providing an additional safeguard to practices such as the introduction of parasitoids to control plagues. These practical aspects are certainly worth exploring further, together with a more explicit account of the influence of the abiotic conditions and the characteristics of the invaded communities on the success and speed of biological invasions. REFERENCES Hill, J.K., Griffiths, H.M. & Thomas, C.D. (2011) Climate change and evolutionary adaptations at species' range margins. Annual Review of Entomology, 56, 143-159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144746 Hui, C., Pyšek, P. & Richardson, D.M. (2023) Disentangling the relationships among abundance, invasiveness and invasibility in trait space. npj Biodiversity, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-023-00019-1 Hutchinson, G.E. (1978) An introduction to population biology. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT. Levins, R. (1966) The strategy of model building in population biology. American Scientist, 54, 421-431. Mestre, A., Poulin, R. & Hortal, J. (2020) A niche perspective on the range expansion of symbionts. Biological Reviews, 95, 491-516. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12574 Morel-Journel, T., Haond, M., Duan, L., Mailleret, L. & Vercken, E. (2023) Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion. bioRxiv, 2022.11.13.516255, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255 Snäll, T., B. O'Hara, R. & Arjas, E. (2007) A mathematical and statistical framework for modelling dispersal. Oikos, 116, 1037-1050. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15604.x Sakai, A.K., Allendorf, F.W., Holt, J.S., Lodge, D.M., Molofsky, J., With, K.A., Baughman, S., Cabin, R.J., Cohen, J.E., Ellstrand, N.C., McCauley, D.E., O'Neil, P., Parker, I.M., Thompson, J.N. & Weller, S.G. (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 305-332. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114037 Soberón, J. (2007) Grinnellian and Eltonian niches and geographic distributions of species. Ecology Letters, 10, 1115-1123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01107.x Tischendorf, L., Grez, A., Zaviezo, T. & Fahrig, L. (2005) Mechanisms affecting population density in fragmented habitat. Ecology and Society, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-01265-100107 Whitney, K.D. & Gabler, C.A. (2008) Rapid evolution in introduced species, 'invasive traits' and recipient communities: challenges for predicting invasive potential. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 569-580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2008.00473.x | Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion | Thibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken | <p>Demographic processes that occur at the local level, such as positive density dependence in growth or dispersal, are known to shape population range expansion, notably by linking carrying capacity to invasion speed. As a result of these process... |  | Biological invasions, Colonization, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Landscape ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Joaquín Hortal | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-11-16 15:52:08 | View |
05 Apr 2022
Late-acting self-incompatible system, preferential allogamy and delayed selfing in the heterostylous invasive populations of Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetalaLuis O. Portillo Lemus, Maryline Harang, Michel Bozec, Jacques Haury, Solenn Stoeckel, Dominique Barloy https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.15.452457Water primerose (Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala) auto- and allogamy: an ecological perspectiveRecommended by Antoine Vernay based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Emiliano Mora-Carrera and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Juan Arroyo, Emiliano Mora-Carrera and 1 anonymous reviewer
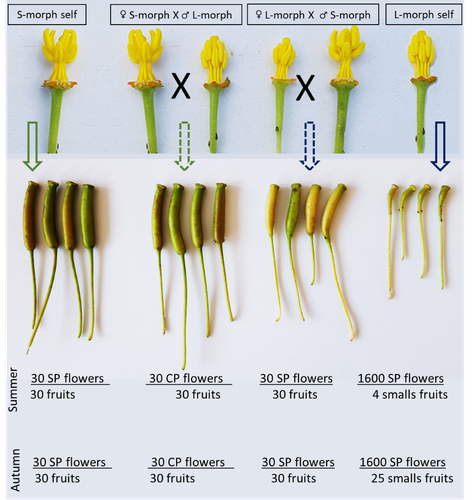
Invasive plant species are widely studied by the ecologist community, especially in wetlands. Indeed, alien plants are considered one of the major threats to wetland biodiversity (Reid et al., 2019). Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala (Hook. & Arn.) G.L.Nesom & Kartesz, 2000 (Lgh) is one of them and has received particular attention for a long time (Hieda et al., 2020; Thouvenot, Haury, & Thiebaut, 2013). The ecology of this invasive species and its effect on its biotic and abiotic environment has been studied in previous works. Different processes were demonstrated to explain their invasibility such as allelopathic interference (Dandelot et al., 2008), resource competition (Gérard et al., 2014), and high phenotypic plasticity (Thouvenot, Haury, & Thiébaut, 2013), to cite a few of them. However, although vegetative reproduction is a well-known invasive process for alien plants like Lgh (Glover et al., 2015), the sexual reproduction of this species is still unclear and may help to understand the Lgh population dynamics. Portillo Lemus et al. (2021) showed that two floral morphs of Lgh co-exist in natura, involving self-compatibility for short-styled phenotype and self-incompatibility for long-styled phenotype processes. This new article (Portillo Lemus et al., 2022) goes further and details the underlying mechanisms of the sexual reproduction of the two floral morphs. Complementing their previous study, the authors have described a late self-incompatible process associated with the long-styled morph, which authorized a small proportion of autogamy. Although this represents a small fraction of the L-morph reproduction, it may have a considerable impact on the L-morph population dynamics. Indeed, authors report that “floral morphs are mostly found in allopatric monomorphic populations (i.e., exclusively S-morph or exclusively L-morph populations)” with a large proportion of L-morph populations compared to S-morph populations in the field. It may seem counterintuitive as L-morph mainly relies on cross-fecundation. Results show that L-morph autogamy mainly occurs in the fall, late in the reproduction season. Therefore, the reproduction may be ensured if no exogenous pollen reaches the stigma of L-morph individuals. It partly explains the large proportion of L-morph populations in the field. Beyond the description of late-acting self-incompatibility, which makes the Onagraceae a third family of Myrtales with this reproductive adaptation, the study raises several ecological questions linked to the results presented in the article. First, it seems that even if autogamy is possible, Lgh would favour allogamy, even in S-morph, through the faster development of pollen tubes from other individuals. This may confer an adaptative and evolutive advantage for the Lgh, increasing its invasive potential. The article shows this faster pollen tube development in S-morph but does not test the evolutive consequences. It is an interesting perspective for future research. It would also be interesting to describe cellular processes which recognize and then influence the speed of the pollen tube. Second, the importance of sexual reproduction vs vegetative reproduction would also provide information on the benefits of sexual dimorphism within populations. For instance, how fruit production increases the dispersal potential of Lgh would help to understand Lgh population dynamics and to propose adapted management practices (Delbart et al., 2013; Meisler, 2009). To conclude, the study proposes a morphological, reproductive and physiological description of the Lgh sexual reproduction process. However, underlying ecological questions are well included in the article and the ecophysiological results enlighten some questions about the role of sexual reproduction in the invasiveness of Lgh. I advise the reader to pay attention to the reviewers’ comments; the debates were very constructive and, thanks to the great collaboration with the authorship, lead to an interesting paper about Lgh reproduction and with promising perspectives in ecology and invasion ecology. References Dandelot S, Robles C, Pech N, Cazaubon A, Verlaque R (2008) Allelopathic potential of two invasive alien Ludwigia spp. Aquatic Botany, 88, 311–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2007.12.004 Delbart E, Mahy G, Monty A (2013) Efficacité des méthodes de lutte contre le développement de cinq espèces de plantes invasives amphibies : Crassula helmsii, Hydrocotyle ranunculoides, Ludwigia grandiflora, Ludwigia peploides et Myriophyllum aquaticum (synthèse bibliographique). BASE, 17, 87–102. https://popups.uliege.be/1780-4507/index.php?id=9586 Gérard J, Brion N, Triest L (2014) Effect of water column phosphorus reduction on competitive outcome and traits of Ludwigia grandiflora and L. peploides, invasive species in Europe. Aquatic Invasions, 9, 157–166. https://doi.org/10.3391/ai.2014.9.2.04 Glover R, Drenovsky RE, Futrell CJ, Grewell BJ (2015) Clonal integration in Ludwigia hexapetala under different light regimes. Aquatic Botany, 122, 40–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquabot.2015.01.004 Hieda S, Kaneko Y, Nakagawa M, Noma N (2020) Ludwigia grandiflora (Michx.) Greuter & Burdet subsp. hexapetala (Hook. & Arn.) G. L. Nesom & Kartesz, an Invasive Aquatic Plant in Lake Biwa, the Largest Lake in Japan. Acta Phytotaxonomica et Geobotanica, 71, 65–71. https://doi.org/10.18942/apg.201911 Meisler J (2009) Controlling Ludwigia hexaplata in Northern California. Wetland Science and Practice, 26, 15–19. https://doi.org/10.1672/055.026.0404 Portillo Lemus LO, Harang M, Bozec M, Haury J, Stoeckel S, Barloy D (2022) Late-acting self-incompatible system, preferential allogamy and delayed selfing in the heteromorphic invasive populations of Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala. bioRxiv, 2021.07.15.452457, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.15.452457 Portillo Lemus LO, Bozec M, Harang M, Coudreuse J, Haury J, Stoeckel S, Barloy D (2021) Self-incompatibility limits sexual reproduction rather than environmental conditions in an invasive water primrose. Plant-Environment Interactions, 2, 74–86. https://doi.org/10.1002/pei3.10042 Reid AJ, Carlson AK, Creed IF, Eliason EJ, Gell PA, Johnson PTJ, Kidd KA, MacCormack TJ, Olden JD, Ormerod SJ, Smol JP, Taylor WW, Tockner K, Vermaire JC, Dudgeon D, Cooke SJ (2019) Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biological Reviews, 94, 849–873. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12480 Thouvenot L, Haury J, Thiebaut G (2013) A success story: water primroses, aquatic plant pests. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 23, 790–803. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.2387 Thouvenot L, Haury J, Thiébaut G (2013) Seasonal plasticity of Ludwigia grandiflora under light and water depth gradients: An outdoor mesocosm experiment. Flora - Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants, 208, 430–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2013.07.004 | Late-acting self-incompatible system, preferential allogamy and delayed selfing in the heterostylous invasive populations of Ludwigia grandiflora subsp. hexapetala | Luis O. Portillo Lemus, Maryline Harang, Michel Bozec, Jacques Haury, Solenn Stoeckel, Dominique Barloy | <p style="text-align: justify;">Breeding system influences local population genetic structure, effective size, offspring fitness and functional variation. Determining the respective importance of self- and cross-fertilization in hermaphroditic flo... |  | Biological invasions, Botany, Freshwater ecology, Pollination | Antoine Vernay | 2021-07-16 09:53:50 | View | |
12 Jun 2019
Environmental heterogeneity drives tsetse fly population dynamics and controlCecilia H, Arnoux S, Picault S, Dicko A, Seck MT, Sall B, Bassene M, Vreysen M, Pagabeleguem S, Bance A, Bouyer J, Ezanno P https://doi.org/10.1101/493650Modeling jointly landscape complexity and environmental heterogeneity to envision new strategies for tsetse flies controlRecommended by Benjamin Roche based on reviews by Timothée Vergne and 1 anonymous reviewerToday, understanding spatio-temporal dynamics of pathogens is pivotal to understand their transmission and controlling them. First, understanding this dynamics can reveal the ecology of their transmission [1]. Indeed, such knowledge, based on data that are quite easy to access, can shed light on transmission modes, which could rely on different animal species that can be spatially distributed in a non-uniform way [2]. This is especially true for pathogens with complex life-cycles, despite that investigating such dynamics is very challenging and rely mostly on mathematical models. References [1] Grenfell, B. T., Bjørnstad, O. N., & Kappey, J. (2001). Travelling waves and spatial hierarchies in measles epidemics. Nature, 414(6865), 716-723. doi: 10.1038/414716a | Environmental heterogeneity drives tsetse fly population dynamics and control | Cecilia H, Arnoux S, Picault S, Dicko A, Seck MT, Sall B, Bassene M, Vreysen M, Pagabeleguem S, Bance A, Bouyer J, Ezanno P | <p>A spatially and temporally heterogeneous environment may lead to unexpected population dynamics. Knowledge still is needed on which of the local environment properties favour population maintenance at larger scale. For pathogen vectors, such as... |  | Biological control, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Benjamin Roche | 2018-12-14 12:13:39 | View | |
30 Mar 2020
Environmental variables determining the distribution of an avian parasite: the case of the Philornis torquans complex (Diptera: Muscidae) in South AmericaPablo F. Cuervo, Alejandro Percara, Lucas Monje, Pablo M. Beldomenico, Martín A. Quiroga https://doi.org/10.1101/839589Catching the fly in dystopian timesRecommended by Rodrigo Medel based on reviews by 4 anonymous reviewersHost-parasite interactions are ubiquitous on Earth. They are present in almost every conceivable ecosystem and often result from a long history of antagonist coevolution [1,2]. Recent studies on climate change have revealed, however, that modification of abiotic variables are often accompanied by shifts in the distributional range of parasites to habitats far beyond their original geographical distribution, creating new interactions in novel habitats with unpredictable consequences for host community structure and organization [3,4]. This situation may be especially critical for endangered host species having small population abundance and restricted distribution range. The infestation of bird species with larvae of the muscid fly genus Philornis is a case in point. At least 250 bird species inhabiting mostly Central and South America are infected by Philornis flies [5,6]. Fly larval development occurs in bird faeces, nesting material, or inside nestlings, affecting the development and nestling survival. References [1] Thompson JN (1994) The Coevolutionary Process. University of Chicago Press. | Environmental variables determining the distribution of an avian parasite: the case of the Philornis torquans complex (Diptera: Muscidae) in South America | Pablo F. Cuervo, Alejandro Percara, Lucas Monje, Pablo M. Beldomenico, Martín A. Quiroga | <p>*Philornis* flies are the major cause of myasis in altricial nestlings of neotropical birds. Its impact ranges from subtle to lethal, being of major concern in endangered bird species with geographically-restricted, fragmented and small-sized p... |  | Biogeography, Macroecology, Parasitology, Species distributions | Rodrigo Medel | 2019-11-26 21:31:33 | View | |
31 Oct 2022

Ten simple rules for working with high resolution remote sensing dataAdam L. Mahood, Maxwell Benjamin Joseph, Anna Spiers, Michael J. Koontz, Nayani Ilangakoon, Kylen Solvik, Nathan Quarderer, Joe McGlinchy, Victoria Scholl, Lise St. Denis, Chelsea Nagy, Anna Braswell, Matthew W. Rossi, Lauren Herwehe, Leah wasser, Megan Elizabeth Cattau, Virginia Iglesias, Fangfang Yao, Stefan Leyk, Jennifer Balch https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/kehqzPreventing misuse of high-resolution remote sensing dataRecommended by Eric Goberville based on reviews by Jane Wyngaard and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jane Wyngaard and 1 anonymous reviewer
To observe, characterise, identify, understand, predict... This is the approach that researchers follow every day. This sequence is tirelessly repeated as the biological model, the targeted ecosystem and/or the experimental, environmental or modelling conditions change. This way of proceeding is essential in a world of rapid change in response to the frenetic pace of intensifying pressures and forcings that impact ecosystems. To better understand our Earth and the dynamics of its components, to map ecosystems and diversity patterns, and to identify changes, humanity had to demonstrate inventiveness and defy gravity. Gustave Hermite and Georges Besançon were the first to launch aloft balloons equipped with radio transmitters, making possible the transmission of meteorological data to observers in real time [1]. The development of aviation in the middle of the 20th century constituted a real leap forward for the frequent acquisition of aerial observations, leading to a significant improvement in weather forecasting models. The need for systematic collection of data as holistic as possible – an essential component for the observation of complex biological systems - has resulted in pushing the limits of technological prowess. The conquest of space and the concurrent development of satellite observations has largely contributed to the collection of a considerable mass of data, placing our Earth under the "macroscope" - a concept introduced to ecology in the early 1970s by Howard T. Odum (see [2]), and therefore allowing researchers to move towards a better understanding of ecological systems, deterministic and stochastic patterns … with the ultimate goal of improving management actions [2,3]. Satellite observations have been carried out for nearly five decades now [3] and have greatly contributed to a better qualitative and quantitative understanding of the functioning of our planet, its diversity, its climate... and to a better anticipation of possible future changes (e.g., [4-7]). This access to rich and complex sources of information, for which both spatial and temporal resolutions are increasingly fine, results in the implementation of increasingly complex computation-based analyses, in order to meet the need for a better understanding of ecological mechanisms and processes, and their possible changes. Steven Levitt stated that "Data is one of the most powerful mechanisms for telling stories". This is so true … Data should not be used as a guide to thinking and a critical judgment at each stage of the data exploitation process should not be neglected. This is what Mahood et al. [8] rightly remind us in their article "Ten simple rules for working with high-resolution remote sensing data" in which they provide the fundamentals to consider when working with data of this nature, a still underutilized resource in several topics, such as conservation biology [3]. In this unconventional article, presented in a pedagogical way, the authors remind different generations of readers how satellite data should be handled and processed. The authors aim to make the readers aware of the most frequent pitfalls encouraging them to use data adapted to their original question, the most suitable tools/methods/procedures, to avoid methodological overkill, and to ensure both ethical use of data and transparency in the research process. While access to high-resolution data is increasingly easy thanks to the implementation of dedicated platforms [4], and because of the development of easy-to-use processing software and pipelines, it is important to take the time to recall some of the essential rules and guidelines for managing them, from new users with little or no experience who will find in this article the recommendations, resources and advice necessary to start exploiting remote sensing data, to more experienced researchers. References [1] Jeannet P, Philipona R, and Richner H (2016). 8 Swiss upper-air balloon soundings since 1902. In: Willemse S, Furger M (2016) From weather observations to atmospheric and climate sciences in Switzerland: Celebrating 100 years of the Swiss Society for Meteorology. vdf Hochschulverlag AG. [2] Odum HT (2007) Environment, Power, and Society for the Twenty-First Century: The Hierarchy of Energy. Columbia University Press. [3] Boyle SA, Kennedy CM, Torres J, Colman K, Pérez-Estigarribia PE, Sancha NU de la (2014) High-Resolution Satellite Imagery Is an Important yet Underutilized Resource in Conservation Biology. PLOS ONE, 9, e86908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086908 [4] Le Traon P-Y, Antoine D, Bentamy A, Bonekamp H, Breivik LA, Chapron B, Corlett G, Dibarboure G, DiGiacomo P, Donlon C, Faugère Y, Font J, Girard-Ardhuin F, Gohin F, Johannessen JA, Kamachi M, Lagerloef G, Lambin J, Larnicol G, Le Borgne P, Leuliette E, Lindstrom E, Martin MJ, Maturi E, Miller L, Mingsen L, Morrow R, Reul N, Rio MH, Roquet H, Santoleri R, Wilkin J (2015) Use of satellite observations for operational oceanography: recent achievements and future prospects. Journal of Operational Oceanography, 8, s12–s27. https://doi.org/10.1080/1755876X.2015.1022050 [5] Turner W, Rondinini C, Pettorelli N, Mora B, Leidner AK, Szantoi Z, Buchanan G, Dech S, Dwyer J, Herold M, Koh LP, Leimgruber P, Taubenboeck H, Wegmann M, Wikelski M, Woodcock C (2015) Free and open-access satellite data are key to biodiversity conservation. Biological Conservation, 182, 173–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.048 [6] Melet A, Teatini P, Le Cozannet G, Jamet C, Conversi A, Benveniste J, Almar R (2020) Earth Observations for Monitoring Marine Coastal Hazards and Their Drivers. Surveys in Geophysics, 41, 1489–1534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-020-09594-5 [7] Zhao Q, Yu L, Du Z, Peng D, Hao P, Zhang Y, Gong P (2022) An Overview of the Applications of Earth Observation Satellite Data: Impacts and Future Trends. Remote Sensing, 14, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081863 [8] Mahood AL, Joseph MB, Spiers A, Koontz MJ, Ilangakoon N, Solvik K, Quarderer N, McGlinchy J, Scholl V, Denis LS, Nagy C, Braswell A, Rossi MW, Herwehe L, Wasser L, Cattau ME, Iglesias V, Yao F, Leyk S, Balch J (2021) Ten simple rules for working with high resolution remote sensing data. OSFpreprints, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/kehqz | Ten simple rules for working with high resolution remote sensing data | Adam L. Mahood, Maxwell Benjamin Joseph, Anna Spiers, Michael J. Koontz, Nayani Ilangakoon, Kylen Solvik, Nathan Quarderer, Joe McGlinchy, Victoria Scholl, Lise St. Denis, Chelsea Nagy, Anna Braswell, Matthew W. Rossi, Lauren Herwehe, Leah wasser,... | <p>Researchers in Earth and environmental science can extract incredible value from high-resolution (sub-meter, sub-hourly or hyper-spectral) remote sensing data, but these data can be difficult to use. Correct, appropriate and competent use of su... |  | Biogeography, Landscape ecology, Macroecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Terrestrial ecology | Eric Goberville | 2021-10-19 21:41:22 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










