Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree
Sébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret
https://doi.org/10.1101/351197
Growth trajectories, better than organ-level functional traits, reveal intraspecific response to environmental variation
Recommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz
Functional traits are “morpho-physio-phenological traits which impact fitness indirectly via their effects on growth, reproduction and survival” [1]. Most functional traits are defined at organ level, e.g. for leaves, roots and stems, and reflect key aspects of resource acquisition and resource use by organisms for their development and reproduction [2]. More rarely, some functional traits can be related to spatial development, such as vegetative height and lateral spread in plants.
Organ-level traits are especially popular because they can be measured in a standard way and easily compared over many plants. But these traits can broadly vary during the life of an organism. For instance, Roggy et al. [3] found that Leaf Mass Area can vary from 30 to 140 g.m^(-2) between seedling and adult stages for the canopy tree Dicorynia guianensis in French Guiana. Fortunel et al. [4] have also showed that developmental stages much contribute to functional trait variation within several Micropholis tree species in lowland Amazonia.
The way plants grow and invest resources into organs is variable during life and allows defining specific developmental sequences and architectural models [5,6]. There is clear ontogenic variation in leaf number, leaf properties and ramification patterns. Ontogenic variations reflect changing adaptation of an individual over its life, depending on the changing environmental conditions.
In this regard, measuring a single functional trait at organ level in adult trees should miss the variation of resource acquisition and use strategies over time. Thus we should built a more integrative approach of ecological development, also called “eco-devo” approach [7].
Although the ecological significance of ontogeny and developmental strategies is now well known, the extent to which it contributes to explain species survival and coexistence in communities is still broadly ignored in functional ecology. Levionnois et al. [8] investigated intraspecific variation of functional traits and growth trajectories in a typical, early-successional tree species in French Guiana, Amazonia. This species, Cecropia obtusa, is generalist regarding soil type and can be found on both white sand and ferralitic soil. The study examines whether there in intraspecific variation in functional traits and growth trajectories of C. obtusa in response to the contrasted soil types.
The tree communities observed on the two types of soils include species with distinctive functional trait values, that is, there are changes in species composition related to different species strategies along the classical wood and leaf economic spectra. The populations of C. obtusa found on the two soils showed some difference in functional traits, but it did not concern traits related to the main economic spectra. Conversely, the populations showed different growth strategies, in terms of spatial and temporal development.
The major lessons we can learn from the study are:
(i) Functional traits measured at organ level cannot reflect well how long-lived plants collect and invest resources during their life. The results show the potential of considering architectural and developmental traits together with organ-level functional traits, to better acknowledge the variation in ecological strategies over plant life, and thus to better understand community assembly processes.
(ii) What makes functional changes between communities differs when considering interspecific and intraspecific variation. Species turnover should encompass different corteges of soil specialists. These specialists are sorted along economic spectra, as shown in tropical rainforests and globally [2]. Conversely, a generalist species such as C. obtusa does occur on contrasted soil, which entails that it can accommodate the contrasted ecological conditions. However, the phenotypic adjustment is not related to how leaves and wood ensure photosynthesis, water and nutrient acquisition, but regards the way the resources are allocated to growth and reproduction over time.
The results of the study stress the need to better integrate growth strategies and ontogeny in the research agenda of functional ecology. We can anticipate that organ-level functional traits and growth trajectories will be more often considered together in ecological studies. The integration should help better understand the temporal niche of organisms, and how organisms can coexist in space and time with other organisms during their life. Recently, Klimešová et al. [9] have proposed standardized protocols for collecting plant modularity traits. Such effort to propose easy-to-measure traits representing plant development and ontogeny, with clear functional roles, should foster the awaited development of an “eco-devo” approach.
References
[1] Violle, C., Navas, M. L., Vile, D., Kazakou, E., Fortunel, C., Hummel, I., & Garnier, E. (2007). Let the concept of trait be functional!. Oikos, 116(5), 882-892. doi: 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15559.x
[2] Díaz, S. et al. (2016). The global spectrum of plant form and function. Nature, 529(7585), 167-171. doi: 10.1038/nature16489
[3] Roggy, J. C., Nicolini, E., Imbert, P., Caraglio, Y., Bosc, A., & Heuret, P. (2005). Links between tree structure and functional leaf traits in the tropical forest tree Dicorynia guianensis Amshoff (Caesalpiniaceae). Annals of forest science, 62(6), 553-564. doi: 10.1051/forest:2005048
[4] Fortunel, C., Stahl, C., Heuret, P., Nicolini, E. & Baraloto, C. (2020). Disentangling the effects of environment and ontogeny on tree functional dimensions for congeneric species in tropical forests. New Phytologist. doi: 10.1111/nph.16393
[5] Barthélémy, D., & Caraglio, Y. (2007). Plant architecture: a dynamic, multilevel and comprehensive approach to plant form, structure and ontogeny. Annals of botany, 99(3), 375-407. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl260
[6] Hallé, F., & Oldeman, R. A. (1975). An essay on the architecture and dynamics of growth of tropical trees. Kuala Lumpur: Penerbit Universiti Malaya.
[7] Sultan, S. E. (2007). Development in context: the timely emergence of eco-devo. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 22(11), 575-582. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2007.06.014
[8] Levionnois, S., Tysklind, N., Nicolini, E., Ferry, B., Troispoux, V., Le Moguedec, G., Morel, H., Stahl, C., Coste, S., Caron, H. & Heuret, P. (2020). Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree. bioRxiv, 351197, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/351197
[9] Klimešová, J. et al. (2019). Handbook of standardized protocols for collecting plant modularity traits. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics, 40, 125485. doi: 10.1016/j.ppees.2019.125485
| Soil variation response is mediated by growth trajectories rather than functional traits in a widespread pioneer Neotropical tree | Sébastien Levionnois, Niklas Tysklind, Eric Nicolini, Bruno Ferry, Valérie Troispoux, Gilles Le Moguedec, Hélène Morel, Clément Stahl, Sabrina Coste, Henri Caron, Patrick Heuret | <p style="text-align: justify;">1- Trait-environment relationships have been described at the community level across tree species. However, whether interspecific trait-environment relationships are consistent at the intraspecific level is yet unkn... |  | Botany, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Habitat selection, Ontogeny, Tropical ecology | François Munoz | | 2018-06-21 17:13:17 | View |
Recommendations to address uncertainties in environmental risk assessment using toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics models
Virgile Baudrot and Sandrine Charles
https://doi.org/10.1101/356469
Addressing uncertainty in Environmental Risk Assessment using mechanistic toxicological models coupled with Bayesian inference
Recommended by Luis Schiesari based on reviews by Andreas Focks and 2 anonymous reviewers
Environmental Risk Assessment (ERA) is a strategic conceptual framework to characterize the nature and magnitude of risks, to humans and biodiversity, of the release of chemical contaminants in the environment. Several measures have been suggested to enhance the science and application of ERA, including the identification and acknowledgment of uncertainties that potentially influence the outcome of risk assessments, and the appropriate consideration of temporal scale and its linkage to assessment endpoints [1].
Baudrot & Charles [2] proposed to approach these questions by coupling toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics models, which describe the time-course of processes leading to the adverse effects of a toxicant, with Bayesian inference. TKTD models separate processes influencing an organismal internal exposure (´toxicokinetics´, i.e., the uptake, bioaccumulation, distribution, biotransformation and elimination of a toxicant) from processes leading to adverse effects and ultimately its death (´toxicodynamics´) [3]. Although species and substance specific, the mechanistic nature of TKTD models facilitates the comparison of different toxicants, species, life stages, environmental conditions and endpoints [4].
Baudrot & Charles [2] investigated the use of a Bayesian framework to assess the uncertainties surrounding the calibration of General Unified Threshold Models of Survival (a category of TKTD) with data from standard toxicity tests, and their propagation to predictions of regulatory toxicity endpoints such as LC(x,t) [the lethal concentration affecting any x% of the population at any given exposure duration of time t] and MF(x,t) [an exposure multiplication factor leading to any x% effect reduction due to the contaminant at any time t].
Once calibrated with empirical data, GUTS models were used to explore individual survival over time, and under untested exposure conditions. Lethal concentrations displayed a strong curvilinear decline with time of exposure. For a given total amount of contaminant, pulses separated by short time intervals yielded higher mortality than pulses separated by long time intervals, as did few pulses of high amplitude when compared to multiple pulses of low amplitude. The response to a pulsed contaminant exposure was strongly influenced by contaminant depuration times. These findings highlight one important contribution of TKTD modelling in ecotoxicology: they represent just a few of the hundreds of exposure scenarios that could be mathematically explored, and that would be unfeasible or even unethical to conduct experimentally.
GUTS models were also used for interpolations or extrapolations of assessment endpoints, and their marginal distributions. A case in point is the incipient lethal concentration. The responses of model organisms to contaminants in standard toxicity tests are typically assessed at fixed times of exposure (e.g. 24h or 48h in the Daphnia magna acute toxicity test). However, because lethal concentrations are strongly time-dependent, it has been suggested that a more meaningful endpoint would be the incipient (i.e. asymptotic) lethal concentration when time of exposure increases to infinity. The authors present a mathematical solution for calculating the marginal distribution of such incipient lethal concentration, thereby providing both more relevant information and a way of comparing experiments, compounds or species tested for different periods of time.
Uncertainties were found to change drastically with time of exposure, being maximal at extreme values of x for both LC(x,t) and MF(x,t). In practice this means that assessment endpoints estimated when the effects of the contaminant are weak (such as LC10, the contaminant concentration resulting in the mortality of 10% of the experimental population), a commonly used assessment value in ERA, are prone to be highly variable.
The authors end with recommendations for improved experimental design, including (i) using assessment endpoints at intermediate values of x (e.g., LC50 instead of LC10) (ii) prolonging exposure and recording mortality over the course of the experiment (iii) experimenting one or few peaks of high amplitude close to each other when assessing pulsed exposure. Whereas these recommendations are not that different from current practices, they are based on a more coherent mechanistic grounding.
Overall, this and other contributions from Charles, Baudrot and their research group contribute to turn TKTD models into a real tool for Environmental Risk Assessment. Further enhancement of ERA´s science and application could be achieved by extending the use of TKTD models to sublethal rather than lethal effects, and to chronic rather than acute exposure, as these are more controversial issues in decision-making regarding contaminated sites.
References
[1] Dale, V. H., Biddinger, G. R., Newman, M. C., Oris, J. T., Suter, G. W., Thompson, T., ... & Chapman, P. M. (2008). Enhancing the ecological risk assessment process. Integrated environmental assessment and management, 4(3), 306-313. doi: 10.1897/IEAM_2007-066.1
[2] Baudrot, V., & Charles, S. (2018). Recommendations to address uncertainties in environmental risk assessment using toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics models. bioRxiv, 356469, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecol. doi: 10.1101/356469
[3] EFSA Panel on Plant Protection Products and their Residues (PPR), Ockleford, C., Adriaanse, P., Berny, P., Brock, T., Duquesne, S., ... & Kuhl, T. (2018). Scientific Opinion on the state of the art of Toxicokinetic/Toxicodynamic (TKTD) effect models for regulatory risk assessment of pesticides for aquatic organisms. EFSA Journal, 16(8), e05377. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5377
[4] Jager, T., Albert, C., Preuss, T. G., & Ashauer, R. (2011). General unified threshold model of survival-a toxicokinetic-toxicodynamic framework for ecotoxicology. Environmental science & technology, 45(7), 2529-2540. doi: 10.1021/es103092a
| Recommendations to address uncertainties in environmental risk assessment using toxicokinetics-toxicodynamics models | Virgile Baudrot and Sandrine Charles | <p>Providing reliable environmental quality standards (EQS) is a challenging issue for environmental risk assessment (ERA). These EQS are derived from toxicity endpoints estimated from dose-response models to identify and characterize the environm... | 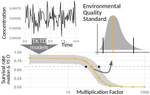 | Chemical ecology, Ecotoxicology, Experimental ecology, Statistical ecology | Luis Schiesari | | 2018-06-27 21:33:30 | View |
Photosynthesis of Laminaria digitata during the immersion and emersion periods of spring tidal cycles during hot, sunny weather
Aline Migné, Gaspard Delebecq, Dominique Davoult, Nicolas Spilmont, Dominique Menu, Marie-Andrée Janquin and François Gévaert
https://hal.sorbonne-universite.fr/hal-01827565v4
Evaluating physiological responses of a kelp to environmental changes at its vulnerable equatorward range limit
Recommended by Matthew Bracken based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Understanding processes at species’ range limits is of paramount importance in an era of global change. For example, the boreal kelp Laminaria digitata, which dominates low intertidal and shallow subtidal rocky reefs in northwestern Europe, is declining in the equatorward portion of its range [1]. In this contribution, Migné and colleagues [2] focus on L. digitata near its southern range limit on the coast of France and use a variety of techniques to paint a complete picture of the physiological responses of the kelp to environmental changes. Importantly, and in contrast to earlier work on the species which focused on subtidal individuals (e.g. [3]), Migné et al. [2] describe responses not only in the most physiologically stressful portion of the species’ range but also in the most stressful portion of its local environment: the upper portion of its zone on the shoreline, where it is periodically exposed to aerial conditions and associated thermal and desiccation stresses.
The authors show that whereas L. digitata possesses mechanisms to protect it from irradiance stress at low tide, these mechanisms are not sufficient to prevent damage to photosynthetic pathways (e.g., reduction in optimal quantum yields of photosystem II). This species experiences severe heat stress associated with mid-day low tides during the summer, and the cumulative damage associated with these stresses is likely associated with the range contraction that is currently underway. Given the important role that L. digitata plays as food and habitat for other organisms, its loss will have cascading impacts on community structure and ecosystem functioning. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these declines is essential to understanding the impacts of climate change on species, communities, and ecosystems.
References
[1] Raybaud, V., Beaugrand, G., Goberville, E., Delebecq, G., Destombe, C., Valero, M., Davoult, D., Morin, P. & Gevaert, F. (2013). Decline in kelp in west Europe and climate. PloS one, 8(6), e66044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066044
[2] Delebecq, G., Davoult, D., Menu, D., Janquin, M. A., Migné, A., Dauvin, J. C., & Gevaert, F. (2011). In situ photosynthetic performance of Laminaria digitata (Phaeophyceae) during spring tides in Northern Brittany. CBM-Cahiers de Biologie Marine, 52(4), 405. doi: 10.21411/CBM.A.C9EE91F
[3] Migné, A., Delebecq, G., Davoult, D., Spilmont, N., Menu, D., Janquin, M.-A., and Gevaert, F. (2019). Photosynthesis of Laminaria digitata during the immersion and emersion periods of spring tidal cycles during hot, sunny weather. Hal, 01827565, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. hal-01827565
| Photosynthesis of Laminaria digitata during the immersion and emersion periods of spring tidal cycles during hot, sunny weather | Aline Migné, Gaspard Delebecq, Dominique Davoult, Nicolas Spilmont, Dominique Menu, Marie-Andrée Janquin and François Gévaert | The boreal kelp Laminaria digitata dominates the low intertidal and upper subtidal zones of moderately exposed rocky shores in north-western Europe. Due to ocean warming, this foundation species is predicted to disappear from French coasts in the ... |  | Marine ecology | Matthew Bracken | | 2018-07-02 18:03:11 | View |
Is behavioral flexibility manipulatable and, if so, does it improve flexibility and problem solving in a new context?
Corina Logan, Carolyn Rowney, Luisa Bergeron, Benjamin Seitz, Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Kelsey McCune
http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_flexmanip.html
Can context changes improve behavioral flexibility? Towards a better understanding of species adaptability to environmental changes
Recommended by Aurélie Coulon based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin
Behavioral flexibility is a key for species adaptation to new environments. Predicting species responses to new contexts hence requires knowledge on the amount to and conditions in which behavior can be flexible. This is what Logan and collaborators propose to assess in a series of experiments on the great-tailed grackles, in a context of rapid range expansion. This pre-registration is integrated into this large research project and concerns more specifically the manipulability of the cognitive aspects of behavioral flexibility. Logan and collaborators will use reversal learning tests to test whether (i) behavioral flexibility is manipulatable, (ii) manipulating flexibility improves flexibility and problem solving in a new context, (iii) flexibility is repeatable within individuals, (iv) individuals are faster at problem solving as they progress through serial reversals. The pre-registration carefully details the hypotheses, their associated predictions and alternatives, and the plan of statistical analyses, including power tests. The ambitious program presented in this pre-registration has the potential to provide important pieces to better understand the mechanisms of species adaptability to new environments.
| Is behavioral flexibility manipulatable and, if so, does it improve flexibility and problem solving in a new context? | Corina Logan, Carolyn Rowney, Luisa Bergeron, Benjamin Seitz, Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Kelsey McCune | This is one of the first studies planned for our long-term research on the role of behavioral flexibility in rapid geographic range expansions. Behavioral flexibility, the ability to adapt behavior to new circumstances, is thought to play an impor... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Preregistrations, Zoology | Aurélie Coulon | | 2018-07-03 13:23:10 | View |
Sex makes them sleepy: host reproductive status induces diapause in a parasitoid population experiencing harsh winters
Tougeron K., Brodeur J., van Baaren J., Renault D. and Le Lann C.
https://doi.org/10.1101/371385
The response of interacting species to biotic seasonal cues
Recommended by Adele Mennerat and Enric Frago based on reviews by Anne Duplouy and 1 anonymous reviewer
In temperate regions, food abundance and quality vary greatly throughout the year, and the ability of organisms to synchronise their phenology to these changes is a key determinant of their reproductive success. Successful synchronisation requires that cues are perceived prior to change, leaving time for physiological adjustments.
But what are the cues used to anticipate seasonal changes? Abiotic factors like temperature and photoperiod are known for their driving role in the phenology of a wide range of plant an animal species [1,2] . Arguably though, biotic cues directly linked to upcoming changes in food abundance could be as important as abiotic factors, but the response of organisms to these cues remains relatively unexplored.
Biotic cues may be particularly important for higher trophic levels because of their tight interaction with the hosts or preys they depend on. In this study Tougeron and colleagues [3] address this topic using interacting insects, namely herbivorous aphids and the parasitic wasps (or parasitoids) that feed on them. The key finding of the study by Tougeron et al. [3] is that the host morph in which parasitic wasp larvae develop is a major driver of diapause induction. More importantly, the aphid morph that triggers diapause in the wasp is the one that will lay overwintering eggs in autumn at the onset of harsh winter conditions. Its neatly designed experimental setup also provides evidence that this response may vary across populations as host-dependent diapause induction was only observed in a wasp population that originated from a cold area. As the authors suggests, this may be caused by local adaptation to environmental conditions because, relative to warmer regions, missing the time window to enter diapause in colder regions may have more dramatic consequences. The study also shows that different aphid morphs differ greatly in their chemical composition, and points to particular types of metabolites like sugars and polyols as specific cues for diapause induction.
This study provides a nice example of the complexity of biological interactions, and of the importance of phenological synchrony between parasites and their hosts. The authors provide evidence that phenological synchrony is likely to be achieved via chemical cues derived from the host. A similar approach was used to demonstrate that the herbivorous beetle Leptinotarsa decemlineata uses plant chemical cues to enter diapause [4]. Beetles fed on plants exposed to pre-wintering conditions entered diapause in higher proportions than those fed on control plants grown at normal conditions. As done by Tougeron et al. [3], in [4] the authors associated diapause induction to changes in the composition of metabolites in the plant. In both studies, however, the missing piece is to unveil the particular chemical involved, an answer that may be provided by future experiments.
Latitudinal clines in diapause induction have been described in a number of insect species [5]. Correlative studies, in which the phenology of different trophic levels has been monitored, suggest that these clines may in part be governed by lower trophic levels. For example, Phillimore et al. [6] explored the relative contribution of temperature and of host plant phenology on adult flight periods of the butterfly Anthocharis cardamines. Tougeron et al. [3], by using aphids and their associated parasitoids, take the field further by moving from observational studies to experiments. Besides, aphids are not only a tractable host-parasite system in the laboratory, they are important agricultural pests. Improving our basic knowledge of their ecological interactions may ultimately contribute to improving pest control techniques. The study by Tougeron et al. [3] exemplifies the multiple benefits that can be gained from addressing fundamental questions in species that are also directly relevant to society.
References
[1] Tauber, M. J., Tauber, C. A., and Masaki, S. (1986). Seasonal Adaptations of Insects. Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press.
[2] Bradshaw, W. E., and Holzapfel, C. M. (2007). Evolution of Animal Photoperiodism. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 38(1), 1–25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.37.091305.110115
[3] Tougeron, K., Brodeur, J., Baaren, J. van, Renault, D., and Lann, C. L. (2019b). Sex makes them sleepy: host reproductive status induces diapause in a parasitoid population experiencing harsh winters. bioRxiv, 371385, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/371385
[4] Izzo, V. M., Armstrong, J., Hawthorne, D., and Chen, Y. (2014). Time of the season: the effect of host photoperiodism on diapause induction in an insect herbivore, Leptinotarsa decemlineata. Ecological Entomology, 39(1), 75–82. doi: 10.1111/een.12066
[5] Hut Roelof A., Paolucci Silvia, Dor Roi, Kyriacou Charalambos P., and Daan Serge. (2013). Latitudinal clines: an evolutionary view on biological rhythms. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 280(1765), 20130433. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2013.0433
[6] Phillimore, A. B., Stålhandske, S., Smithers, R. J., and Bernard, R. (2012). Dissecting the Contributions of Plasticity and Local Adaptation to the Phenology of a Butterfly and Its Host Plants. The American Naturalist, 180(5), 655–670. doi: 10.1086/667893
| Sex makes them sleepy: host reproductive status induces diapause in a parasitoid population experiencing harsh winters | Tougeron K., Brodeur J., van Baaren J., Renault D. and Le Lann C. | <p>When organisms coevolve, any change in one species can induce phenotypic changes in traits and ecology of the other species. The role such interactions play in ecosystems is central, but their mechanistic bases remain underexplored. Upper troph... |  | Coexistence, Evolutionary ecology, Experimental ecology, Host-parasite interactions, Physiology | Adele Mennerat | | 2018-07-18 18:51:03 | View |
Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits
Legay Nicolas, Grassein Fabrice, Arnoldi Cindy, Segura Raphaël, Laîné Philippe, Lavorel Sandra, Clément Jean-Christophe
https://doi.org/10.1101/372235
Nitrate or not nitrate. That is the question
Recommended by Sébastien Barot based on reviews by Vincent Maire and 1 anonymous reviewer
The article by Legay et al. [1] addresses two main issues: the links between belowground and aboveground plant traits and the links between plant strategies (as defined by these traits) and the capacity to absorb nitrate and ammonium. I recommend this work because these are important and current issues. The literature on plant traits is extremely rich and the existence of a leaf economic spectrum linked to a gradient between conservative and acquisitive plants is now extremely well established [2-3]. Many teams are now working on belowground traits and possible links with the aboveground gradients [4-5]. It seems indeed that there is a root economic spectrum but this spectrum is apparently less pronounced than the leaf economic spectrum. The existence of links between the two spectrums are still controversial and are likely not universal as suggested by discrepant results and after all a plant could have a conservative strategy aboveground and an acquisitive strategy belowground (or vice-versa) because, indeed, constraints are different belowground and aboveground (for example because in given ecosystem/vegetation type light may be abundant but not water or mineral nutrients). The various results obtained also suggest that we do not full understand the diversity of belowground strategies, what is at stake with these strategies, and the links with root characteristics.
Each time I give a conference on the work we are carrying out on African grasses that likely absorb ammonium preferentially because they inhibit nitrification [6-7], somebody asks me a question about the fact that plant essentially absorb nitrate because ammonium is toxic and nitrate more available in the soil. The present article confirms that this is not the case and that, though there are currently some teams working on the subject, we do not really know for the moment whether plants absorb nitrate or ammonium, in which proportion, how plastic this proportion is within individuals and within species. This subject seems to me crucial because it is linked to (1) the capacity of ecosystems to conserve nitrogen [8], because nitrate, much more than ammonium, goes out of ecosystems through leaching and denitrification, (2) to carbon cycling and plant energy budget because absorbing nitrate requires spending mucho more energy than absorbing ammonium because nitrate must be reduced before being incorporated in plant biomass, which is very energy costly. These two issues are naturally very relevant to develop efficient cropping systems in terms of carbon and nitrogen.
Interestingly, the present article, comparing three grass species in different sites, suggests that there is no trade-off between the absorption of nitrate and ammonium: more acquisitive individuals tend to absorb more ammonium and nitrate. This is contrary to hypotheses we made to predict the outcome of competition between plants absorbing nitrate and ammonium in different proportions [9] but should be tested in the future comparing many different types of plants. The results also suggest that more conservative plants absorb relatively more ammonium, which makes sense because this allows them to spare the energy necessary to reduce nitrate. This leads to the question of the effect of these strategies on nitrogen retention within the ecosystem. If nitrification is high (low), absorbing ammonium is not efficient and likely leads to high (low) nitrogen losses. This should be tested in the future. Moreover, the authors have measured the absorption of nitrate and ammonium through measurements at the root scale on cut roots. This should be complemented by measurements at the whole plant scale.
References
[1] Legay, N., Grassein, F., Arnoldi, C., Segura, R., Laîné, P., Lavorel, S. and Clément, J.-C. (2020). Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits. bioRxiv, 372235, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/372235
[2] Shipley, B., Lechowicz, M.J., Wright, I. & Reich, P.B. (2006) Fundamental trade-offs generating the worldwide leaf economics spectrum. Ecology, 87, 535-541. doi: 10.1890/05-1051
[3] Reich, P.B. (2014) The world-wide ‘fast-slow’ plant economics spectrum: a traits manifesto. J. Ecol., 102, 275-301. doi: 10.1111/1365-2745.12211
[4] Maire, V., Gross, N., Pontes, L.D.S., Picon-Cochard, C. & Soussana, J.F. (2009) Trade-off between root nitrogen acquisition and shoot nitrogen utilization across 13 co-occurring pasture grass species. Func. Ecol., 23, 668-679. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2009.01557.x
[5] Roumet, C., Birouste, M., Picon-Cochard, C., Ghestem, M., Osman, N., Vrignon-Brenas, S., Cao, K.F. & Stokes, A. (2016) Root structure-function relationships in 74 species: evidence of a root economics spectrum related to carbon economy. New. Phytol., 210, 815-826. doi: 10.1111/nph.13828
[6] Lata, J.-C., Degrange, V., Raynaud, X., Maron, P.-A., Lensi, R. & Abbadie, L. (2004) Grass populations control nitrification in savanna soils. Funct. Ecol., 18, 605-611. doi: 10.1111/j.0269-8463.2004.00880.x
[7] Srikanthasamy, T., Leloup, J., N’Dri, A.B., Barot, S., Gervaix, J., Koné, A.W., Koffi, K.F., Le Roux, X., Raynaud, X. & Lata, J.-C. (2018) Contrasting effects of grasses and trees on microbial N-cycling in an African humid savanna. Soil Biol. Biochem., 117, 153-163. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.11.016
[8] Boudsocq, S., Lata, J.C., Mathieu, J., Abbadie, L. & Barot, S. (2009) Modelling approach to analyze the effects of nitrification inhibition on primary production. Func. Ecol., 23, 220-230. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01476.x
[9] Boudsocq, S., Niboyet, A., Lata, J.-C., Raynaud, X., Loeuille, N., Mathieu, J., Blouin, M., Abbadie, L. & Barot, S. (2012) Plant preference for ammonium versus nitrate: a neglected determinant of ecosystem functioning? Am. Nat., 180, 60-69. doi: 10.1086/665997
| Studies of NH4+ and NO3- uptake ability of subalpine plants and resource-use strategy identified by their functional traits | Legay Nicolas, Grassein Fabrice, Arnoldi Cindy, Segura Raphaël, Laîné Philippe, Lavorel Sandra, Clément Jean-Christophe | <p>The leaf economics spectrum (LES) is based on a suite of leaf traits related to plant functioning and ranges from resource-conservative to resource-acquisitive strategies. However, the relationships with root traits, and the associated belowgro... |  | Community ecology, Physiology, Terrestrial ecology | Sébastien Barot | | 2018-07-19 14:22:28 | View |
The taxonomic and functional biogeographies of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities across boreal lakes
Nicolas F St-Gelais, Richard J Vogt, Paul A del Giorgio, Beatrix E Beisner
https://doi.org/10.1101/373332
The difficult interpretation of species co-distribution
Recommended by Dominique Gravel based on reviews by Anthony Maire and Emilie Macke
Ecology is the study of the distribution of organisms in space and time and their interactions. As such, there is a tradition of studies relating abiotic environmental conditions to species distribution, while another one is concerned by the effects of consumers on the abundance of their resources. Interestingly, joining the dots appears more difficult than it would suggest: eluding the effect of species interactions on distribution remains one of the greatest challenges to elucidate nowadays (Kissling et al. 2012). Theory suggests that yes, species interactions such as predation and competition should influence range limits (Godsoe et al. 2017), but the common intuition among many biogeographers remains that over large areas such as regions and continents, environmental drivers like temperature and precipitation overwhelm their local effects. Answering this question is of primary importance in the context where species are moving around with climate warming. Inconsistencies in food web structure may arise with asynchronized movements of consumers and their resources, leading to a major disruption in regulation and potentially ecosystem functioning. Solving this problem, however, remains very challenging because we have to rely on observational data since experiments are hard to perform at the biogeographical scale.
The study of St-Gelais is an interesting step forward to solve this problem. Their main objective was to assess the strength of the association between phytoplankton and zooplankton communities at a large spatial scale, looking at the spatial covariation of both taxonomic and functional composition. To do so, they undertook a massive survey of more than 100 lakes across three regions of the boreal region of Québec. Species and functional composition were recorded, along with a set of abiotic variables. Classic community ecology at this point. The difficulty they faced was to disentangle the multiple causal relationships involved in the distribution of both trophic levels. Teasing apart bottom-up and top-down forces driving the assembly of plankton communities using observational data is not an easy task. On the one hand, both trophic levels could respond to variations in temperature, nutrient availability and dissolved organic carbon. The interpretation is fairly straightforward if the two levels respond to different factors, but the situation is much more complicated when they do respond similarly. There are potentially three possible underlying scenarios. First, the phyto and zooplankton communities may share the same environmental requirements, thereby generating a joint distribution over gradients such as temperature and nutrient availability. Second, the abiotic environment could drive the distribution of the phytoplankton community, which would then propagate up and influence the distribution of the zooplankton community. Alternatively, the abiotic environment could constrain the distribution of the zooplankton, which could then affect the one of phytoplankton. In addition to all of these factors, St-Gelais et al also consider that dispersal may limit the distribution, well aware of previous studies documenting stronger dispersal limitations for zooplankton communities.
Unfortunately, there is not a single statistical approach that could be taken from the shelf and used to elucidate drivers of co-distribution. Joint species distribution was once envisioned as a major step forward in this direction (Warton et al. 2015), but there are several limits preventing the direct interpretation that co-occurrence is linked to interactions (Blanchet et al. 2020). Rather, St-Gelais used a variety of multivariate statistics to reveal the structure in their observational data. First, using a Procrustes analysis (a method testing if the spatial variation of one community is correlated to the structure of another community), they found a significant correlation between phytoplankton and zooplankton communities, indicating a taxonomic coupling between the groups. Interestingly, this observation was maintained for functional composition only when interaction-related traits were considered. At this point, these results strongly suggest that interactions are involved in the correlation, but it's hard to decipher between bottom-up and top-down perspectives. A complementary analysis performed with a constrained ordination, per trophic level, provided complementary pieces of information. First observation was that only functional variation was found to be related to the different environmental variables, not taxonomic variation. Despite that trophic levels responded to water quality variables, spatial autocorrelation was more important for zooplankton communities and the two layers appear to respond to different variables.
It is impossible with those results to formulate a strong conclusion about whether grazing influence the co-distribution of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities. That's the mere nature of observational data. While there is a strong spatial association between them, there are also diverging responses to the different environmental variables considered. But the contrast between taxonomic and functional composition is nonetheless informative and it seems that beyond the idiosyncrasies of species composition, trait distribution may be more informative and general. Perhaps the most original contribution of this study is the hierarchical approach to analyze the data, combined with the simultaneous analysis of taxonomic and functional distributions. Having access to a vast catalog of multivariate statistical techniques, a careful selection of analyses helps revealing key features in the data, rejecting some hypotheses and accepting others. Hopefully, we will see more and more of such multi-trophic approaches to distribution because it is now clear that the factors driving distribution are much more complicated than anticipated in more traditional analyses of community data. Biodiversity is more than a species list, it is also all of the interactions between them, influencing their distribution and abundance (Jordano 2016).
References
Blanchet FG, Cazelles K, Gravel D (2020) Co-occurrence is not evidence of ecological interactions. Ecology Letters, 23, 1050–1063. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.13525
Godsoe W, Jankowski J, Holt RD, Gravel D (2017) Integrating Biogeography with Contemporary Niche Theory. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 32, 488–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2017.03.008
Jordano P (2016) Chasing Ecological Interactions. PLOS Biology, 14, e1002559. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1002559
Kissling WD, Dormann CF, Groeneveld J, Hickler T, Kühn I, McInerny GJ, Montoya JM, Römermann C, Schiffers K, Schurr FM, Singer A, Svenning J-C, Zimmermann NE, O’Hara RB (2012) Towards novel approaches to modelling biotic interactions in multispecies assemblages at large spatial extents. Journal of Biogeography, 39, 2163–2178. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2011.02663.x
St-Gelais NF, Vogt RJ, Giorgio PA del, Beisner BE (2021) The taxonomic and functional biogeographies of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities across boreal lakes. bioRxiv, 373332, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/373332
Warton DI, Blanchet FG, O’Hara RB, Ovaskainen O, Taskinen S, Walker SC, Hui FKC (2015) So Many Variables: Joint Modeling in Community Ecology. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 30, 766–779. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2015.09.007
Wisz MS, Pottier J, Kissling WD, Pellissier L, Lenoir J, Damgaard CF, Dormann CF, Forchhammer MC, Grytnes J-A, Guisan A, Heikkinen RK, Høye TT, Kühn I, Luoto M, Maiorano L, Nilsson M-C, Normand S, Öckinger E, Schmidt NM, Termansen M, Timmermann A, Wardle DA, Aastrup P, Svenning J-C (2013) The role of biotic interactions in shaping distributions and realised assemblages of species: implications for species distribution modelling. Biological Reviews, 88, 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-185X.2012.00235.x
| The taxonomic and functional biogeographies of phytoplankton and zooplankton communities across boreal lakes | Nicolas F St-Gelais, Richard J Vogt, Paul A del Giorgio, Beatrix E Beisner | <p>Strong trophic interactions link primary producers (phytoplankton) and consumers (zooplankton) in lakes. However, the influence of such interactions on the biogeographical distribution of the taxa and functional traits of planktonic organ... |  | Biogeography, Community ecology, Species distributions | Dominique Gravel | | 2018-07-24 15:01:51 | View |
Inferring macro-ecological patterns from local species' occurrences
Anna Tovo, Marco Formentin, Samir Suweis, Samuele Stivanello, Sandro Azaele, Amos Maritan
https://doi.org/10.1101/387456
Upscaling the neighborhood: how to get species diversity, abundance and range distributions from local presence/absence data
Recommended by Matthieu Barbier based on reviews by Kevin Cazelles and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Kevin Cazelles and 1 anonymous reviewer
How do you estimate the biodiversity of a whole community, or the distribution of abundances and ranges of its species, from presence/absence data in scattered samples?
It all starts with the collector's dilemma: if you double the number of samples, you will not get double the number of species, since you will find many of the same common species, and only a few new rare ones.
This non-additivity has prompted many ecologists to study the Species-Area Relationship. A common theoretical approach has been to connect this spatial pattern to the overall distribution of how common or rare a species can be. At least since Fisher's celebrated log-series [1], ecologists have been trying to, first, infer the shape of the Species Abundance Distribution, and then, use it to predict how many species should be found in a given area or a given number of samples. This has found many applications, from microbial communities to tropical forests, from estimating the number of yet-unknown species to predicting how much biodiversity may be lost if a fraction of the habitat is removed.
In this elegant work, Tovo et al. [2] propose a method that starts only from presence/absence data over a number of samples, and provides the community's diversity, as well as its abundance and range size distributions. This method is simple, analytically explicit, and accurate: the authors test it on the classic Pasoh and Barro Colorado Island tropical forest datasets, and on simulated data. They make a very laudable effort in both explaining its theoretical underpinnings, and proposing a straightforward step-by-step guide to applying it to data.
The core of Tovo et al's method is a simple property: the scale invariance of the Negative Binomial (NB) distribution. Subsampling from a NB gives another NB, where a single parameter has changed. Therefore, if the Species Abundance Distribution is close enough to some NB (which is flexible enough to accommodate all the data here), we can estimate how this parameter changes when going from (1) a single sample to (2) all the available samples, and from there, extrapolate to (3) the entire community.
This principle was first applied by the authors in a previous study [3] that required abundance data in the samples, rather than just presence/absence. Given that binary occurrence data is far more available in a variety of empirical settings, this extension is worthwhile (including its new predictions on range size distributions), and it deserves to be widely known and tested.
ADDITIONAL COMMENTS
1) To explain the novelty of the authors' contribution, it is useful to look at competing techniques.
Some ""parametric"" approaches try to infer the whole-community Species Abundance Distribution (SAD) by guessing its functional form (Gaussian, power-law, log-series...) and fitting its parameters from sampled data. The issue is that this distribution shape may not remain in the same family as we increase the sampling effort or area, so the regression problem may not be well-defined. This is where the Negative Binomial's scale invariance is useful.
Other ""non-parametric"" approaches have renounced guessing the whole SAD: they simply try to approximate of its tail of rare species, by looking at how many species are found in only one (or a few) samples. From this, they derive an estimate of biodiversity that is agnostic to the rest of the SAD. Tovo et al. [2] show the issue with these approaches: they extrapolate from the properties of individual samples to the whole community, but do not properly account for the bias introduced by the amount of sampling (the intermediate scale (2) in the summary above).
2) The main condition for all such approaches to work is well-mixedness: each sample should be sufficiently like a lot drawn from the same skewed lottery. As long as that condition applies, finding the best approach is a theoretical matter of probabilities and combinatorics that may, in time, be given a definite answer.
The authors also show that ""well-mixed"" is not as restrictive as it sounds: the method works both on real data (which is never perfectly mixed) and on simulations where species are even more spatially clustered than the empirical data. In addition, the Negative Binomial's scale invariance entails that, if it works well enough at some spatial scale, it will also work at all higher scales (until one reaches the edges of the sufficiently-well-mixed community)
3) One may ask: why the Negative Binomial as a Species Abundance Distribution?
If one wishes for some dynamical explanation, the Negative Binomial can be derived from neutral birth and death process with immigration, as shown by the authors in [3]. But to be applied to data, it should only be able to approximate the empirical distribution well enough (at all relevant scales). Depending on one's taste, this type of probabilistic approaches can be interpreted as:
- purely phenomenological, describing only the observational process of sampling from an existing state of affairs, not the ecological processes that gave rise to that state.
- a null model, from which everything in practice is expected to deviate to some extent.
- or a way to capture the statistical forces that tend to induce stable relationships between different patterns (as long as no ecological process opposes them strongly enough).
References
[1] Fisher, R. A., Corbet, A. S., & Williams, C. B. (1943). The relation between the number of species and the number of individuals in a random sample of an animal population. The Journal of Animal Ecology, 42-58. doi: 10.2307/1411
[2] Tovo, A., Formentin, M., Suweis, S., Stivanello, S., Azaele, S., & Maritan, A. (2019). Inferring macro-ecological patterns from local species' occurrences. bioRxiv, 387456, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecol. doi: 10.1101/387456
[3] Tovo, A., Suweis, S., Formentin, M., Favretti, M., Volkov, I., Banavar, J. R., Azaele, S., & Maritan, A. (2017). Upscaling species richness and abundances in tropical forests. Science Advances, 3(10), e1701438. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701438
| Inferring macro-ecological patterns from local species' occurrences | Anna Tovo, Marco Formentin, Samir Suweis, Samuele Stivanello, Sandro Azaele, Amos Maritan | <p>Biodiversity provides support for life, vital provisions, regulating services and has positive cultural impacts. It is therefore important to have accurate methods to measure biodiversity, in order to safeguard it when we discover it to be thre... |  | Macroecology, Species distributions, Statistical ecology, Theoretical ecology | Matthieu Barbier | | 2018-08-09 16:44:09 | View |
Do the more flexible individuals rely more on causal cognition? Observation versus intervention in causal inference in great-tailed grackles
Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Luisa Bergeron, Carolyn Rowney, Benjamin Seitz, Kelsey McCune, Corina Logan
http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_causal.html
From cognition to range dynamics: advancing our understanding of macroecological patterns
Recommended by Emanuel A. Fronhofer based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Understanding the distribution of species on earth is one of the fundamental challenges in ecology and evolution. For a long time, this challenge has mainly been addressed from a correlative point of view with a focus on abiotic factors determining a species abiotic niche (classical bioenvelope models; [1]). It is only recently that researchers have realized that behaviour and especially plasticity in behaviour may play a central role in determining species ranges and their dynamics [e.g., 2-5]. Blaisdell et al. propose to take this even one step further and to analyse how behavioural flexibility and possibly associated causal cognition impacts range dynamics.
The current preregistration is integrated in an ambitious long-term research plan that aims at addressing the above outlined question and focuses specifically on investigating whether more behaviourally flexible individuals are better at deriving causal inferences. The model system the authors plan on using are Great-tailed Grackles which have expanded their range into North America during the last century. The preregistration by Blaisdell et al. is a great example of the future of scientific research: it includes conceptual models, alternative hypotheses and testable predictions along with a sound sampling and analysis plan and embraces the principles of Open Science.
Overall, the research the authors propose is fascinating and of highest relevance, as it aims at bridging scales from the microscopic mechanisms that underlie animal behaviour to macroscopic, macroecological consequences (see also [3]). I am very much looking forward to the results the authors will report.
References
[1] Elith, J. & Leathwick, J. R. 2009. Species distribution models: ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 40: 677-697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.110308.120159
[2] Kubisch, A.; Degen, T.; Hovestadt, T. & Poethke, H. J. (2013) Predicting range shifts under global change: the balance between local adaptation and dispersal. Ecography 36: 873-882. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0587.2012.00062.x
[3] Keith, S. A. & Bull, J. W. (2017) Animal culture impacts species' capacity to realise climate-driven range shifts. Ecography, 40: 296-304. doi: 10.1111/ecog.02481
[4] Sullivan, L. L.; Li, B.; Miller, T. E.; Neubert, M. G. & Shaw, A. K. (2017) Density dependence in demography and dispersal generates fluctuating invasion speeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 114: 5053-5058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1618744114
[5] Fronhofer, E. A.; Nitsche, N. & Altermatt, F. (2017) Information use shapes the dynamics of range expansions into environmental gradients. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 26: 400-411. doi: 10.1111/geb.12547
| Do the more flexible individuals rely more on causal cognition? Observation versus intervention in causal inference in great-tailed grackles | Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Luisa Bergeron, Carolyn Rowney, Benjamin Seitz, Kelsey McCune, Corina Logan | This PREREGISTRATION has undergone one round of peer reviews. We have now revised the preregistration and addressed reviewer comments. The DOI was issued by OSF and refers to the whole GitHub repository, which contains multiple files. The specific... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Preregistrations, Zoology | Emanuel A. Fronhofer | | 2018-08-20 11:09:48 | View |
Gene expression plasticity and frontloading promote thermotolerance in Pocillopora corals
K. Brener-Raffalli, J. Vidal-Dupiol, M. Adjeroud, O. Rey, P. Romans, F. Bonhomme, M. Pratlong, A. Haguenauer, R. Pillot, L. Feuillassier, M. Claereboudt, H. Magalon, P. Gélin, P. Pontarotti, D. Aurelle, G. Mitta, E. Toulza
https://doi.org/10.1101/398602
Transcriptomics of thermal stress response in corals
Recommended by Staffan Jacob based on reviews by Mar Sobral
Climate change presents a challenge to many life forms and the resulting loss of biodiversity will critically depend on the ability of organisms to timely respond to a changing environment. Shifts in ecological parameters have repeatedly been attributed to global warming, with the effectiveness of these responses varying among species [1, 2]. Organisms do not only have to face a global increase in mean temperatures, but a complex interplay with another crucial but largely understudied aspect of climate change: thermal fluctuations. Understanding the mechanisms underlying adaptation to thermal fluctuations is thus a timely and critical challenge.
Coral reefs are among the most threaten ecosystems in the context of current global changes [3]. Brener-Raffalli and colleagues [4] provided a very complete study digging into the physiological, symbiont-based and transcriptomic mechanisms underlying response of corals to temperature changes. They used an experimental approach, following the heat stress response of coral colonies from different species of the genus Pocillopora. While the symbiont community composition did not significantly change facing exposure to warmer temperatures, the authors provided evidence for transcriptomic changes especially linked to stress response genes that may underlie plastic responses to heat stress.
The authors furthermore investigated the thermal stress response of corals originating from two sites differing in their natural thermal regimes, and found that they differ in the extent and nature of plastic response, including the expression of gene regulation factors and the basal expression level of some genes. These two sites also differ in a variety of aspects, including the focal coral species, which precludes from concluding about the role of thermal regime adaptation into the differences observed. However, these results still highlight a very interesting and important direction deserving further investigation [5], and point out the importance of variability in thermal stress response among localities [6] that might potentially mediate global warming consequences on coral reefs.
References
[1] Parmesan, C., & Yohe, G. (2003). A globally coherent fingerprint of climate change impacts across natural systems. Nature, 421(6918), 37–42. doi: 10.1038/nature01286
[2] Menzel, A., Sparks, T. H., Estrella, N., Koch, E., Aasa, A., Ahas, R., … Zust, A. (2006). European phenological response to climate change matches the warming pattern. Global Change Biology, 12(10), 1969–1976. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01193.x
[3] Bellwood, D. R., Hughes, T. P., Folke, C., & Nyström, M. (2004). Confronting the coral reef crisis. Nature, 429(6994), 827–833. doi: 10.1038/nature02691
[4] Brener-Raffalli, K., Vidal-Dupiol, J., Adjeroud, M., Rey, O., Romans, P., Bonhomme, F., Pratlong, M., Haguenauer, A., Pillot, R., Feuillassier, L., Claereboudt, M., Magalon, H., Gélin, P., Pontarotti, P., Aurelle, D., Mitta, G. and Toulza, E. (2019). Gene expression plasticity and frontloading promote thermotolerance in Pocillopora corals. BioRxiv, 398602, ver 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.1101/398602
[5] Kenkel, Carly D., and Matz, M. V. (2017). Gene expression plasticity as a mechanism of coral adaptation to a variable environment. Nature Ecology and Evolution, 1(1), 0014. doi: 10.1038/s41559-016-0014
[6] Kenkel, C. D., Meyer, E., and Matz, M. V. (2013). Gene expression under chronic heat stress in populations of the mustard hill coral (Porites astreoides) from different thermal environments. Molecular Ecology, 22(16), 4322–4334. doi: 10.1111/mec.12390
| Gene expression plasticity and frontloading promote thermotolerance in Pocillopora corals | K. Brener-Raffalli, J. Vidal-Dupiol, M. Adjeroud, O. Rey, P. Romans, F. Bonhomme, M. Pratlong, A. Haguenauer, R. Pillot, L. Feuillassier, M. Claereboudt, H. Magalon, P. Gélin, P. Pontarotti, D. Aurelle, G. Mitta, E. Toulza | <p>Ecosystems worldwide are suffering from climate change. Coral reef ecosystems are globally threatened by increasing sea surface temperatures. However, gene expression plasticity provides the potential for organisms to respond rapidly and effect... | 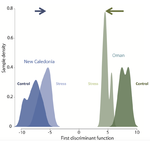 | Climate change, Evolutionary ecology, Marine ecology, Molecular ecology, Phenotypic plasticity, Symbiosis | Staffan Jacob | | 2018-08-29 10:46:55 | View |



 based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz
based on reviews by Georges Kunstler and François Munoz





 based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin
based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin







 based on reviews by Kevin Cazelles and 1 anonymous reviewer
based on reviews by Kevin Cazelles and 1 anonymous reviewer













