Direct submissions to PCI Ecology from bioRxiv.org are possible using the B2J service
Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * ▲ | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 Mar 2024
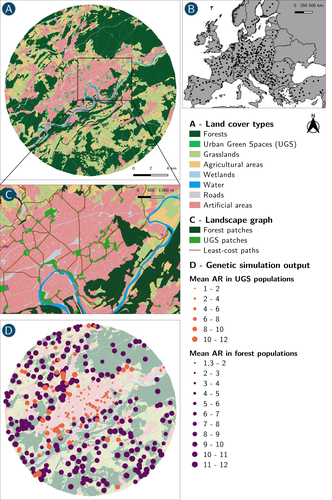
How does dispersal shape the genetic patterns of animal populations in European cities? A simulation approachPaul Savary, Cécile Tannier, Jean-Christophe Foltête, Marc Bourgeois, Gilles Vuidel, Aurélie Khimoun, Hervé Moal, Stéphane Garnier https://doi.org/10.32942/X2JS41Gene flow in the city. Unravelling the mechanisms behind the variability in urbanization effects on genetic patterns.Recommended by Aurélie Coulon based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Worldwide, city expansion is happening at a fast rate and at the same time, urbanists are more and more required to make place for biodiversity. Choices have to be made regarding the area and spatial arrangement of suitable spaces for non-human living organisms, that will favor the long-term survival of their populations. To guide those choices, it is necessary to understand the mechanisms driving the effects of land management on biodiversity. Research results on the effects of urbanization on genetic diversity have been very diverse, with studies showing higher genetic diversity in rural than in urban populations (e.g. Delaney et al. 2010), the contrary (e.g. Miles et al. 2018) or no difference (e.g. Schoville et al. 2013). The same is true for studies investigating genetic differentiation. The reasons for these differences probably lie in the relative intensities of gene flow and genetic drift in each case study, which are hard to disentangle and quantify in empirical datasets. In their paper, Savary et al. (2024) used an elegant and powerful simulation approach to better understand the diversity of observed patterns and investigate the effects of dispersal limitation on genetic patterns (diversity and differentiation). Their simulations involved the landscapes of 325 real European cities, each under three different scenarios mimicking 3 virtual urban tolerant species with different abilities to move within cities while genetic drift intensity was held constant across scenarios. The cities were chosen so that the proportion of artificial areas was held constant (20%) but their location and shape varied. This design allowed the authors to investigate the effect of connectivity and spatial configuration of habitat on the genetic responses to spatial variations in dispersal in cities. The main results of this simulation study demonstrate that variations in dispersal spatial patterns, for a given level of genetic drift, trigger variations in genetic patterns. Genetic diversity was lower and genetic differentiation was larger when species had more difficulties to move through the more hostile components of the urban environment. The increase of the relative importance of drift over gene flow when dispersal was spatially more constrained was visible through the associated disappearance of the pattern of isolation by resistance. Forest patches (usually located at the periphery of the cities) usually exhibited larger genetic diversity and were less differentiated than urban green spaces. But interestingly, the presence of habitat patches at the interface between forest and urban green spaces lowered those differences through the promotion of gene flow. One other noticeable result, from a landscape genetic method point of view, is the fact that there might be a limit to the detection of barriers to genetic clusters through clustering analyses because of the increased relative effect of genetic drift. This result needs to be confirmed, though, as genetic structure has only been investigated with a recent approach based on spatial graphs. It would be interesting to also analyze those results with the usual Bayesian genetic clustering approaches. Overall, this study addresses an important scientific question about the mechanisms explaining the diversity of observed genetic patterns in cities. But it also provides timely cues for connectivity conservation and restoration applied to cities. Delaney, K. S., Riley, S. P., and Fisher, R. N. (2010). A rapid, strong, and convergent genetic response to urban habitat fragmentation in four divergent and widespread vertebrates. PLoS ONE, 5(9):e12767. | How does dispersal shape the genetic patterns of animal populations in European cities? A simulation approach | Paul Savary, Cécile Tannier, Jean-Christophe Foltête, Marc Bourgeois, Gilles Vuidel, Aurélie Khimoun, Hervé Moal, Stéphane Garnier | <p><em>Context and objectives</em></p> <p>Although urbanization is a major driver of biodiversity erosion, it does not affect all species equally. The neutral genetic structure of populations in a given species is affected by both genetic drift a... |  | Biodiversity, Conservation biology, Dispersal & Migration, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Human impact, Landscape ecology, Molecular ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Terrestrial ecology | Aurélie Coulon | 2023-07-25 19:09:16 | View | |
14 Dec 2018
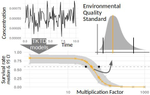
Recommendations to address uncertainties in environmental risk assessment using toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics modelsVirgile Baudrot and Sandrine Charles https://doi.org/10.1101/356469Addressing uncertainty in Environmental Risk Assessment using mechanistic toxicological models coupled with Bayesian inferenceRecommended by Luis Schiesari based on reviews by Andreas Focks and 2 anonymous reviewersEnvironmental Risk Assessment (ERA) is a strategic conceptual framework to characterize the nature and magnitude of risks, to humans and biodiversity, of the release of chemical contaminants in the environment. Several measures have been suggested to enhance the science and application of ERA, including the identification and acknowledgment of uncertainties that potentially influence the outcome of risk assessments, and the appropriate consideration of temporal scale and its linkage to assessment endpoints [1]. References [1] Dale, V. H., Biddinger, G. R., Newman, M. C., Oris, J. T., Suter, G. W., Thompson, T., ... & Chapman, P. M. (2008). Enhancing the ecological risk assessment process. Integrated environmental assessment and management, 4(3), 306-313. doi: 10.1897/IEAM_2007-066.1 | Recommendations to address uncertainties in environmental risk assessment using toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics models | Virgile Baudrot and Sandrine Charles | <p>Providing reliable environmental quality standards (EQS) is a challenging issue for environmental risk assessment (ERA). These EQS are derived from toxicity endpoints estimated from dose-response models to identify and characterize the environm... |  | Chemical ecology, Ecotoxicology, Experimental ecology, Statistical ecology | Luis Schiesari | 2018-06-27 21:33:30 | View | |
05 Apr 2019

Using a large-scale biodiversity monitoring dataset to test the effectiveness of protected areas at conserving North-American breeding birdsVictor Cazalis, Soumaya Belghali, Ana S.L. Rodrigues https://doi.org/10.1101/433037Protected Areas effects on biodiversity: a test using bird data that hopefully will give ideas for much more studies to comeRecommended by Paul Caplat based on reviews by Willson Gaul and 1 anonymous reviewerIn the face of worldwide declines in biodiversity, evaluating the effectiveness of conservation practices is an absolute necessity. Protected Areas (PA) are a key tool for conservation, and the question “Are PA effective” has been on many a research agenda, as the introduction to this preprint will no doubt convince you. A challenge we face is that, until now, few studies have been explicitly designed to evaluate PA, and despite the rise of meta-analyses on the topic, our capacity to quantify their effect on biodiversity remains limited. References [1] Cazalis, V., Belghali, S., & Rodrigues, A. S. (2019). Using a large-scale biodiversity monitoring dataset to test the effectiveness of protected areas at conserving North-American breeding birds. bioRxiv, 433037, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/433037 | Using a large-scale biodiversity monitoring dataset to test the effectiveness of protected areas at conserving North-American breeding birds | Victor Cazalis, Soumaya Belghali, Ana S.L. Rodrigues | <p>Protected areas currently cover about 15% of the global land area, and constitute one of the main tools in biodiversity conservation. Quantifying their effectiveness at protecting species from local decline or extinction involves comparing prot... |  | Biodiversity, Conservation biology, Human impact, Landscape ecology, Macroecology | Paul Caplat | 2018-10-04 08:43:34 | View | |
20 Feb 2024
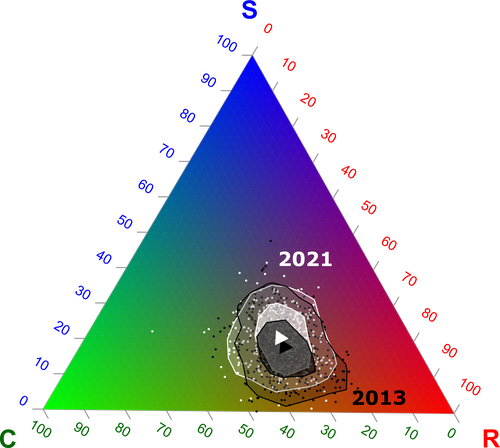
Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practicesIsis Poinas, Christine N Meynard, Guillaume Fried https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.03.530956Unravelling plant diversity in agricultural field margins in France: plant species better adapted to climate change need other agricultures to persistRecommended by Julia Astegiano based on reviews by Ignasi Bartomeus, Clelia Sirami and Diego Gurvich based on reviews by Ignasi Bartomeus, Clelia Sirami and Diego Gurvich
Agricultural field margin plants, often referred to as “spontaneous” species, are key for the stabilization of several social-ecological processes related to crop production such as pollination or pest control (Tamburini et al. 2020). Because of its beneficial function, increasing the diversity of field margin flora becomes as important as crop diversity in process-based agricultures such as agroecology. Contrary, supply-dependent intensive agricultures produce monocultures and homogenized environments that might benefit their productivity, which generally includes the control or elimination of the field margin flora (Emmerson et al. 2016, Aligner 2018). Considering that different agricultural practices are produced by (and produce) different territories (Moore 2020) and that they are also been shaped by current climate change, we urgently need to understand how agricultural intensification constrains the potential of territories to develop agriculture more resilient to such change (Altieri et al., 2015). Thus, studies unraveling how agricultural practices' effects on agricultural field margin flora interact with those of climate change is of main importance, as plant strategies better adapted to such social-ecological processes may differ. References Alignier, A., 2018. Two decades of change in a field margin vegetation metacommunity as a result of field margin structure and management practice changes. Agric., Ecosyst. & Environ., 251, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.09.013 Altieri, M.A., Nicholls, C.I., Henao, A., Lana, M.A., 2015. Agroecology and the design of climate change-resilient farming systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 869–890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-015-0285-2 Emmerson, M., Morales, M. B., Oñate, J. J., Batary, P., Berendse, F., Liira, J., Aavik, T., Guerrero, I., Bommarco, R., Eggers, S., Pärt, T., Tscharntke, T., Weisser, W., Clement, L. & Bengtsson, J. (2016). How agricultural intensification affects biodiversity and ecosystem services. In Adv. Ecol. Res. 55, 43-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aecr.2016.08.005 Grime, J. P., 1977. Evidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory. The American Naturalist, 111(982), 1169–1194. https://doi.org/10.1086/283244 Grime, J. P., 1988. The C-S-R model of primary plant strategies—Origins, implications and tests. In L. D. Gottlieb & S. K. Jain, Plant Evolutionary Biology (pp. 371–393). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1207-6_14 Moore, J., 2020. El capitalismo en la trama de la vida (Capitalism in The Web of Life). Traficantes de sueños, Madrid, Spain. Poinas, I., Fried, G., Henckel, L., & Meynard, C. N., 2023. Agricultural drivers of field margin plant communities are scale-dependent. Bas. App. Ecol. 72, 55-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2023.08.003 Poinas, I., Meynard, C. N., Fried, G., 2024. Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practices, bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.03.530956 Tamburini, G., Bommarco, R., Wanger, T.C., Kremen, C., Van Der Heijden, M.G., Liebman, M., Hallin, S., 2020. Agricultural diversification promotes multiple ecosystem services without compromising yield. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba1715. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba1715 | Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practices | Isis Poinas, Christine N Meynard, Guillaume Fried | <p style="text-align: justify;">Over the past decades, agricultural intensification and climate change have led to vegetation shifts. However, functional trade-offs linking traits responding to climate and farming practices are rarely analyzed, es... |  | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Botany, Climate change, Community ecology | Julia Astegiano | 2023-03-04 15:40:35 | View | |
26 May 2021

Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunitiesCamille Saade, Sonia Kéfi, Claire Gougat-Barbera, Benjamin Rosenbaum, and Emanuel A. Fronhofer https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.409524Unity makes strength: clustered extinctions have stronger, longer-lasting effects on metacommunities dynamicsRecommended by Elodie Vercken based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker and Frederik De LaenderIn this article, Saade et al. (2021) investigate how the rate of local extinctions and their spatial distribution affect recolonization dynamics in metacommunities. They use an elegant combination of microcosm experiments with metacommunities of freshwater ciliates and mathematical modelling mirroring their experimental system. Their main findings are (i) that local patch extinctions increase both local (α-) and inter-patch (β-) diversity in a transient way during the recolonization process, (ii) that these effects depend more on the spatial distribution of extinctions (dispersed or clustered) than on their amount, and (iii) that they may spread regionally. A major strength of this study is that it highlights the importance of considering the spatial structure explicitly. Recent work on ecological networks has shown repeatedly that network structure affects the propagation of pathogens (Badham and Stocker 2010), invaders (Morel-Journel et al. 2019), or perturbation events (Gilarranz et al. 2017). Here, the spatial structure of the metacommunity is a regular grid of patches, but the distribution of extinction events may be either regularly dispersed (i.e., extinct patches are distributed evenly over the grid and are all surrounded by non-extinct patches only) or clustered (all extinct patches are neighbours). This has a direct effect on the neighbourhood of perturbed patches, and because perturbations have mostly local effects, their recovery dynamics are dominated by the composition of this immediate neighbourhood. In landscapes with dispersed extinctions, the neighbourhood of a perturbed patch is not affected by the amount of extinctions, and neither is its recovery time. In contrast, in landscapes with clustered extinctions, the amount of extinctions affects the depth of the perturbed area, which takes longer to recover when it is larger. Interestingly, the spatial distribution of extinctions here is functionally equivalent to differences in connectivity between perturbed and unperturbed patches, which results in contrasted “rescue recovery” and “mixing recovery” regimes as described by Zelnick et al. (2019).
Levins R (1969) Some Demographic and Genetic Consequences of Environmental Heterogeneity for Biological Control1. Bulletin of the Entomological Society of America, 15, 237–240. https://doi.org/10.1093/besa/15.3.237 Ruokolainen L (2013) Spatio-Temporal Environmental Correlation and Population Variability in Simple Metacommunities. PLOS ONE, 8, e72325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072325 Saade C, Kefi S, Gougat-Barbera C, Rosenbaum B, Fronhofer EA (2021) Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities. bioRxiv, 2020.12.03.409524, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.03.409524 | Spatial distribution of local patch extinctions drives recovery dynamics in metacommunities | Camille Saade, Sonia Kéfi, Claire Gougat-Barbera, Benjamin Rosenbaum, and Emanuel A. Fronhofer | <p style="text-align: justify;">Human activities lead more and more to the disturbance of plant and animal communities with local extinctions as a consequence. While these negative effects are clearly visible at a local scale, it is less clear how... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Colonization, Community ecology, Competition, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Landscape ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Elodie Vercken | 2020-12-08 15:55:20 | View | |
02 Jan 2024
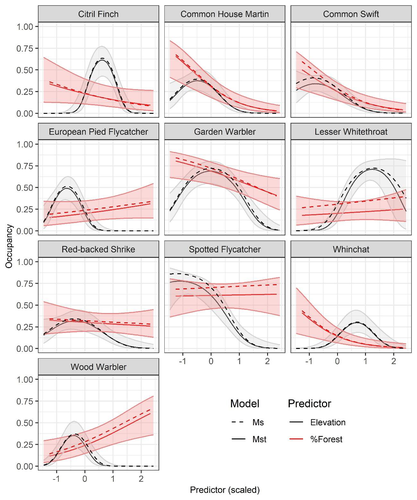
Mt or not Mt: Temporal variation in detection probability in spatial capture-recapture and occupancy modelsRahel Sollmann https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.08.552394Useful clarity on the value of considering temporal variability in detection probabilityRecommended by Benjamin Bolker based on reviews by Dana Karelus and Ben Augustine based on reviews by Dana Karelus and Ben Augustine
As so often quoted, "all models are wrong; more specifically, we always neglect potentially important factors in our models of ecological systems. We may neglect these factors because no-one has built a computational framework to include them; because including them would be computationally infeasible; or because we don't have enough data. When considering whether to include a particular process or form of heterogeneity, the gold standard is to fit models both with and without the component, and then see whether we needed the component in the first place -- that is, whether including that component leads to an important difference in our conclusions. However, this approach is both tedious and endless, because there are an infinite number of components that we could consider adding to any given model. Therefore, thoughtful exercises that evaluate the importance of particular complications under a realistic range of simulations and a representative set of case studies are extremely valuable for the field. While they cannot provide ironclad guarantees, they give researchers a general sense of when they can (probably) safely ignore some factors in their analyses. This paper by Sollmann (2024) shows that for a very wide range of scenarios, temporal and spatiotemporal variability in the probability of detection have little effect on the conclusions of spatial capture-recapture and occupancy models. The author is thoughtful about when such variability may be important, e.g. when variation in detection and density is correlated and thus confounded, or when variation is driven by animals' behavioural responses to being captured. | Mt or not Mt: Temporal variation in detection probability in spatial capture-recapture and occupancy models | Rahel Sollmann | <p>State variables such as abundance and occurrence of species are central to many questions in ecology and conservation, but our ability to detect and enumerate species is imperfect and often varies across space and time. Accounting for imperfect... |  | Euring Conference, Statistical ecology | Benjamin Bolker | Dana Karelus, Ben Augustine, Ben Augustine | 2023-08-10 09:18:56 | View |
21 Oct 2020
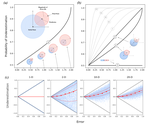
Why scaling up uncertain predictions to higher levels of organisation will underestimate changeJames Orr, Jeremy Piggott, Andrew Jackson, Jean-François Arnoldi https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.05.26.117200Uncertain predictions of species responses to perturbations lead to underestimate changes at ecosystem level in diverse systemsRecommended by Elisa Thebault based on reviews by Carlos Melian and 1 anonymous reviewerDifferent sources of uncertainty are known to affect our ability to predict ecological dynamics (Petchey et al. 2015). However, the consequences of uncertainty on prediction biases have been less investigated, especially when predictions are scaled up to higher levels of organisation as is commonly done in ecology for instance. The study of Orr et al. (2020) addresses this issue. It shows that, in complex systems, the uncertainty of unbiased predictions at a lower level of organisation (e.g. species level) leads to a bias towards underestimation of change at higher level of organisation (e.g. ecosystem level). This bias is strengthened by larger uncertainty and by higher dimensionality of the system. References Cardinale BJ, Duffy JE, Gonzalez A, Hooper DU, Perrings C, Venail P, Narwani A, Mace GM, Tilman D, Wardle DA, Kinzig AP, Daily GC, Loreau M, Grace JB, Larigauderie A, Srivastava DS, Naeem S (2012) Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature, 486, 59–67. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11148 | Why scaling up uncertain predictions to higher levels of organisation will underestimate change | James Orr, Jeremy Piggott, Andrew Jackson, Jean-François Arnoldi | <p>Uncertainty is an irreducible part of predictive science, causing us to over- or underestimate the magnitude of change that a system of interest will face. In a reductionist approach, we may use predictions at the level of individual system com... |  | Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning, Theoretical ecology | Elisa Thebault | Anonymous | 2020-06-02 15:41:12 | View |
26 Apr 2021
Experimental test for local adaptation of the rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea) during its recent rapid colonization on its cultivated apple host (Malus domestica) in EuropeOlvera-Vazquez S.G., Alhmedi A., Miñarro M., Shykoff J. A., Marchadier E., Rousselet A., Remoué C., Gardet R., Degrave A. , Robert P. , Chen X., Porcher J., Giraud T., Vander-Mijnsbrugge K., Raffoux X., Falque M., Alins, G., Didelot F., Beliën T., Dapena E., Lemarquand A. and Cornille A. https://forgemia.inra.fr/amandine.cornille/local_adaptation_dpA planned experiment on local adaptation in a host-parasite system: is adaptation to the host linked to its recent domestication?Recommended by Eric Petit based on reviews by Sharon Zytynska, Alex Stemmelen and 1 anonymous reviewerLocal adaptation shall occur whenever selective pressures vary across space and overwhelm the effects of gene flow and local extinctions (Kawecki and Ebert 2004). Because the intimate interaction that characterizes their relationship exerts a strong selective pressure on both partners, host-parasite systems represent a classical example in which local adaptation is expected from rapidly evolving parasites adapting to more evolutionary constrained hosts (Kaltz and Shykoff 1998). Such systems indeed represent a large proportion of the study-cases in local adaptation research (Runquist et al. 2020). Biotic interactions intervene in many environment-related societal challenges, so that understanding when and how local adaptation arises is important not only for understanding evolutionary dynamics but also for more applied questions such as the control of agricultural pests, biological invasions, or pathogens (Parker and Gilbert 2004). The exact conditions under which local adaptation does occur and can be detected is however still the focus of many theoretical, methodological and empirical studies (Blanquart et al. 2013, Hargreaves et al. 2020, Hoeksema and Forde 2008, Nuismer and Gandon 2008, Richardson et al. 2014). A recent review that evaluates investigations that examined the combined influence of biotic and abiotic factors on local adaptation reaches partial conclusions about their relative importance in different contexts and underlines the many traps that one has to avoid in such studies (Runquist et al. 2020). The authors of this review emphasize that one should evaluate local adaptation using wild-collected strains or populations and over multiple generations, on environmental gradients that span natural ranges of variation for both biotic and abiotic factors, in a theory-based hypothetico-deductive framework that helps interpret the outcome of experiments. These multiple targets are not easy to reach in each local adaptation experiment given the diversity of systems in which local adaptation may occur. Improving research practices may also help better understand when and where local adaptation does occur by adding controls over p-hacking, HARKing or publication bias, which is best achieved when hypotheses, date collection and analytical procedures are known before the research begins (Chambers et al. 2014). In this regard, the route taken by Olvera-Vazquez et al. (2021) is interesting. They propose to investigate whether the rosy aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea) recently adapted to its cultivated host, the apple tree (Malus domestica), and chose to pre-register their hypotheses and planned experiments on PCI Ecology (Peer Community In 2020). Though not fulfilling all criteria mentioned by Runquist et al. (2020), they clearly state five hypotheses that all relate to the local adaptation of this agricultural pest to an economically important fruit tree, and describe in details a powerful, randomized experiment, including how data will be collected and analyzed. The experimental set-up includes comparisons between three sites located along a temperature transect that also differ in local edaphic and biotic factors, and contrasts wild and domesticated apple trees that originate from the three sites and were both planted in the local, sympatric site, and transplanted to allopatric sites. Beyond enhancing our knowledge on local adaptation, this experiment will also test the general hypothesis that the rosy aphid recently adapted to Malus sp. after its domestication, a question that population genetic analyses was not able to answer (Olvera-Vazquez et al. 2020). References Blanquart F, Kaltz O, Nuismer SL, Gandon S (2013) A practical guide to measuring local adaptation. Ecology Letters, 16, 1195–1205. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.12150 Briscoe Runquist RD, Gorton AJ, Yoder JB, Deacon NJ, Grossman JJ, Kothari S, Lyons MP, Sheth SN, Tiffin P, Moeller DA (2019) Context Dependence of Local Adaptation to Abiotic and Biotic Environments: A Quantitative and Qualitative Synthesis. The American Naturalist, 195, 412–431. https://doi.org/10.1086/707322 Chambers CD, Feredoes E, Muthukumaraswamy SD, Etchells PJ, Chambers CD, Feredoes E, Muthukumaraswamy SD, Etchells PJ (2014) Instead of “playing the game” it is time to change the rules: Registered Reports at <em>AIMS Neuroscience</em> and beyond. AIMS Neuroscience, 1, 4–17. https://doi.org/10.3934/Neuroscience.2014.1.4 Hargreaves AL, Germain RM, Bontrager M, Persi J, Angert AL (2019) Local Adaptation to Biotic Interactions: A Meta-analysis across Latitudes. The American Naturalist, 195, 395–411. https://doi.org/10.1086/707323 Hoeksema JD, Forde SE (2008) A Meta‐Analysis of Factors Affecting Local Adaptation between Interacting Species. The American Naturalist, 171, 275–290. https://doi.org/10.1086/527496 Kaltz O, Shykoff JA (1998) Local adaptation in host–parasite systems. Heredity, 81, 361–370. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.1998.00435.x Kawecki TJ, Ebert D (2004) Conceptual issues in local adaptation. Ecology Letters, 7, 1225–1241. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00684.x Nuismer SL, Gandon S (2008) Moving beyond Common‐Garden and Transplant Designs: Insight into the Causes of Local Adaptation in Species Interactions. The American Naturalist, 171, 658–668. https://doi.org/10.1086/587077 Olvera-Vazquez SG, Remoué C, Venon A, Rousselet A, Grandcolas O, Azrine M, Momont L, Galan M, Benoit L, David G, Alhmedi A, Beliën T, Alins G, Franck P, Haddioui A, Jacobsen SK, Andreev R, Simon S, Sigsgaard L, Guibert E, Tournant L, Gazel F, Mody K, Khachtib Y, Roman A, Ursu TM, Zakharov IA, Belcram H, Harry M, Roth M, Simon JC, Oram S, Ricard JM, Agnello A, Beers EH, Engelman J, Balti I, Salhi-Hannachi A, Zhang H, Tu H, Mottet C, Barrès B, Degrave A, Razmjou J, Giraud T, Falque M, Dapena E, Miñarro M, Jardillier L, Deschamps P, Jousselin E, Cornille A (2020) Large-scale geographic survey provides insights into the colonization history of a major aphid pest on its cultivated apple host in Europe, North America and North Africa. bioRxiv, 2020.12.11.421644. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.11.421644 Olvera-Vazquez S.G., Alhmedi A., Miñarro M., Shykoff J. A., Marchadier E., Rousselet A., Remoué C., Gardet R., Degrave A. , Robert P. , Chen X., Porcher J., Giraud T., Vander-Mijnsbrugge K., Raffoux X., Falque M., Alins, G., Didelot F., Beliën T., Dapena E., Lemarquand A. and Cornille A. (2021) Experimental test for local adaptation of the rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea) to its host (Malus domestica) and to its climate in Europe. In principle recommendation by Peer Community In Ecology. https://forgemia.inra.fr/amandine.cornille/local_adaptation_dp, ver. 4. Parker IM, Gilbert GS (2004) The Evolutionary Ecology of Novel Plant-Pathogen Interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 675–700. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.34.011802.132339 Peer Community In. (2020, January 15). Submit your preregistration to Peer Community In for peer review. https://peercommunityin.org/2020/01/15/submit-your-preregistration-to-peer-community-in-for-peer-review/ Richardson JL, Urban MC, Bolnick DI, Skelly DK (2014) Microgeographic adaptation and the spatial scale of evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 29, 165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2014.01.002 | Experimental test for local adaptation of the rosy apple aphid (Dysaphis plantaginea) during its recent rapid colonization on its cultivated apple host (Malus domestica) in Europe | Olvera-Vazquez S.G., Alhmedi A., Miñarro M., Shykoff J. A., Marchadier E., Rousselet A., Remoué C., Gardet R., Degrave A. , Robert P. , Chen X., Porcher J., Giraud T., Vander-Mijnsbrugge K., Raffoux X., Falque M., Alins, G., Didelot F., Beliën T.,... | <p style="text-align: justify;">Understanding the extent of local adaptation in natural populations and the mechanisms enabling populations to adapt to their environment is a major avenue in ecology research. Host-parasite interaction is widely se... | Evolutionary ecology, Preregistrations | Eric Petit | 2020-07-26 18:31:42 | View | ||
07 Jun 2023
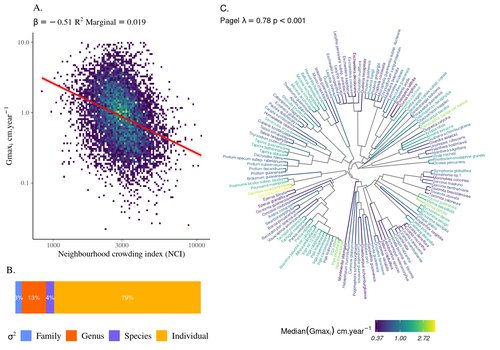
High intraspecific growth variability despite strong evolutionary heritage in a neotropical forestSylvain Schmitt, Bruno Hérault, Géraldine Derroire https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.27.501745Environmental and functional determinants of tree performance in a neotropical forest: the imprint of evolutionary legacy on growth strategiesRecommended by François Munoz based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker, Camille Girard and Jelena Pantel based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker, Camille Girard and Jelena Pantel
The hyperdiverse tropical forests have long fascinated ecologists because the fact that so many species persist at a low density at a local scale remains hard to explain. Both niche-based and neutral hypotheses have been tested, primarily based on analyzing the taxonomic composition of tropical forest plots (Janzen 1970; Hubbell 2001). Studies of the functional and phylogenetic structure of tropical tree communities have further aimed to better assess the importance of niche-based processes. For instance, Baraloto et al. (2012) found that co-occurring species were functionally and phylogenetically more similar in a neotropical forest, suggesting a role of environmental filtering. Likewise, Schmitt et al. (2021) found the influence of environmental filtering on the functional composition of an Indian rainforest. Yet these studies evidenced non-random trait-environment association based on the composition of assemblages only (in terms of occurrences and abundances). A major challenge remains to further address whether and how tree performance varies among species and individuals in tropical forests. Functional traits are related to components of individual fitness (Violle et al. 2007). Recently, more and more emphasis has been put on examining the relationship between functional trait values and demographic parameters (Salguero-Gómez et al. 2018), in order to better understand how functional trait values determine species population dynamics and abundances in assemblages. Fortunel et al. (2018) found an influence of functional traits on species growth variation related to topography, and less clearly to neighborhood density (crowding). Poorter et al. (2018) observed 44% of trait variation within species in a neotropical forest. Although individual trait values would be expected to be better predictors of performance than average values measured at the species level, Poorter et al still found a poor relationship. Schmitt et al. (2023) examined how abiotic conditions and biotic interactions (considering neighborhood density) influenced the variation of individual potential tree growth, in a tropical forest plot located in French Guiana. They also considered the link between species-averaged values of growth potential and functional traits. Schmitt et al. (2023) found substantial variation in growth potential within species, that functional traits explained 40% of the variation of species-averaged growth and, noticeably, that the taxonomic structure (used as random effect in their model) explained a third of the variation in individual growth. Although functional traits of roots, wood and leaves could predict a significant part of species growth potential, much variability of tree growth occurred within species. Intraspecific trait variation can thus be huge in response to changing abiotic and biotic contexts across individuals. The information on phylogenetic relationships can still provide a proxy of the integrated phenotypic variation that is under selection across the phylogeny, and determine a variation in growth strategies among individuals. The similarity of the phylogenetic structure suggests a joint selection of these growth strategies and related functional traits during events of convergent evolution. Baraloto et al. (2012) already noted that phylogenetic distance can be a proxy of niche overlap in tropical tree communities. Here, Schmitt et al. further demonstrate that evolutionary heritage is significantly related to individual growth variation, and plead for better acknowledging this role in future studies. While the role of fitness differences in tropical tree community dynamics remained to be assessed, the present study provides new evidence that individual growth does vary depending on evolutionary relationships, which can reflect the roles of selection and adaptation on growth strategies. Therefore, investigating both the influence of functional traits and phylogenetic relationships on individual performance remains a promising avenue of research, for functional and community ecology in general. REFERENCES Baraloto, Christopher, Olivier J. Hardy, C. E. Timothy Paine, Kyle G. Dexter, Corinne Cruaud, Luke T. Dunning, Mailyn-Adriana Gonzalez, et al. 2012. « Using functional traits and phylogenetic trees to examine the assembly of tropical tree communities ». Journal of Ecology, 100: 690‑701. | High intraspecific growth variability despite strong evolutionary heritage in a neotropical forest | Sylvain Schmitt, Bruno Hérault, Géraldine Derroire | <p style="text-align: justify;">Individual tree growth is a key determinant of species performance and a driver of forest dynamics and composition. Previous studies on tree growth unravelled the variation in species growth as a function of demogra... |  | Community ecology, Demography, Population ecology | François Munoz | Jelena Pantel, David Murray-Stoker | 2022-08-01 14:29:04 | View |
11 Oct 2023

Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysisCédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.02.516908Disentangling microbial exopolymer dynamics in intertidal sedimentsRecommended by Ute Risse-Buhl and Nils Rädecker based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) enables microorganisms to shape and interact with their environment [1]. EPS support cell adhesion and motility, offer protection from unfavorable conditions, and facilitate nutrient acquisition and transfer between microorganisms [2]. EPS production and consumption thus control the formation and structural organization of biofilms [3]. However, in marine environments, our understanding of the sources and composition of EPS is limited. References
| Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysis | Cédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe | <p style="text-align: justify;">Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) refer to a wide variety of high molecular weight molecules secreted outside the cell membrane by biofilm microorganisms. In the present study, EPS from marine microphytobenth... |  | Biodiversity, Ecological stoichiometry, Ecosystem functioning, Food webs, Marine ecology, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Soil ecology | Ute Risse-Buhl | 2022-12-06 14:13:11 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










