Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors▼ | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
18 Mar 2019

Evaluating functional dispersal and its eco-epidemiological implications in a nest ectoparasiteAmalia Rataud, Marlène Dupraz, Céline Toty, Thomas Blanchon, Marion Vittecoq, Rémi Choquet, Karen D. McCoy https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.2592114Limited dispersal in a vector on territorial hostsRecommended by Adele Mennerat based on reviews by Shelly Lachish and 1 anonymous reviewerParasitism requires parasites and hosts to meet and is therefore conditioned by their respective dispersal abilities. While dispersal has been studied in a number of wild vertebrates (including in relation to infection risk), we still have poor knowledge of the movements of their parasites. Yet we know that many parasites, and in particular vectors transmitting pathogens from host to host, possess the ability to move actively during at least part of their lives. References | Evaluating functional dispersal and its eco-epidemiological implications in a nest ectoparasite | Amalia Rataud, Marlène Dupraz, Céline Toty, Thomas Blanchon, Marion Vittecoq, Rémi Choquet, Karen D. McCoy | <p>Functional dispersal (between-site movement, with or without subsequent reproduction) is a key trait acting on the ecological and evolutionary trajectories of a species, with potential cascading effects on other members of the local community. ... |  | Dispersal & Migration, Epidemiology, Parasitology, Population ecology | Adele Mennerat | 2018-11-05 11:44:58 | View | |
16 Nov 2020
Intraspecific diversity loss in a predator species alters prey community structure and ecosystem functionsAllan Raffard, Julien Cucherousset, José M. Montoya, Murielle Richard, Samson Acoca-Pidolle, Camille Poésy, Alexandre Garreau, Frédéric Santoul & Simon Blanchet. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.10.144337Hidden diversity: how genetic richness affects species diversity and ecosystem processes in freshwater pondsRecommended by Frederik De Laender based on reviews by Andrew Barnes and Jes HinesBiodiversity loss can have important consequences for ecosystem functions, as exemplified by a large body of literature spanning at least three decades [1–3]. While connections between species diversity and ecosystem functions are now well-defined and understood, the importance of diversity within species is more elusive. Despite a surge in theoretical work on how intraspecific diversity can affect coexistence in simple community types [4,5], not much is known about how intraspecific diversity drives ecosystem processes in more complex community types. One particular challenge is that intraspecific diversity can be expressed as observable variation of functional traits, or instead subsist as genetic variation of which the consequences for ecosystem processes are harder to grasp. References [1] Tilman D, Downing JA (1994) Biodiversity and stability in grasslands. Nature, 367, 363–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/367363a0 | Intraspecific diversity loss in a predator species alters prey community structure and ecosystem functions | Allan Raffard, Julien Cucherousset, José M. Montoya, Murielle Richard, Samson Acoca-Pidolle, Camille Poésy, Alexandre Garreau, Frédéric Santoul & Simon Blanchet. | <p>Loss in intraspecific diversity can alter ecosystem functions, but the underlying mechanisms are still elusive, and intraspecific biodiversity-ecosystem function relationships (iBEF) have been restrained to primary producers. Here, we manipulat... |  | Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning, Experimental ecology, Food webs, Freshwater ecology | Frederik De Laender | Andrew Barnes | 2020-06-15 09:04:53 | View |
02 Aug 2021

Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimationAline Migné, Gwendoline Duong, Dominique Menu, Dominique Davoult & François Gévaert https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03079617Towards a better understanding of the effects of self-shading on Fucus serratus populationsRecommended by Cédric Hubas based on reviews by Gwenael Abril, Francesca Rossi and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Gwenael Abril, Francesca Rossi and 1 anonymous reviewer
The importance of the vertical structure of vegetation cover for the functioning, management and conservation of ecosystems has received particular attention from ecologists in the last decades. Canopy architecture has many implications for light extinction coefficient, temperature variation reduction, self-shading which are all key parameters for the structuring and functioning of different ecosystems such as grasslands [1,2], forests [3,4], phytoplankton communities [5, 6], macroalgal populations [7] and even underwater animal forests such as octocoral communities [8]. This research topic, therefore, benefits from a large body of literature and the facilitative role of self-shadowing is no longer in question. However, it is always puzzling to note that some of the most common ecosystems turn out to be amongst the least known. This is precisely the case of the Fucus serratus communities which are widespread in Northeast Atlantic along the Atlantic coast of Europe from Svalbard to Portugal, as well as Northwest Atlantic & Gulf of St. Lawrence, easily accessible at low tide, but which have comparatively received less attention than more emblematic macro-algal communities such as Laminariales. The lack of attention paid to these most common Fucales is particularly critical as some species such as F. serratus are proving to be particularly vulnerable to environmental change, leading to a predicted northward retreat from its current southern boundary [9]. In the present study [10], the authors showed the importance of the vegetation cover in resisting tide-induced environmental stresses. The canopy of F. serratus mitigates stress levels experienced in the lower layers during emersion, while various acclimation strategies take over to maintain the photosynthetic apparatus in optimal conditions. They hereby highlight adaptation mechanisms to the extreme environment represented by the intertidal zone. These adaptation strategies were expected and similar mechanisms had been shown at the cellular level previously [11]. The earliest studies on the subject have shown that the structure of the bottom, the movement of water, and light availability all "influence the distribution of Fucaceae and disturb the regularity of their fine zonation, which itself is caused by the most important factor, desiccation", as Zaneveld states in his review [12]. He observed that the causes of the zonal distribution of marine algae are numerous, and identified several points of interest such as the relative period of emersion, the rapidity of desiccation, the loss of water, and the thickness of the cell walls. The present study thus highlights the existence of facilitative mechanisms associated with F. serratus canopy and nicely confirms previous work with in situ observations. It also highlights the importance of the vegetative cover in combating desiccation and introduces the dampening effect as a facilitating mechanism. The effect of the vegetation cover can sometimes even be felt beyond its immediate area of influence. A recent study shows that ground-level ozone is significantly reduced by the combined effects of canopy shading and turbulence [4]. Below the canopy, the light intensity becomes sufficiently low which inhibits ozone formation due to the decrease in the rates of hydroxyl radical formation and the rates of conversion of nitrogen dioxide to nitrogen oxide by photolysis. In addition, reductions in light levels associated with foliage promote ozone-destroying reactions between plant-emitted species, such as nitric oxide and/or alkenes, and ozone itself. The reduction in diffusivity slows the upward transport of surface emitted species, partially decoupling the area under the canopy from the rest of the atmosphere. By analogy with the work of Makar et al [4], and in the light of the results provided by the authors of this study, one may wonder whether the canopy dampening of F. serratus communities (and other common fucoids widely distributed on our coasts) might not also influence atmospheric chemistry, both at the Earth's surface and in the atmospheric boundary layer. The lack of accumulation of reactive oxygen species under the canopy found by the authors is consistent with this hypothesis and suggests that the damping effect of F. serratus may well have much wider consequences than expected. References [1] Jurik TW, Kliebenstein H (2000) Canopy Architecture, Light Extinction and Self-Shading of a Prairie Grass, Andropogon Gerardii. The American Midland Naturalist, 144, 51–65. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3083010 [2] Mitchley J, Willems JH (1995) Vertical canopy structure of Dutch chalk grasslands in relation to their management. Vegetatio, 117, 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00033256 [3] Kane VR, Gillespie AR, McGaughey R, Lutz JA, Ceder K, Franklin JF (2008) Interpretation and topographic compensation of conifer canopy self-shadowing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 3820–3832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.06.001 [4] Makar PA, Staebler RM, Akingunola A, Zhang J, McLinden C, Kharol SK, Pabla B, Cheung P, Zheng Q (2017) The effects of forest canopy shading and turbulence on boundary layer ozone. Nature Communications, 8, 15243. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15243 [5] Shigesada N, Okubo A (1981) Analysis of the self-shading effect on algal vertical distribution in natural waters. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 12, 311–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276919 [6] Barros MP, Pedersén M, Colepicolo P, Snoeijs P (2003) Self-shading protects phytoplankton communities against H2O2-induced oxidative damage. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 30, 275–282. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame030275 [7] Ørberg SB, Krause-Jensen D, Mouritsen KN, Olesen B, Marbà N, Larsen MH, Blicher ME, Sejr MK (2018) Canopy-Forming Macroalgae Facilitate Recolonization of Sub-Arctic Intertidal Fauna and Reduce Temperature Extremes. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00332 [8] Nelson H, Bramanti L (2020) From Trees to Octocorals: The Role of Self-Thinning and Shading in Underwater Animal Forests. In: Perspectives on the Marine Animal Forests of the World (eds Rossi S, Bramanti L), pp. 401–417. Springer International Publishing, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57054-5_12 [9] Jueterbock A, Kollias S, Smolina I, Fernandes JMO, Coyer JA, Olsen JL, Hoarau G (2014) Thermal stress resistance of the brown alga Fucus serratus along the North-Atlantic coast: Acclimatization potential to climate change. Marine Genomics, 13, 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2013.12.008 [10] Migné A, Duong G, Menu D, Davoult D, Gévaert F (2021) Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimation. HAL, hal-03079617, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03079617 [11] Lichtenberg M, Kühl M (2015) Pronounced gradients of light, photosynthesis and O2 consumption in the tissue of the brown alga Fucus serratus. New Phytologist, 207, 559–569. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13396 [12] Zaneveld JS (1937) The Littoral Zonation of Some Fucaceae in Relation to Desiccation. Journal of Ecology, 25, 431–468. https://doi.org/10.2307/2256204 | Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimation | Aline Migné, Gwendoline Duong, Dominique Menu, Dominique Davoult & François Gévaert | <p style="text-align: justify;">The brown alga <em>Fucus serratus</em> forms dense stands on the sheltered low intertidal rocky shores of the Northeast Atlantic coast. In the southern English Channel, these stands have proved to be highly producti... |  | Marine ecology | Cédric Hubas | 2021-01-05 16:24:02 | View | |
21 Feb 2019

Photosynthesis of Laminaria digitata during the immersion and emersion periods of spring tidal cycles during hot, sunny weatherAline Migné, Gaspard Delebecq, Dominique Davoult, Nicolas Spilmont, Dominique Menu, Marie-Andrée Janquin and François Gévaert https://hal.sorbonne-universite.fr/hal-01827565v4Evaluating physiological responses of a kelp to environmental changes at its vulnerable equatorward range limitRecommended by Matthew Bracken based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersUnderstanding processes at species’ range limits is of paramount importance in an era of global change. For example, the boreal kelp Laminaria digitata, which dominates low intertidal and shallow subtidal rocky reefs in northwestern Europe, is declining in the equatorward portion of its range [1]. In this contribution, Migné and colleagues [2] focus on L. digitata near its southern range limit on the coast of France and use a variety of techniques to paint a complete picture of the physiological responses of the kelp to environmental changes. Importantly, and in contrast to earlier work on the species which focused on subtidal individuals (e.g. [3]), Migné et al. [2] describe responses not only in the most physiologically stressful portion of the species’ range but also in the most stressful portion of its local environment: the upper portion of its zone on the shoreline, where it is periodically exposed to aerial conditions and associated thermal and desiccation stresses. References [1] Raybaud, V., Beaugrand, G., Goberville, E., Delebecq, G., Destombe, C., Valero, M., Davoult, D., Morin, P. & Gevaert, F. (2013). Decline in kelp in west Europe and climate. PloS one, 8(6), e66044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066044 | Photosynthesis of Laminaria digitata during the immersion and emersion periods of spring tidal cycles during hot, sunny weather | Aline Migné, Gaspard Delebecq, Dominique Davoult, Nicolas Spilmont, Dominique Menu, Marie-Andrée Janquin and François Gévaert | The boreal kelp Laminaria digitata dominates the low intertidal and upper subtidal zones of moderately exposed rocky shores in north-western Europe. Due to ocean warming, this foundation species is predicted to disappear from French coasts in the ... |  | Marine ecology | Matthew Bracken | 2018-07-02 18:03:11 | View | |
03 Jun 2022
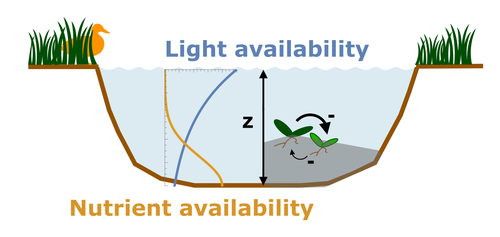
Evolutionary emergence of alternative stable states in shallow lakesAlice Ardichvili, Nicolas Loeuille, Vasilis Dakos https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.23.481597How to evolve an alternative stable stateRecommended by Tim Coulson based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jean-François Arnoldi and 1 anonymous reviewer
Alternative stable states describe ecosystems that can persist in more than one configuration. An ecosystem can shift between stable states following some form of perturbation. There has been much work on predicting when ecosystems will shift between stable states, but less work on why some ecosystems are able to exist in alternative stable states in the first place. The paper by Ardichvili, Loeuille, and Dakos (2022) addresses this question using a simple model of a shallow lake. Their model is based on a trade-off between access to light and nutrient availability in the water column, two essential resources for the macrophytes they model. They then identify conditions when the ancestral macrophyte will diversify resulting in macrophyte species living at new depths within the lake. The authors find a range of conditions where alternative stable states can evolve, but the range is narrow. Nonetheless, their model suggests that for alternative stable states to exist, one requirement is for there to be asymmetric competition between competing species, with one species being a better competitor on one limiting resource, with the other being a better competitor on a second limiting resource. These results are interesting and add to growing literature on how asymmetric competition can aid species coexistence. Asymmetric competition may be widespread in nature, with closely related species often being superior competitors on different resources. Incorporating asymmetric competition, and its evolution, into models does complicate theoretical investigations, but Ardichvili, Loeuille, and Dakos’ paper elegantly shows how substantial progress can be made with a model that is still (relatively) simple. References Ardichvili A, Loeuille N, Dakos V (2022) Evolutionary emergence of alternative stable states in shallow lakes. bioRxiv, 2022.02.23.481597, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.23.481597 | Evolutionary emergence of alternative stable states in shallow lakes | Alice Ardichvili, Nicolas Loeuille, Vasilis Dakos | <p style="text-align: justify;">Ecosystems under stress may respond abruptly and irreversibly through tipping points. Although much is explored on the mechanisms that affect tipping points and alternative stable states, little is known on how ecos... |  | Community ecology, Competition, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Theoretical ecology | Tim Coulson | 2022-03-01 10:54:05 | View | |
12 Oct 2020

Insect herbivory on urban trees: Complementary effects of tree neighbours and predationAlex Stemmelen, Alain Paquette, Marie-Lise Benot, Yasmine Kadiri, Hervé Jactel, Bastien Castagneyrol https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.15.042317Tree diversity is associated with reduced herbivory in urban forestRecommended by Ruth Arabelle Hufbauer and Ian Pearse based on reviews by Ian Pearse and Freerk MollemanUrban ecology, the study of ecological systems in our increasingly urbanized world, is crucial to planning and redesigning cities to enhance ecosystem services (Kremer et al. 2016), human health and well-being and further conservation goals (Dallimer et al. 2012). Urban trees are a crucial component of urban streets and parks that provide shade and cooling through evapotranspiration (Fung and Jim 2019), improve air quality (Lai and Kontokosta 2019), help control storm water (Johnson and Handel 2016), and conserve wildlife (Herrmann et al. 2012; de Andrade et al. 2020). References Airola, D. and Greco, S. (2019). Birds and oaks in California’s urban forest. Int. Oaks, 30, 109–116. | Insect herbivory on urban trees: Complementary effects of tree neighbours and predation | Alex Stemmelen, Alain Paquette, Marie-Lise Benot, Yasmine Kadiri, Hervé Jactel, Bastien Castagneyrol | <p>Insect herbivory is an important component of forest ecosystems functioning and can affect tree growth and survival. Tree diversity is known to influence insect herbivory in natural forest, with most studies reporting a decrease in herbivory wi... |  | Biodiversity, Biological control, Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning, Herbivory | Ruth Arabelle Hufbauer | 2020-04-20 13:49:36 | View | |
12 Jan 2024
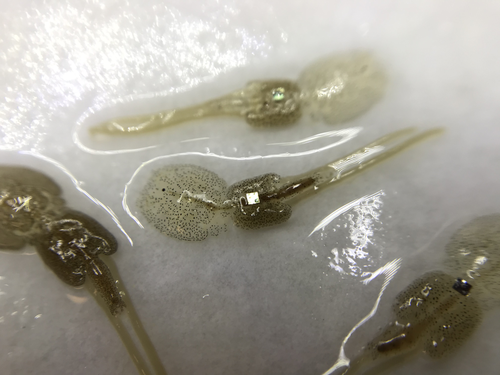
Methods for tagging an ectoparasite, the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonisAlexius Folk, Adele Mennerat https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.31.555695Marking invertebrates using RFID tagsRecommended by Nicolas Schtickzelle based on reviews by Simon Blanchet and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Simon Blanchet and 1 anonymous reviewer
Guiding and monitoring the efficiency of conservation efforts needs robust scientific background information, of which one key element is estimating wildlife abundance and its spatial and temporal variation. As raw counts are by nature incomplete counts of a population, correcting for detectability is required (Clobert, 1995; Turlure et al., 2018). This can be done with Capture-Mark-Recapture protocols (Iijima, 2020). Techniques for marking individuals are diverse, e.g. writing on butterfly wings, banding birds, or using natural specific patterns in the individual’s body such as leopard fur or whale tail. Advancement in technology opens new opportunities for developing marking techniques, including strategies to limit mark identification errors (Burchill & Pavlic, 2019), and for using active marks that can transmit data remotely or be read automatically. The details of such methodological developments frequently remain unpublished, the method being briefly described in studies that use it. For a few years, there has been however a renewed interest in proper publishing of methods for ecology and evolution. This study by Folk & Mennerat (2023) fits in this context, offering a nice example of detailed description and testing of a method to mark salmon ectoparasites using RFID tags. Such tags are extremely small, yet easy to use, even with automatic recording procedure. The study provides a very good basis protocol that should help researchers working for small species, in particular invertebrates. The study is complemented by a video illustrating the placement of the tag so the reader who would like to replicate the procedure can get a very precise idea of it. References Burchill, A. T., & Pavlic, T. P. (2019). Dude, where’s my mark? Creating robust animal identification schemes informed by communication theory. Animal Behaviour, 154, 203–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2019.05.013 Clobert, J. (1995). Capture-recapture and evolutionary ecology: A difficult wedding ? Journal of Applied Statistics, 22(5–6), 989–1008. Folk, A., & Mennerat, A. (2023). Methods for tagging an ectoparasite, the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (p. 2023.08.31.555695). bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.08.31.555695 Iijima, H. (2020). A Review of Wildlife Abundance Estimation Models: Comparison of Models for Correct Application. Mammal Study, 45(3), 177–188. https://doi.org/10.3106/ms2019-0082 Turlure, C., Pe’er, G., Baguette, M., & Schtickzelle, N. (2018). A simplified mark–release–recapture protocol to improve the cost effectiveness of repeated population size quantification. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9(3), 645–656. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12900 | Methods for tagging an ectoparasite, the salmon louse *Lepeophtheirus salmonis* | Alexius Folk, Adele Mennerat | <p style="text-align: justify;">Monitoring individuals within populations is a cornerstone in evolutionary ecology, yet individual tracking of invertebrates and particularly parasitic organisms remains rare. To address this gap, we describe here a... |  | Dispersal & Migration, Evolutionary ecology, Host-parasite interactions, Marine ecology, Parasitology, Terrestrial ecology, Zoology | Nicolas Schtickzelle | 2023-09-04 15:25:08 | View | |
22 Nov 2021
When more competitors means less harvested resourceRecommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Francois Massol, Jeremy Van Cleve and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Francois Massol, Jeremy Van Cleve and 1 anonymous reviewer
In this paper, Alan R. Rogers (2021) examines the dynamics of foraging strategies for a resource that gains value over time (e.g., ripening fruits), while there is a fixed cost of attempting to forage the resource, and once the resource is harvested nothing is left for other harvesters. For this model, not any pure foraging strategy is evolutionary stable. A mixed equilibrium exists, i.e., with a mixture of foraging strategies within the population, which is still evolutionarily unstable. Nonetheless, Alan R. Rogers shows that for a large number of competitors and/or high harvesting cost, the mixture of strategies remains close to the mixed equilibrium when simulating the dynamics. Surprisingly, in a large population individuals will less often attempt to forage the resource and will instead “go fishing”. The paper also exposes an experiment of the game with students, which resulted in a strategy distribution somehow close to the theoretical mixture of strategies. The economist John F. Nash Jr. (1950) gained the Nobel Prize of economy in 1994 for his game theoretical contributions. He gave his name to the “Nash equilibrium”, which represents a set of individual strategies that is reached whenever all the players have nothing to gain by changing their strategy while the strategies of others are unchanged. Alan R. Rogers shows that the mixed equilibrium in the foraging game is such a Nash equilibrium. Yet it is evolutionarily unstable insofar as a distribution close to the equilibrium can invade. The insights of the study are twofold. First, it sheds light on the significance of Nash equilibrium in an ecological context of foraging strategies. Second, it shows that an evolutionarily unstable state can rule the composition of the ecological system. Therefore, the contribution made by the paper should be most significant to better understand the dynamics of competitive communities and their eco-evolutionary trajectories. References Nash JF (1950) Equilibrium points in n-person games. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 36, 48–49. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.36.1.48 Rogers AR (2021) Beating your Neighbor to the Berry Patch. bioRxiv, 2020.11.12.380311, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.11.12.380311
| Beating your neighbor to the berry patch | Alan R. Rogers | <p style="text-align: justify;">Foragers often compete for resources that ripen (or otherwise improve) gradually. What strategy is optimal in this situation? It turns out that there is no optimal strategy. There is no evolutionarily stable strateg... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Evolutionary ecology, Foraging | François Munoz | Erol Akçay, Jorge Peña, Sébastien Lion, François Rousset, Ulf Dieckmann , Troy Day , Corina Tarnita , Florence Debarre , Daniel Friedman , Vlastimil Krivan , Ulf Dieckmann | 2020-12-10 18:38:49 | View |
09 Dec 2019

Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive successAinhoa Magrach, Francisco P. Molina, Ignasi Bartomeus https://doi.org/10.1101/629931Improving our knowledge of species interaction networksRecommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Michael Lattorff, Nicolas Deguines and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Michael Lattorff, Nicolas Deguines and 3 anonymous reviewers
Ecosystems shelter a huge number of species, continuously interacting. Each species interact in various ways, with trophic interactions, but also non-trophic interactions, not mentioning the abiotic and anthropogenic interactions. In particular, pollination, competition, facilitation, parasitism and many other interaction types are simultaneously present at the same place in terrestrial ecosystems [1-2]. For this reason, we need today to improve our understanding of such complex interaction networks to later anticipate their responses. This program is a huge challenge facing ecologists and they today join their forces among experimentalists, theoreticians and modelers. While some of us struggle in theoretical and modeling dimensions [3-4], some others perform brilliant works to observe and/or experiment on the same ecological objects [5-6]. References [1] Campbell, C., Yang, S., Albert, R., and Shea, K. (2011). A network model for plant–pollinator community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(1), 197-202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008204108 | Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive success | Ainhoa Magrach, Francisco P. Molina, Ignasi Bartomeus | <p>Declines in pollinator diversity and abundance have been reported across different regions, with implications for the reproductive success of plant species. However, research has focused primarily on pairwise plant-pollinator interactions, larg... |  | Ecosystem functioning, Interaction networks, Pollination, Terrestrial ecology | Cédric Gaucherel | Nicolas Deguines | 2019-05-07 17:03:23 | View |
01 Mar 2019

Parasite intensity is driven by temperature in a wild birdAdèle Mennerat, Anne Charmantier, Sylvie Hurtrez-Boussès, Philippe Perret, Marcel M Lambrechts https://doi.org/10.1101/323311The global change of species interactionsRecommended by Jan Hrcek based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersWhat kinds of studies are most needed to understand the effects of global change on nature? Two deficiencies stand out: lack of long-term studies [1] and lack of data on species interactions [2]. The paper by Mennerat and colleagues [3] is particularly valuable because it addresses both of these shortcomings. The first one is obvious. Our understanding of the impact of climate on biota improves with longer times series of observations. Mennerat et al. [3] analysed an impressive 18-year series from multiple sites to search for trends in parasitism rates across a range of temperatures. The second deficiency (lack of species interaction data) is perhaps not yet fully appreciated, despite studies pointing this out ten years ago [2,4]. The focus is often on species range limits and how taking species interactions into account changes species range predictions based on climate alone (climate envelope models; [5]). But range limits are not everything, as the function of a species (or community, network, etc.) ultimately depends on the strengths of species interactions and not only on the presence or absence of a given species [2,4]. Mennerat et al. [3] show that in the case of birds and their nest parasites, it is the strength of the interaction that has changed, while the species involved stayed the same. Mennerat et al. [3] found nest parasitism to increase with temperature at the nestling stage. They have also searched for trends of parasitism dynamics dependence on the host, but did not find any, probably because the nest parasites are generalists and attack other bird species within the study sites. This study thus draws attention to wider networks of interacting species, and we urgently need more data to predict how interaction networks will rewire with progressing environmental change [6,7]. References [1] Lindenmayer, D.B., Likens, G.E., Andersen, A., Bowman, D., Bull, C.M., Burns, E., et al. (2012). Value of long-term ecological studies. Austral Ecology, 37(7), 745–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-9993.2011.02351.x | Parasite intensity is driven by temperature in a wild bird | Adèle Mennerat, Anne Charmantier, Sylvie Hurtrez-Boussès, Philippe Perret, Marcel M Lambrechts | <p>Increasing awareness that parasitism is an essential component of nearly all aspects of ecosystem functioning, as well as a driver of biodiversity, has led to rising interest in the consequences of climate change in terms of parasitism and dise... |  | Climate change, Evolutionary ecology, Host-parasite interactions, Parasitology, Zoology | Jan Hrcek | 2018-05-17 14:37:14 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










