
GOBERVILLE Eric
- BOREA, Sorbonne University, Paris, France
- Biodiversity, Biogeography, Climate change, Macroecology, Marine ecology, Species distributions, Statistical ecology
- recommender
Recommendations: 3
Review: 1
Recommendations: 3
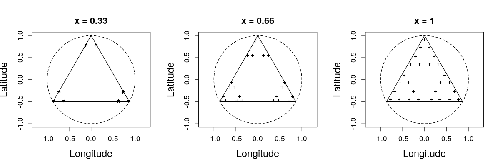
Efficient sampling designs to assess biodiversity spatial autocorrelation : should we go fractal?
Spatial patterns and autocorrelation challenges in ecological conservation
Recommended by Eric Goberville based on reviews by Nigel Yoccoz and Charles J Marsh“Pattern, like beauty, is to some extent in the eye of the beholder” (Grant 1977 in Wiens, 1989)

Ten simple rules for working with high resolution remote sensing data
Preventing misuse of high-resolution remote sensing data
Recommended by Eric Goberville based on reviews by Jane Wyngaard and 1 anonymous reviewerTo observe, characterise, identify, understand, predict... This is the approach that researchers follow every day. This sequence is tirelessly repeated as the biological model, the targeted ecosystem and/or the experimental, environmental or modelling conditions change. This way of proceeding is essential in a world of rapid change in response to the frenetic pace of intensifying pressures and forcings that impact ecosystems. To better understand our Earth and the dynamics of its components, to map ecosystems and diversity patterns, and to identify changes, humanity had to demonstrate inventiveness and defy gravity.
Gustave Hermite and Georges Besançon were the first to launch aloft balloons equipped with radio transmitters, making possible the transmission of meteorological data to observers in real time [1]. The development of aviation in the middle of the 20th century constituted a real leap forward for the frequent acquisition of aerial observations, leading to a significant improvement in weather forecasting models. The need for systematic collection of data as holistic as possible – an essential component for the observation of complex biological systems - has resulted in pushing the limits of technological prowess.
The conquest of space and the concurrent development of satellite observations has largely contributed to the collection of a considerable mass of data, placing our Earth under the "macroscope" - a concept introduced to ecology in the early 1970s by Howard T. Odum (see [2]), and therefore allowing researchers to move towards a better understanding of ecological systems, deterministic and stochastic patterns … with the ultimate goal of improving management actions [2,3]. Satellite observations have been carried out for nearly five decades now [3] and have greatly contributed to a better qualitative and quantitative understanding of the functioning of our planet, its diversity, its climate... and to a better anticipation of possible future changes (e.g., [4-7]).
This access to rich and complex sources of information, for which both spatial and temporal resolutions are increasingly fine, results in the implementation of increasingly complex computation-based analyses, in order to meet the need for a better understanding of ecological mechanisms and processes, and their possible changes. Steven Levitt stated that "Data is one of the most powerful mechanisms for telling stories". This is so true … Data should not be used as a guide to thinking and a critical judgment at each stage of the data exploitation process should not be neglected.
This is what Mahood et al. [8] rightly remind us in their article "Ten simple rules for working with high-resolution remote sensing data" in which they provide the fundamentals to consider when working with data of this nature, a still underutilized resource in several topics, such as conservation biology [3]. In this unconventional article, presented in a pedagogical way, the authors remind different generations of readers how satellite data should be handled and processed. The authors aim to make the readers aware of the most frequent pitfalls encouraging them to use data adapted to their original question, the most suitable tools/methods/procedures, to avoid methodological overkill, and to ensure both ethical use of data and transparency in the research process. While access to high-resolution data is increasingly easy thanks to the implementation of dedicated platforms [4], and because of the development of easy-to-use processing software and pipelines, it is important to take the time to recall some of the essential rules and guidelines for managing them, from new users with little or no experience who will find in this article the recommendations, resources and advice necessary to start exploiting remote sensing data, to more experienced researchers.
References
[1] Jeannet P, Philipona R, and Richner H (2016). 8 Swiss upper-air balloon soundings since 1902. In: Willemse S, Furger M (2016) From weather observations to atmospheric and climate sciences in Switzerland: Celebrating 100 years of the Swiss Society for Meteorology. vdf Hochschulverlag AG.
[2] Odum HT (2007) Environment, Power, and Society for the Twenty-First Century: The Hierarchy of Energy. Columbia University Press.
[3] Boyle SA, Kennedy CM, Torres J, Colman K, Pérez-Estigarribia PE, Sancha NU de la (2014) High-Resolution Satellite Imagery Is an Important yet Underutilized Resource in Conservation Biology. PLOS ONE, 9, e86908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0086908
[4] Le Traon P-Y, Antoine D, Bentamy A, Bonekamp H, Breivik LA, Chapron B, Corlett G, Dibarboure G, DiGiacomo P, Donlon C, Faugère Y, Font J, Girard-Ardhuin F, Gohin F, Johannessen JA, Kamachi M, Lagerloef G, Lambin J, Larnicol G, Le Borgne P, Leuliette E, Lindstrom E, Martin MJ, Maturi E, Miller L, Mingsen L, Morrow R, Reul N, Rio MH, Roquet H, Santoleri R, Wilkin J (2015) Use of satellite observations for operational oceanography: recent achievements and future prospects. Journal of Operational Oceanography, 8, s12–s27. https://doi.org/10.1080/1755876X.2015.1022050
[5] Turner W, Rondinini C, Pettorelli N, Mora B, Leidner AK, Szantoi Z, Buchanan G, Dech S, Dwyer J, Herold M, Koh LP, Leimgruber P, Taubenboeck H, Wegmann M, Wikelski M, Woodcock C (2015) Free and open-access satellite data are key to biodiversity conservation. Biological Conservation, 182, 173–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.048
[6] Melet A, Teatini P, Le Cozannet G, Jamet C, Conversi A, Benveniste J, Almar R (2020) Earth Observations for Monitoring Marine Coastal Hazards and Their Drivers. Surveys in Geophysics, 41, 1489–1534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-020-09594-5
[7] Zhao Q, Yu L, Du Z, Peng D, Hao P, Zhang Y, Gong P (2022) An Overview of the Applications of Earth Observation Satellite Data: Impacts and Future Trends. Remote Sensing, 14, 1863. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14081863
[8] Mahood AL, Joseph MB, Spiers A, Koontz MJ, Ilangakoon N, Solvik K, Quarderer N, McGlinchy J, Scholl V, Denis LS, Nagy C, Braswell A, Rossi MW, Herwehe L, Wasser L, Cattau ME, Iglesias V, Yao F, Leyk S, Balch J (2021) Ten simple rules for working with high resolution remote sensing data. OSFpreprints, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/kehqz
Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly
Environmental heterogeneity drives phytoplankton community assembly patterns in a tropical riverine system
Recommended by Cédric Hubas and Eric Goberville based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique LamyWhat predisposes two individuals to form and maintain a relationship is a fundamental question. Using facial recognition to see whether couples' faces change over time to become more and more similar, psychology researchers have concluded that couples tend to be formed from the start between people whose faces are more similar than average [1]. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together.
And what about in nature? Are these rules of assembly valid for communities of different species?
In his seminal contribution, Robert MacArthur (1984) wrote ‘To do science is to search for repeated patterns’ [2]. Identifying the mechanisms that govern the arrangement of life is a hot research topic in the field of ecology for decades, and an absolutely essential prerequisite to answer the outstanding question of what shape ecological patterns in multi-species communities such as species-area relationships, relative species abundances, or spatial and temporal turnover of community composition; amid others [3]. To explain ecological patterns in nature, some rely on the concept that every species - through evolutionary processes and the acquisition of a unique set of traits that allow a species to be adapted to its abiotic and biotic environment - occupies a unique niche: Species coexistence comes as the result of niche differentiation [4,5]. Such a view has been challenged by the recognition of the key role of neutral processes [6], however, in which demographic stochasticity contributes to shape multi-species communities and to explain why congener species coexist much more frequently than expected by chance [7,8]. While the niche-based and neutral theories appear seemingly opposed at first sight [9], the dichotomy may be more philosophical than empirical [4,5]. Many examples have come to support that both concepts are not incompatible as they together influence the structure, diversity and functioning of communities [10], and are simply extreme cases of a continuum [11]. From this perspective, extrinsic factors, i.e., environmental heterogeneity, may influence the location of a given community along the niche-neutrality continuum.
The walk of species in nature is therefore neither random nor ecologically predestined. In microbial assemblages, the co-existence of these two antagonistic mechanisms has been shown both theoretically and empirically. It has been shown that a combination of stabilising (niche) and equalising (neutral) mechanisms was responsible for the existence of groups of coexistent species (clumps) in a phytoplankton rich community [12]. Analysing interannual changes (2003-2009) in the weekly abundance of diatoms and dinoflagellates located in a temperate coastal ecosystem of the Western English Channel, Mutshinda et al. [13] found a mixture of biomass dynamics consistent with the neutrality-niche continuum hypothesis. While niche processes explained the dynamic of phytoplankton functional groups (i.e., diatoms vs. dinoflagellates) in terms of biomass, neutral processes mainly dominated - 50 to 75% of the time - the dynamics at the species level within functional groups [13]. From one endpoint to another, defining the location of a community along the continuum is all matter of scale [4,11].
In their study, testing predictions made by an emergent neutrality model, Graco-Roza et al. [14] provide empirical evidence that neutral and niche processes joined together to shape and drive planktonic communities in a riverine ecosystem. Body size - the 'master trait' - is used here as a discriminant ecological dimension along the niche axis. From their analysis, they not only show that the specific abundance is organised in clumps and gaps along the niche axis, but also reveal that different clumps exist along the river course. They identify two main clumps in body size - with species belonging to three different morphologically-based functional groups - and characterise that among-species differences in biovolume are driven by functional redundancy at the clump level; species functional distinctiveness being related to the relative biovolume of species. By grouping their variables according to seasons (cold-dry vs. warm-wet) or river elevation profile (upper, medium and lower course), they hereby highlight how environmental heterogeneity contributes to shape species assemblages and their dynamics and conclude that emergent neutrality models are a powerful approach to explain species coexistence; and therefore ecological patterns.
References
[1] Tea-makorn PP, Kosinski M (2020) Spouses’ faces are similar but do not become more similar with time. Scientific Reports, 10, 17001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73971-8.
[2] MacArthur RH (1984) Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species. Princeton University Press.
[3] Vellend M (2020) The Theory of Ecological Communities (MPB-57). Princeton University Press.
[4] Wennekes PL, Rosindell J, Etienne RS (2012) The Neutral—Niche Debate: A Philosophical Perspective. Acta Biotheoretica, 60, 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-012-9144-6.
[5] Gravel D, Guichard F, Hochberg ME (2011) Species coexistence in a variable world. Ecology Letters, 14, 828–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01643.x.
[6] Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press.
[7] Leibold MA, McPeek MA (2006) Coexistence of the Niche and Neutral Perspectives in Community Ecology. Ecology, 87, 1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1399:COTNAN]2.0.CO;2.
[8] Pielou EC (1977) The Latitudinal Spans of Seaweed Species and Their Patterns of Overlap. Journal of Biogeography, 4, 299–311. https://doi.org/10.2307/3038189.
[9] Holt RD (2006) Emergent neutrality. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 531–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.08.003.
[10] Scheffer M, Nes EH van (2006) Self-organized similarity, the evolutionary emergence of groups of similar species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103, 6230–6235. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508024103.
[11] Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 9, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x.
[12] Vergnon R, Dulvy NK, Freckleton RP (2009) Niches versus neutrality: uncovering the drivers of diversity in a species-rich community. Ecology Letters, 12, 1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01364.x.
[13] Mutshinda CM, Finkel ZV, Widdicombe CE, Irwin AJ (2016) Ecological equivalence of species within phytoplankton functional groups. Functional Ecology, 30, 1714–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12641.
[14] Graco-Roza C, Segura AM, Kruk C, Domingos P, Soininen J, Marinho MM (2021) Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly. bioRxiv, 869966, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/869966
Review: 1

Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly
Environmental heterogeneity drives phytoplankton community assembly patterns in a tropical riverine system
Recommended by Cédric Hubas and Eric Goberville based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique LamyWhat predisposes two individuals to form and maintain a relationship is a fundamental question. Using facial recognition to see whether couples' faces change over time to become more and more similar, psychology researchers have concluded that couples tend to be formed from the start between people whose faces are more similar than average [1]. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together.
And what about in nature? Are these rules of assembly valid for communities of different species?
In his seminal contribution, Robert MacArthur (1984) wrote ‘To do science is to search for repeated patterns’ [2]. Identifying the mechanisms that govern the arrangement of life is a hot research topic in the field of ecology for decades, and an absolutely essential prerequisite to answer the outstanding question of what shape ecological patterns in multi-species communities such as species-area relationships, relative species abundances, or spatial and temporal turnover of community composition; amid others [3]. To explain ecological patterns in nature, some rely on the concept that every species - through evolutionary processes and the acquisition of a unique set of traits that allow a species to be adapted to its abiotic and biotic environment - occupies a unique niche: Species coexistence comes as the result of niche differentiation [4,5]. Such a view has been challenged by the recognition of the key role of neutral processes [6], however, in which demographic stochasticity contributes to shape multi-species communities and to explain why congener species coexist much more frequently than expected by chance [7,8]. While the niche-based and neutral theories appear seemingly opposed at first sight [9], the dichotomy may be more philosophical than empirical [4,5]. Many examples have come to support that both concepts are not incompatible as they together influence the structure, diversity and functioning of communities [10], and are simply extreme cases of a continuum [11]. From this perspective, extrinsic factors, i.e., environmental heterogeneity, may influence the location of a given community along the niche-neutrality continuum.
The walk of species in nature is therefore neither random nor ecologically predestined. In microbial assemblages, the co-existence of these two antagonistic mechanisms has been shown both theoretically and empirically. It has been shown that a combination of stabilising (niche) and equalising (neutral) mechanisms was responsible for the existence of groups of coexistent species (clumps) in a phytoplankton rich community [12]. Analysing interannual changes (2003-2009) in the weekly abundance of diatoms and dinoflagellates located in a temperate coastal ecosystem of the Western English Channel, Mutshinda et al. [13] found a mixture of biomass dynamics consistent with the neutrality-niche continuum hypothesis. While niche processes explained the dynamic of phytoplankton functional groups (i.e., diatoms vs. dinoflagellates) in terms of biomass, neutral processes mainly dominated - 50 to 75% of the time - the dynamics at the species level within functional groups [13]. From one endpoint to another, defining the location of a community along the continuum is all matter of scale [4,11].
In their study, testing predictions made by an emergent neutrality model, Graco-Roza et al. [14] provide empirical evidence that neutral and niche processes joined together to shape and drive planktonic communities in a riverine ecosystem. Body size - the 'master trait' - is used here as a discriminant ecological dimension along the niche axis. From their analysis, they not only show that the specific abundance is organised in clumps and gaps along the niche axis, but also reveal that different clumps exist along the river course. They identify two main clumps in body size - with species belonging to three different morphologically-based functional groups - and characterise that among-species differences in biovolume are driven by functional redundancy at the clump level; species functional distinctiveness being related to the relative biovolume of species. By grouping their variables according to seasons (cold-dry vs. warm-wet) or river elevation profile (upper, medium and lower course), they hereby highlight how environmental heterogeneity contributes to shape species assemblages and their dynamics and conclude that emergent neutrality models are a powerful approach to explain species coexistence; and therefore ecological patterns.
References
[1] Tea-makorn PP, Kosinski M (2020) Spouses’ faces are similar but do not become more similar with time. Scientific Reports, 10, 17001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73971-8.
[2] MacArthur RH (1984) Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species. Princeton University Press.
[3] Vellend M (2020) The Theory of Ecological Communities (MPB-57). Princeton University Press.
[4] Wennekes PL, Rosindell J, Etienne RS (2012) The Neutral—Niche Debate: A Philosophical Perspective. Acta Biotheoretica, 60, 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-012-9144-6.
[5] Gravel D, Guichard F, Hochberg ME (2011) Species coexistence in a variable world. Ecology Letters, 14, 828–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01643.x.
[6] Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press.
[7] Leibold MA, McPeek MA (2006) Coexistence of the Niche and Neutral Perspectives in Community Ecology. Ecology, 87, 1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1399:COTNAN]2.0.CO;2.
[8] Pielou EC (1977) The Latitudinal Spans of Seaweed Species and Their Patterns of Overlap. Journal of Biogeography, 4, 299–311. https://doi.org/10.2307/3038189.
[9] Holt RD (2006) Emergent neutrality. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 531–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.08.003.
[10] Scheffer M, Nes EH van (2006) Self-organized similarity, the evolutionary emergence of groups of similar species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103, 6230–6235. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508024103.
[11] Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 9, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x.
[12] Vergnon R, Dulvy NK, Freckleton RP (2009) Niches versus neutrality: uncovering the drivers of diversity in a species-rich community. Ecology Letters, 12, 1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01364.x.
[13] Mutshinda CM, Finkel ZV, Widdicombe CE, Irwin AJ (2016) Ecological equivalence of species within phytoplankton functional groups. Functional Ecology, 30, 1714–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12641.
[14] Graco-Roza C, Segura AM, Kruk C, Domingos P, Soininen J, Marinho MM (2021) Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly. bioRxiv, 869966, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/869966