
GAUCHEREL Cédric
- UMR AMAP, INRA, Montpellier, France
- Agroecology, Biodiversity, Climate change, Community ecology, Ecological successions, Ecosystem functioning, Food webs, Interaction networks, Landscape ecology, Macroecology, Paleoecology & Paleontology, Social structure, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Terrestrial ecology, Theoretical ecology, Tropical ecology
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2
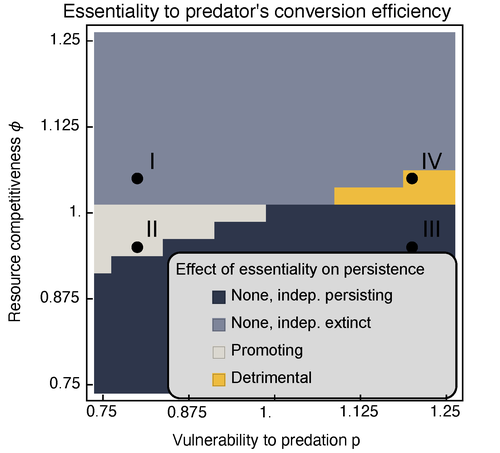
Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs
High-order interactions in food webs may strongly impact persistence of species
Recommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Jean-Christophe POGGIALE and 1 anonymous reviewerMichael Raatz (2023) provides here a relevant exploration of higher-order interactions, i.e. interactions involving more than two related species (Terry et al. 2019), in the case of food web and competition interactions. More precisely, he shows by modeling that essential resources may significantly mediate focal species' persistence. Simultaneously, the provision of essential resources may strongly affect the resulting community structure, by driving to extinction first the predator and then, depending on the higher-order interaction, potentially also the associated competitor.
Today, all ecologists should be aware of the potential effects of high-order interactions on species' (and likely on ecosystem's) fate (Golubski et al. 2016, Grilli et al. 2017). Yet, we should soon be prepared to include any high-order interaction into any interaction network (i.e. not only between species, but also between species and abiotic components, and between biotic, anthropogenic and abiotic components too). For this purpose, we will need innovative approaches such as hypergraphs (Golubski et al. 2016) and discrete-event models (Gaucherel and Pommereau 2019, Thomas et al. 2022) able to manage highly complex interactions, with numerous interacting components and variables. Such a rigorous study is a necessary and preliminary step in taking into account such a higher complexity.
References
Gaucherel, C. and F. Pommereau. 2019. Using discrete systems to exhaustively characterize the dynamics of an integrated ecosystem. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 00:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13242
Golubski, A. J., E. E. Westlund, J. Vandermeer, and M. Pascual. 2016. Ecological Networks over the Edge: Hypergraph Trait-Mediated Indirect Interaction (TMII) Structure trends in Ecology & Evolution 31:344-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.006
Grilli, J., G. Barabas, M. J. Michalska-Smith, and S. Allesina. 2017. Higher-order interactions stabilize dynamics in competitive network models. Nature 548:210-213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23273
Raatz, M. 2023. Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525839
Terry, J. C. D., R. J. Morris, and M. B. Bonsall. 2019. Interaction modifications lead to greater robustness than pairwise non-trophic effects in food webs. Journal of Animal Ecology 88:1732-1742. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.13057
Thomas, C., M. Cosme, C. Gaucherel, and F. Pommereau. 2022. Model-checking ecological state-transition graphs. PLoS Computational Biology 18:e1009657. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009657

Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive success
Improving our knowledge of species interaction networks
Recommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Michael Lattorff, Nicolas Deguines and 3 anonymous reviewersEcosystems shelter a huge number of species, continuously interacting. Each species interact in various ways, with trophic interactions, but also non-trophic interactions, not mentioning the abiotic and anthropogenic interactions. In particular, pollination, competition, facilitation, parasitism and many other interaction types are simultaneously present at the same place in terrestrial ecosystems [1-2]. For this reason, we need today to improve our understanding of such complex interaction networks to later anticipate their responses. This program is a huge challenge facing ecologists and they today join their forces among experimentalists, theoreticians and modelers. While some of us struggle in theoretical and modeling dimensions [3-4], some others perform brilliant works to observe and/or experiment on the same ecological objects [5-6]. In this nice study [6], Magrach et al. succeed in studying relatively large plant-pollinator interaction networks in the field, in Mediterranean ecosystems. For the first time to my knowledge, they study community-wide interactions instead of traditional and easier accessible pairwise interactions. On the basis of a statistically relevant survey, they focus on plant reproductive success and on the role of pollinator interactions in such a success. A more reductionist approach based on simpler pairwise interactions between plants and pollinators would not be able to highlight the interaction network structure (the topology) possibly impacting its responses [1,5], among which the reproductive success of some (plant) species. Yet, such a network analysis requires a fine control of probable biases, as those linked to size or autocorrelation between data of various sites. Here, Magrach et al. did a nice work in capturing rigorously the structures and trends behind this community-wide functioning. To grasp possible relationships between plant and pollinator species is a first mandatory step, but the next critical step requires understanding processes hidden behind such relationships. Here, the authors succeed to reach this step too, by starting interpreting the processes at stake in their studied plant-pollinator networks [7]. In particular, the niche complementarity has been demonstrated to play a determinant role in the plant reproductive success, and has a positive impact on it [6]. When will we be able to detect a community-wise process? This is one of my team’s objectives, and we developed new kind of models with this aim. Also, authors focus here on plant-pollinator network, but the next step might be to gather every kind of interactions into a huge ecosystem network which we call the socio-ecosystemic graph [4]. Indeed, why to limit our view to certain interactions only? It will take time to grasp the whole interaction network an ecosystem is sheltering, but this should be our next challenge. And this paper of Magrach et al. [6] is a first fascinating step in this direction. **References** [1] Campbell, C., Yang, S., Albert, R., and Shea, K. (2011). A network model for plant–pollinator community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(1), 197-202. doi: [10.1073/pnas.1008204108](https://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008204108) [2] Kéfi, S., Miele, V., Wieters, E. A., Navarrete, S. A., and Berlow, E. L. (2016). How structured is the entangled bank? The surprisingly simple organization of multiplex ecological networks leads to increased persistence and resilience. PLoS biology, 14(8), e1002527. doi: [10.1371/journal.pbio.1002527](https://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002527) [3] Gaucherel, C. (2019). The Languages of Nature. When nature writes to itself. Lulu editions, Paris, France. [4] Gaucherel, C., and Pommereau, F. Using discrete systems to exhaustively characterize the dynamics of an integrated ecosystem. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10(9), 1615-1627. doi: [10.1111/2041-210X.13242](https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13242) [5] Bennett, J. M. et al. (2018). A review of European studies on pollination networks and pollen limitation, and a case study designed to fill in a gap. AoB Plants, 10(6), ply068. doi: [10.1093/aobpla/ply068](https://dx.doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/ply068) [6] Magrach, A., Molina, F. P., and Bartomeus, I. (2020). Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive success. bioRxiv, 629931, ver. 7 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: [10.1101/629931](https://dx.doi.org/10.1101/629931) [7] Bastolla, U., Fortuna, M. A., Pascual-García, A., Ferrera, A., Luque, B., and Bascompte, J. (2009). The architecture of mutualistic networks minimizes competition and increases biodiversity. Nature, 458(7241), 1018-1020. doi: [10.1038/nature07950](https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature07950)