Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors▼ | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 Jan 2021

Comparing statistical and mechanistic models to identify the drivers of mortality within a rear-edge beech populationCathleen Petit-Cailleux, Hendrik Davi, François Lefevre, Christophe Hurson, Joseph Garrigue, Jean-André Magdalou, Elodie Magnanou and Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio https://doi.org/10.1101/645747The complexity of predicting mortality in treesRecommended by Lucía DeSoto based on reviews by Lisa Hülsmann and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the main issues of forest ecosystems is rising tree mortality as a result of extreme weather events (Franklin et al., 1987). Eventually, tree mortality reduces forest biomass (Allen et al., 2010), although its effect on forest ecosystem fluxes seems not lasting too long (Anderegg et al., 2016). This controversy about the negative consequences of tree mortality is joined to the debate about the drivers triggering and the mechanisms accelerating tree decline. For instance, there is still room for discussion about carbon starvation or hydraulic failure determining the decay processes (Sevanto et al., 2014) or about the importance of mortality sources (Reichstein et al., 2013). Therefore, understanding and predicting tree mortality has become one of the challenges for forest ecologists in the last decade, doubling the rate of articles published on the topic (*). Although predicting the responses of ecosystems to environmental change based on the traits of species may seem a simplistic conception of ecosystem functioning (Sutherland et al., 2013), identifying those traits that are involved in the proneness of a tree to die would help to predict how forests will respond to climate threatens. (*) Number (and percentage) of articles found in Web of Sciences after searching (December the 10th, 2020) “tree mortality”: from 163 (0.006%) in 2010 to 412 (0.013%) in 2020. References Allen et al. (2010). A global overview of drought and heat-induced tree mortality reveals emerging climate change risks for forests. Forest ecology and management, 259(4), 660-684. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2009.09.001 | Comparing statistical and mechanistic models to identify the drivers of mortality within a rear-edge beech population | Cathleen Petit-Cailleux, Hendrik Davi, François Lefevre, Christophe Hurson, Joseph Garrigue, Jean-André Magdalou, Elodie Magnanou and Sylvie Oddou-Muratorio | <p>Since several studies have been reporting an increase in the decline of forests, a major issue in ecology is to better understand and predict tree mortality. The interactions between the different factors and the physiological processes giving ... |  | Climate change, Physiology, Population ecology | Lucía DeSoto | 2019-05-24 11:37:38 | View | |
17 Mar 2021

Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslandsCatherine Picon-Cochard, Nathalie Vassal, Raphaël Martin, Damien Herfurth, Priscilla Note, Frédérique Louault https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.23.263137Resolving herbivore influences under climate variabilityRecommended by Jennifer Krumins based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersWe know that herbivory can have profound influences on plant communities with respect to their distribution and productivity (recently reviewed by Jia et al. 2018). However, the degree to which these effects are realized belowground in the rhizosphere is far less understood. Indeed, many independent studies and synthesis find that the environmental context can be more important than the direct effects of herbivore activity and its removal of plant biomass (Andriuzzi and Wall 2017, Schrama et al. 2013). In spite of dedicated attention, generalizable conclusions remain a bit elusive (Sitters and Venterink 2015). Picon-Cochard and colleagues (2021) help address this research conundrum in an elegant analysis that demonstrates the interaction between long-term cattle grazing and climatic variability on primary production aboveground and belowground. Over the course of two years, Picon-Cochard et al. (2021) measured above and belowground net primary productivity in French grasslands that had been subject to ten years of managed cattle grazing. When they compared these data with climatic trends, they find an interesting interaction among grazing intensity and climatic factors influencing plant growth. In short, and as expected, plants allocate more resources to root growth in dry years and more to above ground biomass in wet and cooler years. However, this study reveals the degree to which this is affected by cattle grazing. Grazed grasslands support warmer and dryer soils creating feedback that further and significantly promotes root growth over green biomass production. The implications of this work to understanding the capacity of grassland soils to store carbon is profound. This study addresses one brief moment in time of the long trajectory of this grazed ecosystem. The legacy of grazing does not appear to influence soil ecosystem functioning with respect to root growth except within the environmental context, in this case, climate. This supports the notion that long-term research in animal husbandry and grazing effects on landscapes is deeded. It is my hope that this study is one of many that can be used to synthesize many different data sets and build a deeper understanding of the long-term effects of grazing and herd management within the context of a changing climate. Herbivory has a profound influence upon ecosystem health and the distribution of plant communities (Speed and Austrheim 2017), global carbon storage (Chen and Frank 2020) and nutrient cycling (Sitters et al. 2020). The analysis and results presented by Picon-Cochard (2021) help to resolve the mechanisms that underly these complex effects and ultimately make projections for the future. References Andriuzzi WS, Wall DH. 2017. Responses of belowground communities to large aboveground herbivores: Meta‐analysis reveals biome‐dependent patterns and critical research gaps. Global Change Biology 23:3857-3868. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13675 Chen J, Frank DA. 2020. Herbivores stimulate respiration from labile and recalcitrant soil carbon pools in grasslands of Yellowstone National Park. Land Degradation & Development 31:2620-2634. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3656 Jia S, Wang X, Yuan Z, Lin F, Ye J, Hao Z, Luskin MS. 2018. Global signal of top-down control of terrestrial plant communities by herbivores. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115:6237-6242. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1707984115 Picon-Cochard C, Vassal N, Martin R, Herfurth D, Note P, Louault F. 2021. Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslands. bioRxiv, 2020.08.23.263137, version 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.23.263137 Schrama M, Veen GC, Bakker EL, Ruifrok JL, Bakker JP, Olff H. 2013. An integrated perspective to explain nitrogen mineralization in grazed ecosystems. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 15:32-44. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2012.12.001 Sitters J, Venterink HO. 2015. The need for a novel integrative theory on feedbacks between herbivores, plants and soil nutrient cycling. Plant and Soil 396:421-426. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2679-y Sitters J, Wubs EJ, Bakker ES, Crowther TW, Adler PB, Bagchi S, Bakker JD, Biederman L, Borer ET, Cleland EE. 2020. Nutrient availability controls the impact of mammalian herbivores on soil carbon and nitrogen pools in grasslands. Global Change Biology 26:2060-2071. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15023 Speed JD, Austrheim G. 2017. The importance of herbivore density and management as determinants of the distribution of rare plant species. Biological Conservation 205:77-84. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.11.030 | Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslands | Catherine Picon-Cochard, Nathalie Vassal, Raphaël Martin, Damien Herfurth, Priscilla Note, Frédérique Louault | <p>Background and Aims: Understanding how direct and indirect changes in climatic conditions, management, and species composition affect root production and root traits is of prime importance for the delivery of carbon sequestration services of gr... |  | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Botany, Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning | Jennifer Krumins | 2020-08-30 19:27:30 | View | |
26 May 2021

Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunitiesCamille Saade, Sonia Kéfi, Claire Gougat-Barbera, Benjamin Rosenbaum, and Emanuel A. Fronhofer https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.409524Unity makes strength: clustered extinctions have stronger, longer-lasting effects on metacommunities dynamicsRecommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker and Frederik De LaenderIn this article, Saade et al. (2021) investigate how the rate of local extinctions and their spatial distribution affect recolonization dynamics in metacommunities. They use an elegant combination of microcosm experiments with metacommunities of freshwater ciliates and mathematical modelling mirroring their experimental system. Their main findings are (i) that local patch extinctions increase both local (α-) and inter-patch (β-) diversity in a transient way during the recolonization process, (ii) that these effects depend more on the spatial distribution of extinctions (dispersed or clustered) than on their amount, and (iii) that they may spread regionally. A major strength of this study is that it highlights the importance of considering the spatial structure explicitly. Recent work on ecological networks has shown repeatedly that network structure affects the propagation of pathogens (Badham and Stocker 2010), invaders (Morel-Journel et al. 2019), or perturbation events (Gilarranz et al. 2017). Here, the spatial structure of the metacommunity is a regular grid of patches, but the distribution of extinction events may be either regularly dispersed (i.e., extinct patches are distributed evenly over the grid and are all surrounded by non-extinct patches only) or clustered (all extinct patches are neighbours). This has a direct effect on the neighbourhood of perturbed patches, and because perturbations have mostly local effects, their recovery dynamics are dominated by the composition of this immediate neighbourhood. In landscapes with dispersed extinctions, the neighbourhood of a perturbed patch is not affected by the amount of extinctions, and neither is its recovery time. In contrast, in landscapes with clustered extinctions, the amount of extinctions affects the depth of the perturbed area, which takes longer to recover when it is larger. Interestingly, the spatial distribution of extinctions here is functionally equivalent to differences in connectivity between perturbed and unperturbed patches, which results in contrasted “rescue recovery” and “mixing recovery” regimes as described by Zelnick et al. (2019).
Levins R (1969) Some Demographic and Genetic Consequences of Environmental Heterogeneity for Biological Control1. Bulletin of the Entomological Society of America, 15, 237–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/besa/15.3.237 Ruokolainen L (2013) Spatio-Temporal Environmental Correlation and Population Variability in Simple Metacommunities. PLOS ONE, 8, e72325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072325 Saade C, Kefi S, Gougat-Barbera C, Rosenbaum B, Fronhofer EA (2021) Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities. bioRxiv, 2020.12.03.409524, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.409524 | Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities | Camille Saade, Sonia Kéfi, Claire Gougat-Barbera, Benjamin Rosenbaum, and Emanuel A. Fronhofer | <p style="text-align: justify;">Human activities lead more and more to the disturbance of plant and animal communities with local extinctions as a consequence. While these negative effects are clearly visible at a local scale, it is less clear how... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Colonization, Community ecology, Competition, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Landscape ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Elodie Vercken | 2020-12-08 15:55:20 | View | |
10 Jan 2024
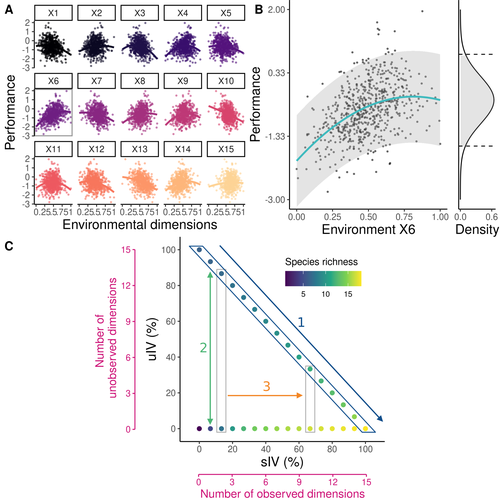
Beyond variance: simple random distributions are not a good proxy for intraspecific variability in systems with environmental structureCamille Girard-Tercieux, Ghislain Vieilledent, Adam Clark, James S. Clark, Benoit Courbaud, Claire Fortunel, Georges Kunstler, Raphaël Pélissier, Nadja Rüger, Isabelle Maréchaux https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.06.503032Two paradigms for intraspecific variabilityRecommended by Matthieu Barbier based on reviews by Simon Blanchet and Bart Haegeman based on reviews by Simon Blanchet and Bart Haegeman
Community ecology usually concerns itself with understanding the causes and consequences of diversity at a given taxonomic resolution, most classically at the species level. Yet there is no doubt that diversity exists at all scales, and phenotypic variability within a taxon can be comparable to differences between taxa, as observed from bacteria to fish and trees. The question that motivates an active and growing body of work (e.g. Raffard et al 2019) is not so much whether intraspecific variability matters, but what we get wrong by ignoring it and how to incorporate it into our understanding of communities. There is no established way to think about diversity at multiple nested taxonomic levels, and it is tempting to summarize intraspecific variability simply by measuring species mean and variance in any trait and metric. In this study, Girard-Tercieux et al (2023a) propose that, to understand its impact on community-level outcomes and in particular on species coexistence, we should carefully distinguish between two ways of thinking about intraspecific variability: -"unstructured" variation, where every individual's features are like an independent random draw from a species-specific distribution, for instance, due to genetic lottery and developmental accidents -"structured" variation that is due to each individual encountering a different but enduring microenvironment. The latter type of variability may still appear complex and random-like when the environment is high-dimensional (i.e. multifaceted, with many different factors contributing to each individual's performance and development). Thus, it is not necessarily "structured" in the sense of being easily understood -- we may need to measure more aspects of the environment than is practical if we want to fully predict these variations. What distinguishes this "structured" variability is that it is, in a loose sense, inheritable: individuals from the same species that grow in the same microenvironment will have the same performance, in a repeatable fashion. Thus, if each species is best at exploiting at least a fraction of environmental conditions, it is likely to avoid extinction by competition, except in the unlucky case of no propagule reaching any of the favorable sites. The core intuition, that the complex spatial structure and high-dimensional nature of the environment plays a key explanatory role in species coexistence, is a running thread through several of the authors' work (e.g. Clark et al 2010), clearly inspired by their focus on tropical forests. This study, by tackling the question of intraspecific determinants of interspecific outcomes, makes a compelling addition to this line of investigation, coming as a theoretical companion to a more data-oriented study (Girard-Tercieux et al 2023b). But I believe it raises a question that is even broader in scope. This kind of intraspecific variability, due to different individuals growing in different microenvironments, is perhaps most relevant for trees and other sessile organisms, but the distinction made here between "unstructured" and "structured" variability can likely be extended to many other ecological settings. In my understanding, what matters most in "structured" variability is not so much it stemming from a fixed environment, but rather it being maintained across generations, rather than possibly lost by drift. This difference between variability in the form of "frozen" randomness and in the form of stochastic drift over time is highly relevant in other theoretical fields (e.g. in physics, where it is the difference between a disordered solid and a liquid), and thus, I expect that it is a meaningful distinction to make throughout community ecology. References James S. Clark, David Bell, Chengjin Chu, Benoit Courbaud, Michael Dietze, Michelle Hersh, Janneke HilleRisLambers et al. (2010) "High‐dimensional coexistence based on individual variation: a synthesis of evidence." Ecological Monographs 80, no. 4 : 569-608. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1541.1 Camille Girard-Tercieux, Ghislain Vieilledent, Adam Clark, James S. Clark, Benoît Courbaud, Claire Fortunel, Georges Kunstler, Raphaël Pélissier, Nadja Rüger, Isabelle Maréchaux (2023a) "Beyond variance: simple random distributions are not a good proxy for intraspecific variability in systems with environmental structure." bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.06.503032 Camille Girard‐Tercieux, Isabelle Maréchaux, Adam T. Clark, James S. Clark, Benoît Courbaud, Claire Fortunel, Joannès Guillemot et al. (2023b) "Rethinking the nature of intraspecific variability and its consequences on species coexistence." Ecology and Evolution 13, no. 3 : e9860. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.9860 Allan Raffard, Frédéric Santoul, Julien Cucherousset, and Simon Blanchet. (2019) "The community and ecosystem consequences of intraspecific diversity: A meta‐analysis." Biological Reviews 94, no. 2: 648-661. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12472 | Beyond variance: simple random distributions are not a good proxy for intraspecific variability in systems with environmental structure | Camille Girard-Tercieux, Ghislain Vieilledent, Adam Clark, James S. Clark, Benoit Courbaud, Claire Fortunel, Georges Kunstler, Raphaël Pélissier, Nadja Rüger, Isabelle Maréchaux | <p>The role of intraspecific variability (IV) in shaping community dynamics and species coexistence has been intensively discussed over the past decade and modelling studies have played an important role in that respect. However, these studies oft... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Community ecology, Competition, Theoretical ecology | Matthieu Barbier | 2022-08-07 12:51:30 | View | |
25 May 2021
Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assemblyCaio Graco-Roza, Angel M. Segura, Carla Kruk, Patricia Domingos, Janne Soininen, Marcelo M. Marinho https://doi.org/10.1101/869966Environmental heterogeneity drives phytoplankton community assembly patterns in a tropical riverine systemRecommended by Cédric Hubas and Eric Goberville and Eric Goberville based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique Lamy based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique Lamy
What predisposes two individuals to form and maintain a relationship is a fundamental question. Using facial recognition to see whether couples' faces change over time to become more and more similar, psychology researchers have concluded that couples tend to be formed from the start between people whose faces are more similar than average [1]. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together. And what about in nature? Are these rules of assembly valid for communities of different species? In his seminal contribution, Robert MacArthur (1984) wrote ‘To do science is to search for repeated patterns’ [2]. Identifying the mechanisms that govern the arrangement of life is a hot research topic in the field of ecology for decades, and an absolutely essential prerequisite to answer the outstanding question of what shape ecological patterns in multi-species communities such as species-area relationships, relative species abundances, or spatial and temporal turnover of community composition; amid others [3]. To explain ecological patterns in nature, some rely on the concept that every species - through evolutionary processes and the acquisition of a unique set of traits that allow a species to be adapted to its abiotic and biotic environment - occupies a unique niche: Species coexistence comes as the result of niche differentiation [4,5]. Such a view has been challenged by the recognition of the key role of neutral processes [6], however, in which demographic stochasticity contributes to shape multi-species communities and to explain why congener species coexist much more frequently than expected by chance [7,8]. While the niche-based and neutral theories appear seemingly opposed at first sight [9], the dichotomy may be more philosophical than empirical [4,5]. Many examples have come to support that both concepts are not incompatible as they together influence the structure, diversity and functioning of communities [10], and are simply extreme cases of a continuum [11]. From this perspective, extrinsic factors, i.e., environmental heterogeneity, may influence the location of a given community along the niche-neutrality continuum. The walk of species in nature is therefore neither random nor ecologically predestined. In microbial assemblages, the co-existence of these two antagonistic mechanisms has been shown both theoretically and empirically. It has been shown that a combination of stabilising (niche) and equalising (neutral) mechanisms was responsible for the existence of groups of coexistent species (clumps) in a phytoplankton rich community [12]. Analysing interannual changes (2003-2009) in the weekly abundance of diatoms and dinoflagellates located in a temperate coastal ecosystem of the Western English Channel, Mutshinda et al. [13] found a mixture of biomass dynamics consistent with the neutrality-niche continuum hypothesis. While niche processes explained the dynamic of phytoplankton functional groups (i.e., diatoms vs. dinoflagellates) in terms of biomass, neutral processes mainly dominated - 50 to 75% of the time - the dynamics at the species level within functional groups [13]. From one endpoint to another, defining the location of a community along the continuum is all matter of scale [4,11]. In their study, testing predictions made by an emergent neutrality model, Graco-Roza et al. [14] provide empirical evidence that neutral and niche processes joined together to shape and drive planktonic communities in a riverine ecosystem. Body size - the 'master trait' - is used here as a discriminant ecological dimension along the niche axis. From their analysis, they not only show that the specific abundance is organised in clumps and gaps along the niche axis, but also reveal that different clumps exist along the river course. They identify two main clumps in body size - with species belonging to three different morphologically-based functional groups - and characterise that among-species differences in biovolume are driven by functional redundancy at the clump level; species functional distinctiveness being related to the relative biovolume of species. By grouping their variables according to seasons (cold-dry vs. warm-wet) or river elevation profile (upper, medium and lower course), they hereby highlight how environmental heterogeneity contributes to shape species assemblages and their dynamics and conclude that emergent neutrality models are a powerful approach to explain species coexistence; and therefore ecological patterns. References [1] Tea-makorn PP, Kosinski M (2020) Spouses’ faces are similar but do not become more similar with time. Scientific Reports, 10, 17001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73971-8. [2] MacArthur RH (1984) Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species. Princeton University Press. [3] Vellend M (2020) The Theory of Ecological Communities (MPB-57). Princeton University Press. [4] Wennekes PL, Rosindell J, Etienne RS (2012) The Neutral—Niche Debate: A Philosophical Perspective. Acta Biotheoretica, 60, 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-012-9144-6. [5] Gravel D, Guichard F, Hochberg ME (2011) Species coexistence in a variable world. Ecology Letters, 14, 828–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01643.x. [6] Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press. [7] Leibold MA, McPeek MA (2006) Coexistence of the Niche and Neutral Perspectives in Community Ecology. Ecology, 87, 1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1399:COTNAN]2.0.CO;2. [8] Pielou EC (1977) The Latitudinal Spans of Seaweed Species and Their Patterns of Overlap. Journal of Biogeography, 4, 299–311. https://doi.org/10.2307/3038189. [9] Holt RD (2006) Emergent neutrality. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 531–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.08.003. [10] Scheffer M, Nes EH van (2006) Self-organized similarity, the evolutionary emergence of groups of similar species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103, 6230–6235. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508024103. [11] Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 9, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x. [12] Vergnon R, Dulvy NK, Freckleton RP (2009) Niches versus neutrality: uncovering the drivers of diversity in a species-rich community. Ecology Letters, 12, 1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01364.x. [13] Mutshinda CM, Finkel ZV, Widdicombe CE, Irwin AJ (2016) Ecological equivalence of species within phytoplankton functional groups. Functional Ecology, 30, 1714–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12641. [14] Graco-Roza C, Segura AM, Kruk C, Domingos P, Soininen J, Marinho MM (2021) Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly. bioRxiv, 869966, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/869966
| Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly | Caio Graco-Roza, Angel M. Segura, Carla Kruk, Patricia Domingos, Janne Soininen, Marcelo M. Marinho | <p style="text-align: justify;">Emergent neutrality (EN) suggests that species must be sufficiently similar or sufficiently different in their niches to avoid interspecific competition. Such a scenario results in a transient pattern with clumps an... |  | Coexistence, Community ecology, Theoretical ecology | Cédric Hubas | 2020-01-23 16:11:32 | View | |
30 Mar 2021
Do the more flexible individuals rely more on causal cognition? Observation versus intervention in causal inference in great-tailed gracklesBlaisdell A, Seitz B, Rowney C, Folsom M, MacPherson M, Deffner D, Logan CJ https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/z4p6sFrom cognition to range dynamics – and from preregistration to peer-reviewed preprintRecommended by Emanuel A. Fronhofer based on reviews by Laure Cauchard and 1 anonymous reviewerIn 2018 Blaisdell and colleagues set out to study how causal cognition may impact large scale macroecological patterns, more specifically range dynamics, in the great-tailed grackle (Fronhofer 2019). This line of research is at the forefront of current thought in macroecology, a field that has started to recognize the importance of animal behaviour more generally (see e.g. Keith and Bull (2017)). Importantly, the authors were pioneering the use of preregistrations in ecology and evolution with the aim of improving the quality of academic research. Now, nearly 3 years later, it is thanks to their endeavour of making research better that we learn that the authors are “[...] unable to speculate about the potential role of causal cognition in a species that is rapidly expanding its geographic range.” (Blaisdell et al. 2021; page 2). Is this a success or a failure? Every reader will have to find an answer to this question individually and there will certainly be variation in these answers as becomes clear from the referees’ comments. In my opinion, this is a success story of a more stringent and transparent approach to doing research which will help us move forward, both methodologically and conceptually. References Fronhofer (2019) From cognition to range dynamics: advancing our understanding of macroe- Keith, S. A. and Bull, J. W. (2017) Animal culture impacts species' capacity to realise climate-driven range shifts. Ecography, 40: 296-304. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.02481 Blaisdell, A., Seitz, B., Rowney, C., Folsom, M., MacPherson, M., Deffner, D., and Logan, C. J. (2021) Do the more flexible individuals rely more on causal cognition? Observation versus intervention in causal inference in great-tailed grackles. PsyArXiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. doi: https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/z4p6s | Do the more flexible individuals rely more on causal cognition? Observation versus intervention in causal inference in great-tailed grackles | Blaisdell A, Seitz B, Rowney C, Folsom M, MacPherson M, Deffner D, Logan CJ | <p>Behavioral flexibility, the ability to change behavior when circumstances change based on learning from previous experience, is thought to play an important role in a species’ ability to successfully adapt to new environments and expand its geo... | Preregistrations | Emanuel A. Fronhofer | 2020-11-27 09:49:55 | View | ||
27 Apr 2021

Joint species distributions reveal the combined effects of host plants, abiotic factors and species competition as drivers of species abundances in fruit fliesBenoit Facon, Abir Hafsi, Maud Charlery de la Masselière, Stéphane Robin, François Massol, Maxime Dubart, Julien Chiquet, Enric Frago, Frédéric Chiroleu, Pierre-François Duyck & Virginie Ravigné https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.07.414326Understanding the interplay between host-specificity, environmental conditions and competition through the sound application of Joint Species Distribution ModelsRecommended by Joaquín Hortal based on reviews by Joaquín Calatayud and Carsten DormannUnderstanding why and how species coexist in local communities is one of the central questions in ecology. There is general agreement that species distribution and coexistence are determined by a number of key mechanisms, including the environmental requirements of species, dispersal, evolutionary constraints, resource availability and selection, metapopulation dynamics, and biotic interactions (e.g. Soberón & Nakamura 2009; Colwell & Rangel 2009; Ricklefs 2015). These factors are however intricately intertwined in a scale-structured fashion (Hortal et al. 2010; D’Amen et al. 2017), making it particularly difficult to tease apart the effects of each one of them. This could be addressed by the novel field of Joint Species Distribution Modelling (JSDM; Okasvainen & Abrego 2020), as it allows assessing the effects of several sets of factors and the co-occurrence and/or covariation in abundances of potentially interacting species at the same time (Pollock et al. 2014; Ovaskainen et al. 2016; Dormann et al. 2018). However, the development of JSDM has been hampered by the general lack of good-quality detailed data on species co-occurrences and abundances (see Hortal et al. 2015). Facon et al. (2021) use a particularly large compilation of field surveys to study the abundance and co-occurrence of Tephritidae fruit flies in c. 400 orchards, gardens and natural areas throughout the island of Réunion. Further, they combine such information with lab data on their host-selection fundamental niche (i.e. in the absence of competitors), codifying traits of female choice and larval performances in 21 host species. They use Poisson Log-Normal models, a type of mixed model that allows one to jointly model the random effects associated with all species, and retrieve the covariations in abundance that are not explained by environmental conditions or differences in sampling effort. Then, they use a series of models to evaluate the effects on these matrices of ecological covariates (date, elevation, habitat, climate and host plant), species interactions (by comparing with a constrained residual variance-covariance matrix) and the species’ host-selection fundamental niches (through separate models for each fly species). The eight Tephritidae species inhabiting Réunion include both generalists and specialists in Solanaceae and Cucurbitaceae with a known history of interspecific competition. Facon et al. (2021) use a comprehensive JSDM approach to assess the effects of different factors separately and altogether. This allows them to identify large effects of plant hosts and the fundamental host-selection niche on species co-occurrence, but also to show that ecological covariates and weak –though not negligible– species interactions are necessary to account for all residual variance in the matrix of joint species abundances per site. Further, they also find evidence that the fitness per host measured in the lab has a strong influence on the abundances in each host plant in the field for specialist species, but not for generalists. Indeed, the stronger effects of competitive exclusion were found in pairs of Cucurbitaceae specialist species. However, these analyses fail to provide solid grounds to assess why generalists are rarely found in Cucurbitaceae and Solanaceae. Although they argue that this may be due to Connell’s (1980) ghost of competition past (past competition that led to current niche differentiation), further data on the evolutionary history of these fruit flies is needed to assess this hypothesis. Finding evidence for the effects of competitive interactions on species’ occurrences and spatial distributions is often difficult, perhaps because these effects occur over longer time scales than the ones usually studied by ecologists (Yackulic 2017). The work by Facon and colleagues shows that weak effects of competition can be detected also at the short ecological timescales that determine coexistence in local communities, under the virtuous combination of good-quality data and sound analytical designs that account for several aspects of species’ niches, their biotopes and their joint population responses. This adds a new dimension to the application of Hutchinson’s (1978) niche framework to understand the spatial dynamics of species and communities (see also Colwell & Rangel 2009), although further advances to incorporate dispersal-driven metacommunity dynamics (see, e.g., Ovaskainen et al. 2016; Leibold et al. 2017) are certainly needed. Nonetheless, this work shows the potential value of in-depth analyses of species coexistence based on combining good-quality field data with well-thought out JSDM applications. If many studies like this are conducted, it is likely that the uprising field of Joint Species Distribution Modelling will improve our understanding of the hierarchical relationships between the different factors affecting species coexistence in ecological communities in the near future.
References Colwell RK, Rangel TF (2009) Hutchinson’s duality: The once and future niche. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 19651–19658. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901650106 Connell JH (1980) Diversity and the Coevolution of Competitors, or the Ghost of Competition Past. Oikos, 35, 131–138. https://doi.org/10.2307/3544421 D’Amen M, Rahbek C, Zimmermann NE, Guisan A (2017) Spatial predictions at the community level: from current approaches to future frameworks. Biological Reviews, 92, 169–187. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12222 Dormann CF, Bobrowski M, Dehling DM, Harris DJ, Hartig F, Lischke H, Moretti MD, Pagel J, Pinkert S, Schleuning M, Schmidt SI, Sheppard CS, Steinbauer MJ, Zeuss D, Kraan C (2018) Biotic interactions in species distribution modelling: 10 questions to guide interpretation and avoid false conclusions. Global Ecology and Biogeography, 27, 1004–1016. https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12759 Facon B, Hafsi A, Masselière MC de la, Robin S, Massol F, Dubart M, Chiquet J, Frago E, Chiroleu F, Duyck P-F, Ravigné V (2021) Joint species distributions reveal the combined effects of host plants, abiotic factors and species competition as drivers of community structure in fruit flies. bioRxiv, 2020.12.07.414326. ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.07.414326 Hortal J, de Bello F, Diniz-Filho JAF, Lewinsohn TM, Lobo JM, Ladle RJ (2015) Seven Shortfalls that Beset Large-Scale Knowledge of Biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 46, 523–549. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-112414-054400 Hortal J, Roura‐Pascual N, Sanders NJ, Rahbek C (2010) Understanding (insect) species distributions across spatial scales. Ecography, 33, 51–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0587.2009.06428.x Hutchinson, G.E. (1978) An introduction to population biology. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT. Leibold MA, Chase JM, Ernest SKM (2017) Community assembly and the functioning of ecosystems: how metacommunity processes alter ecosystems attributes. Ecology, 98, 909–919. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.1697 Ovaskainen O, Abrego N (2020) Joint Species Distribution Modelling: With Applications in R. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108591720 Ovaskainen O, Roy DB, Fox R, Anderson BJ (2016) Uncovering hidden spatial structure in species communities with spatially explicit joint species distribution models. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 428–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12502 Pollock LJ, Tingley R, Morris WK, Golding N, O’Hara RB, Parris KM, Vesk PA, McCarthy MA (2014) Understanding co-occurrence by modelling species simultaneously with a Joint Species Distribution Model (JSDM). Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 397–406. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12180 Ricklefs RE (2015) Intrinsic dynamics of the regional community. Ecology Letters, 18, 497–503. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12431 Soberón J, Nakamura M (2009) Niches and distributional areas: Concepts, methods, and assumptions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 19644–19650. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0901637106 Yackulic CB (2017) Competitive exclusion over broad spatial extents is a slow process: evidence and implications for species distribution modeling. Ecography, 40, 305–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.02836 | Joint species distributions reveal the combined effects of host plants, abiotic factors and species competition as drivers of species abundances in fruit flies | Benoit Facon, Abir Hafsi, Maud Charlery de la Masselière, Stéphane Robin, François Massol, Maxime Dubart, Julien Chiquet, Enric Frago, Frédéric Chiroleu, Pierre-François Duyck & Virginie Ravigné | <p style="text-align: justify;">The relative importance of ecological factors and species interactions for phytophagous insect species distributions has long been a controversial issue. Using field abundances of eight sympatric Tephritid fruit fli... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Community ecology, Competition, Herbivory, Interaction networks, Species distributions | Joaquín Hortal | Carsten Dormann, Joaquín Calatayud | 2020-12-08 06:44:25 | View |
01 Feb 2020

Touchy matter: the delicate balance between Morgan’s canon and open-minded description of advanced cognitive skills in the animalRecommended by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor
In a recent paper published in PNAS, Fayet et al. [1] reported scarce field observations of two Atlantic puffins (four years apart) apparently scratching their bodies using sticks, which was interpreted by the authors as evidence of tool use in this species. In a short response, Benjamin Farrar [2] raises serious concerns about this interpretation and proposes simpler, more parsimonious, mechanisms explaining the observed behaviour: a textbook case of Morgan's canon. References [1] Fayet, A. L., Hansen, E. S., and Biro, D. (2020). Evidence of tool use in a seabird. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(3), 1277–1279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918060117 | Evidence of tool use in a seabird? | Benjamin G. Farrar | Fayet, Hansen and Biro (1) provide two observations of Atlantic puffins, *Fratercula arctica*, performing self-directed actions while holding a stick in their beaks. The authors interpret this as evidence of tool use as they suggest that the stick... |  | Behaviour & Ethology | Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont | 2020-01-22 11:55:27 | View | |
22 Mar 2021

Host-mediated, cross-generational intraspecific competition in a herbivore speciesBastien Castagneyrol, Inge van Halder, Yasmine Kadiri, Laura Schillé, Hervé Jactel https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.30.228544Plants preserve the ghost of competition past for herbivores, but mothers don’t careRecommended by Sara Magalhães based on reviews by Inês Fragata and Raul Costa-PereiraSome biological hypotheses are widely popular, so much so that we tend to forget their original lack of success. This is particularly true for hypotheses with catchy names. The ‘Ghost of competition past’ is part of the title of a paper by the great ecologist, JH Connell, one of the many losses of 2020 (Connell 1980). The hypothesis states that, even though we may not detect competition in current populations, their traits and distributions may be shaped by past competition events. Although this hypothesis has known a great success in the ecological literature, the original paper actually ends with “I will no longer be persuaded by such invoking of "the Ghost of Competition Past"”. Similarly, the hypothesis that mothers of herbivores choose host plants where their offspring will have a higher fitness was proposed by John Jaenike in 1978 (Jaenike 1978), and later coined the ‘mother knows best’ hypothesis. The hypothesis was readily questioned or dismissed: “Mother doesn't know best” (Courtney and Kibota 1990), or “Does mother know best?” (Valladares and Lawton 1991), but remains widely popular. It thus seems that catchy names (and the intuitive ideas behind them) have a heuristic value that is independent from the original persuasion in these ideas and the accumulation of evidence that followed it. The paper by Castagneryol et al. (2021) analyses the preference-performance relationship in the box tree moth (BTM) Cydalima perspectalis, after defoliation of their host plant, the box tree, by conspecifics. It thus has bearings on the two previously mentioned hypotheses. Specifically, they created an artificial population of potted box trees in a greenhouse, in which 60 trees were infested with BTM third instar larvae, whereas 61 were left uninfested. One week later, these larvae were removed and another three weeks later, they released adult BTM females and recorded their host choice by counting egg clutches laid by these females on the plants. Finally, they evaluated the effect of previously infested vs uninfested plants on BTM performance by measuring the weight of third instar larvae that had emerged from those eggs. This experimental design was adopted because BTM is a multivoltine species. When the second generation of BTM arrives, plants have been defoliated by the first generation and did not fully recover. Indeed, Castagneryol et al. (2021) found that larvae that developed on previously infested plants were much smaller than those developing on uninfested plants, and the same was true for the chrysalis that emerged from those larvae. This provides unequivocal evidence for the existence of a ghost of competition past in this system. However, the existence of this ghost still does not result in a change in the distribution of BTM, precisely because mothers do not know best: they lay as many eggs on plants previously infested than on uninfested plants. The demonstration that the previous presence of a competitor affects the performance of this herbivore species confirms that ghosts exist. However, whether this entails that previous (interspecific) competition shapes species distributions, as originally meant, remains an open question. Species phenology may play an important role in exposing organisms to the ghost, as this time-lagged competition may have been often overlooked. It is also relevant to try to understand why mothers don’t care in this, and other systems. One possibility is that they will have few opportunities to effectively choose in the real world, due to limited dispersal or to all plants being previously infested. References Castagneyrol, B., Halder, I. van, Kadiri, Y., Schillé, L. and Jactel, H. (2021) Host-mediated, cross-generational intraspecific competition in a herbivore species. bioRxiv, 2020.07.30.228544, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.30.228544 Connell, J. H. (1980). Diversity and the coevolution of competitors, or the ghost of competition past. Oikos, 131-138. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/3544421 Courtney, S. P. and Kibota, T. T. (1990) in Insect-plant interactions (ed. Bernays, E.A.) 285-330. Jaenike, J. (1978). On optimal oviposition behavior in phytophagous insects. Theoretical population biology, 14(3), 350-356. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-5809(78)90012-6 Valladares, G., and Lawton, J. H. (1991). Host-plant selection in the holly leaf-miner: does mother know best?. The Journal of Animal Ecology, 227-240. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/5456
| Host-mediated, cross-generational intraspecific competition in a herbivore species | Bastien Castagneyrol, Inge van Halder, Yasmine Kadiri, Laura Schillé, Hervé Jactel | <p>Conspecific insect herbivores co-occurring on the same host plant interact both directly through interference competition and indirectly through exploitative competition, plant-mediated interactions and enemy-mediated interactions. However, the... |  | Competition, Herbivory, Zoology | Sara Magalhães | 2020-08-03 15:50:23 | View | |
15 Jul 2023
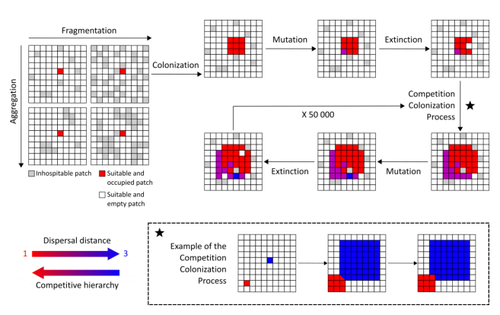
Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulationsBasile Finand, Thibaud Monnin, Nicolas Loeuille https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.08.495260The spatial dynamics of habitat fragmentation drives the evolution of dispersal and metapopulation persistenceRecommended by Frédéric Guichard based on reviews by Eva Kisdi, David Murray-Stoker, Shripad Tuljapurkar and 1 anonymous reviewerThe persistence of populations facing the destruction of their habitat is a multifaceted question that has mobilized theoreticians and empiricists alike for decades. As an ecological question, persistence has been studied as the spatial rescue of populations via dispersal into remaining suitable habitats. The spatial aggregation of habitat destruction has been a key component of these studies, and it has been applied to the problem of coexistence by integrating competition-colonization tradeoffs. There is a rich ecological literature on this topic, both from theoretical and field studies (Fahrig 2003). The relationship between life-history strategies of species and their resilience to spatially structured habitat fragmentation is also an important component of conservation strategies through the management of land use, networks of protected areas, and the creation of corridors. In the context of environmental change, the ability of species to adapt to changes in landscape configuration and availability can be treated as an eco-evolutionary process by considering the possibility of evolutionary rescue (Heino and Hanski 2001; Bell 2017). However, eco-evolutionary dynamics considering spatially structured changes in landscapes and life-history tradeoffs remains an outstanding question. Finand et al. (2023) formulate the problem of persistence in fragmented landscapes over evolutionary time scales by studying models for the evolution of dispersal in relation to habitat fragmentation and spatial aggregation. Their simulations were conducted on a spatial grid where individuals can colonize suitable patch as a function of their competitive rank that decreases as a function of their (ii) dispersal distance trait. Simulations were run under fixed habitat fragmentation (proportion of unsuitable habitat) and aggregation, and with an explicit rate of habitat destruction to study evolutionary rescue. Their results reveal a balance between the selection for high dispersal under increasing habitat fragmentation and selection for lower dispersal in response to habitat aggregation. This balance leads to the coexistence of polymorphic dispersal strategies in highly aggregated landscapes with low fragmentation where high dispersers inhabit aggregated habitats while low dispersers are found in isolated habitats. The authors then integrate the spatial rescue mechanism to the problem of evolutionary rescue in response to temporally increasing fragmentation. There they show how rapid evolution allows for evolutionary rescue through the evolution of high dispersal. They also show the limits to this evolutionary rescue to cases where both aggregation and fragmentation are not too high. Interestingly, habitat aggregation prevents evolutionary rescue by directly affecting the evolutionary potential of dispersal. The study is based on simple scenarios that ignore the complexity of relationships between dispersal, landscape properties, and species interactions. This simplicity is the strength of the study, revealing basic mechanisms that can now be tested against other life-history tradeoffs and species interactions. Finand et al. (2023) provide a novel foundation for the study of eco-evolutionary dynamics in metacommunities exposed to spatially structured habitat destruction. They point to important assumptions that must be made along the way, including the relationships between dispersal distance and fecundity (they assume a positive relationship), and the nature of life-history tradeoffs between dispersal rate and local competitive abilities.
Bell, G. 2017. Evolutionary Rescue. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 48:605–627. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-023011 | Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulations | Basile Finand, Thibaud Monnin, Nicolas Loeuille | <p>Because it affects dispersal risk and modifies competition levels, habitat fragmentation directly constrains dispersal evolution. When dispersal is traded-off against competitive ability, increased fragmentation is often expected to select high... |  | Colonization, Competition, Dispersal & Migration, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Frédéric Guichard | 2022-06-10 13:51:15 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










