Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender▼ | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
19 Aug 2020
Three points of consideration before testing the effect of patch connectivity on local species richness: patch delineation, scaling and variability of metricsF. Laroche, M. Balbi, T. Grébert, F. Jabot & F. Archaux https://doi.org/10.1101/640995Good practice guidelines for testing species-isolation relationships in patch-matrix systemsRecommended by Damaris Zurell based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersConservation biology is strongly rooted in the theory of island biogeography (TIB). In island systems where the ocean constitutes the inhospitable matrix, TIB predicts that species richness increases with island size as extinction rates decrease with island area (the species-area relationship, SAR), and species richness increases with connectivity as colonisation rates decrease with island isolation (the species-isolation relationship, SIR)[1]. In conservation biology, patches of habitat (habitat islands) are often regarded as analogous to islands within an unsuitable matrix [2], and SAR and SIR concepts have received much attention as habitat loss and habitat fragmentation are increasingly threatening biodiversity [3,4]. References [1] MacArthur, R.H. and Wilson, E.O. (1967) The theory of island biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton. | Three points of consideration before testing the effect of patch connectivity on local species richness: patch delineation, scaling and variability of metrics | F. Laroche, M. Balbi, T. Grébert, F. Jabot & F. Archaux | <p>The Theory of Island Biogeography (TIB) promoted the idea that species richness within sites depends on site connectivity, i.e. its connection with surrounding potential sources of immigrants. TIB has been extended to a wide array of fragmented... |  | Biodiversity, Community ecology, Dispersal & Migration, Landscape ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Damaris Zurell | 2019-05-20 16:03:47 | View | |
24 Nov 2023
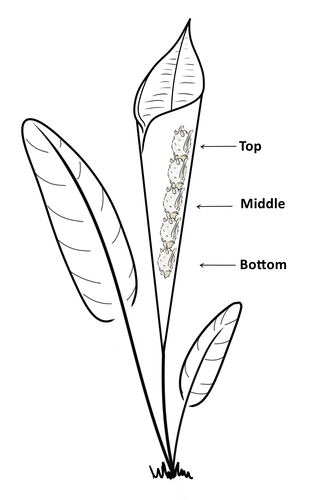
Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged batsGiada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223Consistent individual differences in habitat use in a tropical leaf roosting batRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Annemarie van der Marel and 2 anonymous reviewersConsistent individual differences in habitat use are found across species and can play a role in who an individual mates with, their risk of predation, and their ability to compete with others (Stuber et al. 2022). However, the data informing such hypotheses come primarily from temperate regions (Stroud & Thompson 2019, Titley et al. 2017). This calls into question the generalizability of the conclusions from this research until further investigations can be conducted in tropical regions. Giacomini and colleagues (2023) tackled this task in an investigation of consistent individual differences in habitat use in the Central American tropics. They explored whether Spix’s disc-winged bats form positional hierarchies in roosts, which is an excellent start to learning more about the social behavior of this species - a species that is difficult to directly observe. They found that individual bats use their roosting habitat in predictable ways by positioning themselves consistently either in the bottom, middle, or top of the roost leaf. Individuals chose the same positions across time and across different roost sites. They also found that age and sex play a role in which sections individuals are positioned in. Their research shows that consistent individual differences in habitat use are present in a tropical system, and sets the stage for further investigations into social behavior in this species, particularly whether there is a dominance hierarchy among individuals and whether some positions in the roost are more protective and sought after than others. References Giacomini G, Chaves-Ramirez S, Hernandez-Pinson A, Barrantes JP, Chaverri G. (2023). Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223 Stroud, J. T., & Thompson, M. E. (2019). Looking to the past to understand the future of tropical conservation: The importance of collecting basic data. Biotropica, 51(3), 293-299. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12665 Stuber, E. F., Carlson, B. S., & Jesmer, B. R. (2022). Spatial personalities: a meta-analysis of consistent individual differences in spatial behavior. Behavioral Ecology, 33(3), 477-486. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arab147 Titley, M. A., Snaddon, J. L., & Turner, E. C. (2017). Scientific research on animal biodiversity is systematically biased towards vertebrates and temperate regions. PloS one, 12(12), e0189577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189577 | Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats | Giada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri | <p style="text-align: justify;">Individuals within both moving and stationary groups arrange themselves in a predictable manner; for example, some individuals are consistently found at the front of the group or in the periphery and others in the c... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Social structure, Zoology | Corina Logan | 2022-11-05 17:39:35 | View | |
11 Aug 2023

Implementing Code Review in the Scientific Workflow: Insights from Ecology and Evolutionary BiologyEdward Ivimey-Cook, Joel Pick, Kevin Bairos-Novak, Antica Culina, Elliot Gould, Matthew Grainger, Benjamin Marshall, David Moreau, Matthieu Paquet, Raphaël Royauté, Alfredo Sanchez-Tojar, Inês Silva, Saras Windecker https://doi.org/10.32942/X2CG64A handy “How to” review code for ecologists and evolutionary biologistsRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Serena Caplins and 1 anonymous reviewerIvimey Cook et al. (2023) provide a concise and useful “How to” review code for researchers in the fields of ecology and evolutionary biology, where the systematic review of code is not yet standard practice during the peer review of articles. Consequently, this article is full of tips for authors on how to make their code easier to review. This handy article applies not only to ecology and evolutionary biology, but to many fields that are learning how to make code more reproducible and shareable. Taking this step toward transparency is key to improving research rigor (Brito et al. 2020) and is a necessary step in helping make research trustable by the public (Rosman et al. 2022). References Brito, J. J., Li, J., Moore, J. H., Greene, C. S., Nogoy, N. A., Garmire, L. X., & Mangul, S. (2020). Recommendations to enhance rigor and reproducibility in biomedical research. GigaScience, 9(6), giaa056. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/giaa056 Ivimey-Cook, E. R., Pick, J. L., Bairos-Novak, K., Culina, A., Gould, E., Grainger, M., Marshall, B., Moreau, D., Paquet, M., Royauté, R., Sanchez-Tojar, A., Silva, I., Windecker, S. (2023). Implementing Code Review in the Scientific Workflow: Insights from Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. EcoEvoRxiv, ver 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2CG64 Rosman, T., Bosnjak, M., Silber, H., Koßmann, J., & Heycke, T. (2022). Open science and public trust in science: Results from two studies. Public Understanding of Science, 31(8), 1046-1062. https://doi.org/10.1177/09636625221100686 | Implementing Code Review in the Scientific Workflow: Insights from Ecology and Evolutionary Biology | Edward Ivimey-Cook, Joel Pick, Kevin Bairos-Novak, Antica Culina, Elliot Gould, Matthew Grainger, Benjamin Marshall, David Moreau, Matthieu Paquet, Raphaël Royauté, Alfredo Sanchez-Tojar, Inês Silva, Saras Windecker | <p>Code review increases reliability and improves reproducibility of research. As such, code review is an inevitable step in software development and is common in fields such as computer science. However, despite its importance, code review is not... |  | Meta-analyses, Statistical ecology | Corina Logan | 2023-05-19 15:54:01 | View | |
12 Mar 2023
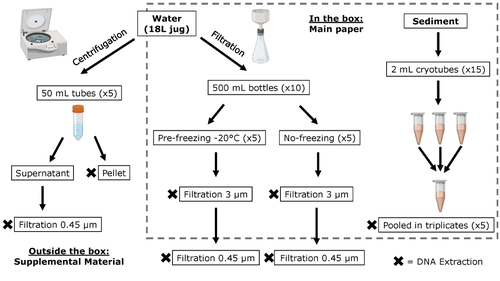
Different approaches to processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters have distinct effects for fish, bacterial and archaea communities.Rachel Turba, Glory H. Thai, and David K Jacobs https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.495388Processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters from coastal lagoonsRecommended by Claudia Piccini based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker and Rutger De WitCoastal lagoons are among the most productive natural ecosystems on Earth. These relatively closed basins are important habitats and nursery for endemic and endangered species and are extremely vulnerable to nutrient input from the surrounding catchment; therefore, they are highly susceptible to anthropogenic influence, pollution and invasion (Pérez-Ruzafa et al., 2019). In general, coastal lagoons exhibit great spatial and temporal variability in their physicochemical water characteristics due to the sporadic mixing of freshwater with marine influx. One of the alternatives for monitoring communities or target species in aquatic ecosystems is the environmental DNA (eDNA), since overcomes some limitations from traditional methods and enables the investigation of multiple species from a single sample (Thomsen and Willerslev, 2015). In coastal lagoons, where the water turbidity is highly variable, there is a major challenge for monitoring the eDNA because filtering turbid water to obtain the eDNA is problematic (filters get rapidly clogged, there is organic and inorganic matter accumulation, etc.). The study by Turba et al. (2023) analyzes different ways of dealing with eDNA sampling and processing in turbid waters and sediments of coastal lagoons, and offers guidelines to obtain unbiased results from the subsequent sequencing using 12S (fish) and 16S (Bacteria and Archaea) universal primers. They analyzed the effect on taxa detection of: i) freezing or not prior to filtering; ii) freezing prior to centrifugation to obtain a sample pellet; and iii) using frozen sediment samples as a proxy of what happens in the water. The authors propose these different alternatives (freeze, do not freeze, sediment sampling) because they consider that they are the easiest to carry out. They found that freezing before filtering using a 3 µm pore size filter had no effects on community composition for either primer, and therefore it is a worthwhile approach for comparison of fish, bacteria and archaea in this kind of system. However, significantly different bacterial community composition was found for sediment compared to water samples. Also, in sediment samples the replicates showed to be more heterogeneous, so the authors suggest increasing the number of replicates when using sediment samples. Something that could be a concern with the study is that the rarefaction curves based on sequencing effort for each protocol did not saturate in any case, this being especially evident in sediment samples. The authors were aware of this, used the slopes obtained from each curve as a measure of comparison between samples and considering that the sequencing depth did not meet their expectations, they managed to achieve their goal and to determine which protocol is the most promising for eDNA monitoring in coastal lagoons. Although there are details that could be adjusted in relation to this item, I consider that the approach is promising for this type of turbid system. References Pérez-Ruzafa A, Campillo S, Fernández-Palacios JM, García-Lacunza A, García-Oliva M, Ibañez H, Navarro-Martínez PC, Pérez-Marcos M, Pérez-Ruzafa IM, Quispe-Becerra JI, Sala-Mirete A, Sánchez O, Marcos C (2019) Long-Term Dynamic in Nutrients, Chlorophyll a, and Water Quality Parameters in a Coastal Lagoon During a Process of Eutrophication for Decades, a Sudden Break and a Relatively Rapid Recovery. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00026 Thomsen PF, Willerslev E (2015) Environmental DNA – An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 183, 4–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.019 Turba R, Thai GH, Jacobs DK (2023) Different approaches to processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters have distinct effects for fish, bacterial and archaea communities. bioRxiv, 2022.06.17.495388, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.495388 | Different approaches to processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters have distinct effects for fish, bacterial and archaea communities. | Rachel Turba, Glory H. Thai, and David K Jacobs | <p style="text-align: justify;">Coastal lagoons are an important habitat for endemic and threatened species in California that have suffered impacts from urbanization and increased drought. Environmental DNA has been promoted as a way to aid in th... |  | Biodiversity, Community genetics, Conservation biology, Freshwater ecology, Marine ecology, Molecular ecology | Claudia Piccini | David Murray-Stoker | 2022-06-20 20:31:51 | View |
10 Jun 2018

A reply to “Ranging Behavior Drives Parasite Richness: A More Parsimonious Hypothesis”Charpentier MJE, Kappeler PM https://arxiv.org/abs/1805.08151v3Does elevated parasite richness in the environment affect daily path length of animals or is it the converse? An answer bringing some new elements of discussionRecommended by Cédric Sueur based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
In 2015, Brockmeyer et al. [1] suggested that mandrills (Mandrillus sphinx) may accept additional ranging costs to avoid heavily parasitized areas. Following this paper, Bicca-Marques and Calegaro-Marques [2] questioned this interpretation and presented other hypotheses. To summarize, whilst Brockmeyer et al. [1] proposed that elevated daily path length may be a consequence of elevated parasite richness, Bicca-Marques and Calegaro-Marques [2] viewed it as a cause. In this current paper, Charpentier and Kappeler [3] respond to some of the criticisms by Bicca-Marques and Calegaro-Marques and discuss the putative parsimony of the two competing scenarios. The manuscript is interesting and focuses on an important question concerning the discussion about the social organization and home range use in wild mandrills. This answer helps to move this debate forward and should stimulate more empirical studies of the role of environmentally-transmitted parasites in shaping ranging and movement patterns of wild vertebrates. Given the elements this paper brings to the topics, it should have been published in American Journal of Primatology, the journal that published the two previous articles. References [1] Brockmeyer, T., Kappeler, P. M., Willaume, E., Benoit, L., Mboumba, S., & Charpentier, M. J. E. (2015). Social organization and space use of a wild mandrill (Mandrillus sphinx) group. American Journal of Primatology, 77(10), 1036–1048. doi: 10.1002/ajp.22439 | A reply to “Ranging Behavior Drives Parasite Richness: A More Parsimonious Hypothesis” | Charpentier MJE, Kappeler PM | In a recent article, Bicca-Marques and Calegaro-Marques [2016] discussed the putative assumptions related to an interpretation we provided regarding an observed positive relationship between weekly averaged parasite richness of a group of mandrill... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Evolutionary ecology, Foraging, Host-parasite interactions, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Zoology | Cédric Sueur | 2018-05-22 10:59:33 | View | |
29 Sep 2023
MoveFormer: a Transformer-based model for step-selection animal movement modellingOndřej Cífka, Simon Chamaillé-Jammes, Antoine Liutkus https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.05.531080A deep learning model to unlock secrets of animal movement and behaviourRecommended by Cédric Sueur based on reviews by Jacob Davidson and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jacob Davidson and 1 anonymous reviewer
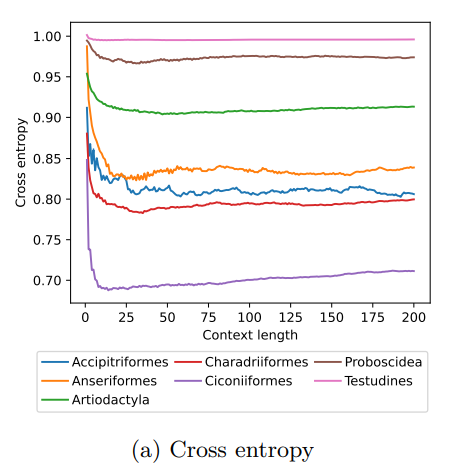
The study of animal movement is essential for understanding their behaviour and how ecological or global changes impact their routines [1]. Recent technological advancements have improved the collection of movement data [2], but limited statistical tools have hindered the analysis of such data [3–5]. Animal movement is influenced not only by environmental factors but also by internal knowledge and memory, which are challenging to observe directly [6,7]. Routine movement behaviours and the incorporation of memory into models remain understudied. Researchers have developed ‘MoveFormer’ [8], a deep learning-based model that predicts future movements based on past context, addressing these challenges and offering insights into the importance of different context lengths and information types. The model has been applied to a dataset of over 1,550 trajectories from various species, and the authors have made the MoveFormer source code available for further research. Inspired by the step-selection framework and efforts to quantify uncertainty in movement predictions, MoveFormer leverages deep learning, specifically the Transformer architecture, to encode trajectories and understand how past movements influence current and future ones – a critical question in movement ecology. The results indicate that integrating information from a few days to two or three weeks before the movement enhances predictions. The model also accounts for environmental predictors and offers insights into the factors influencing animal movements. Its potential impact extends to conservation, comparative analyses, and the generalisation of uncertainty-handling methods beyond ecology, with open-source code fostering collaboration and innovation in various scientific domains. Indeed, this method could be applied to analyse other kinds of movements, such as arm movements during tool use [9], pen movements, or eye movements during drawing [10], to better understand anticipation in actions and their intentionality. References 1. Méndez, V.; Campos, D.; Bartumeus, F. Stochastic Foundations in Movement Ecology: Anomalous Diffusion, Front Propagation and Random Searches; Springer Series in Synergetics; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-39009-8. | MoveFormer: a Transformer-based model for step-selection animal movement modelling | Ondřej Cífka, Simon Chamaillé-Jammes, Antoine Liutkus | <p style="text-align: justify;">The movement of animals is a central component of their behavioural strategies. Statistical tools for movement data analysis, however, have long been limited, and in particular, unable to account for past movement i... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Habitat selection | Cédric Sueur | 2023-03-22 16:32:14 | View | |
25 May 2021
Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assemblyCaio Graco-Roza, Angel M. Segura, Carla Kruk, Patricia Domingos, Janne Soininen, Marcelo M. Marinho https://doi.org/10.1101/869966Environmental heterogeneity drives phytoplankton community assembly patterns in a tropical riverine systemRecommended by Cédric Hubas and Eric Goberville and Eric Goberville based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique Lamy based on reviews by Eric Goberville and Dominique Lamy
What predisposes two individuals to form and maintain a relationship is a fundamental question. Using facial recognition to see whether couples' faces change over time to become more and more similar, psychology researchers have concluded that couples tend to be formed from the start between people whose faces are more similar than average [1]. As the saying goes, birds of a feather flock together. And what about in nature? Are these rules of assembly valid for communities of different species? In his seminal contribution, Robert MacArthur (1984) wrote ‘To do science is to search for repeated patterns’ [2]. Identifying the mechanisms that govern the arrangement of life is a hot research topic in the field of ecology for decades, and an absolutely essential prerequisite to answer the outstanding question of what shape ecological patterns in multi-species communities such as species-area relationships, relative species abundances, or spatial and temporal turnover of community composition; amid others [3]. To explain ecological patterns in nature, some rely on the concept that every species - through evolutionary processes and the acquisition of a unique set of traits that allow a species to be adapted to its abiotic and biotic environment - occupies a unique niche: Species coexistence comes as the result of niche differentiation [4,5]. Such a view has been challenged by the recognition of the key role of neutral processes [6], however, in which demographic stochasticity contributes to shape multi-species communities and to explain why congener species coexist much more frequently than expected by chance [7,8]. While the niche-based and neutral theories appear seemingly opposed at first sight [9], the dichotomy may be more philosophical than empirical [4,5]. Many examples have come to support that both concepts are not incompatible as they together influence the structure, diversity and functioning of communities [10], and are simply extreme cases of a continuum [11]. From this perspective, extrinsic factors, i.e., environmental heterogeneity, may influence the location of a given community along the niche-neutrality continuum. The walk of species in nature is therefore neither random nor ecologically predestined. In microbial assemblages, the co-existence of these two antagonistic mechanisms has been shown both theoretically and empirically. It has been shown that a combination of stabilising (niche) and equalising (neutral) mechanisms was responsible for the existence of groups of coexistent species (clumps) in a phytoplankton rich community [12]. Analysing interannual changes (2003-2009) in the weekly abundance of diatoms and dinoflagellates located in a temperate coastal ecosystem of the Western English Channel, Mutshinda et al. [13] found a mixture of biomass dynamics consistent with the neutrality-niche continuum hypothesis. While niche processes explained the dynamic of phytoplankton functional groups (i.e., diatoms vs. dinoflagellates) in terms of biomass, neutral processes mainly dominated - 50 to 75% of the time - the dynamics at the species level within functional groups [13]. From one endpoint to another, defining the location of a community along the continuum is all matter of scale [4,11]. In their study, testing predictions made by an emergent neutrality model, Graco-Roza et al. [14] provide empirical evidence that neutral and niche processes joined together to shape and drive planktonic communities in a riverine ecosystem. Body size - the 'master trait' - is used here as a discriminant ecological dimension along the niche axis. From their analysis, they not only show that the specific abundance is organised in clumps and gaps along the niche axis, but also reveal that different clumps exist along the river course. They identify two main clumps in body size - with species belonging to three different morphologically-based functional groups - and characterise that among-species differences in biovolume are driven by functional redundancy at the clump level; species functional distinctiveness being related to the relative biovolume of species. By grouping their variables according to seasons (cold-dry vs. warm-wet) or river elevation profile (upper, medium and lower course), they hereby highlight how environmental heterogeneity contributes to shape species assemblages and their dynamics and conclude that emergent neutrality models are a powerful approach to explain species coexistence; and therefore ecological patterns. References [1] Tea-makorn PP, Kosinski M (2020) Spouses’ faces are similar but do not become more similar with time. Scientific Reports, 10, 17001. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-73971-8. [2] MacArthur RH (1984) Geographical Ecology: Patterns in the Distribution of Species. Princeton University Press. [3] Vellend M (2020) The Theory of Ecological Communities (MPB-57). Princeton University Press. [4] Wennekes PL, Rosindell J, Etienne RS (2012) The Neutral—Niche Debate: A Philosophical Perspective. Acta Biotheoretica, 60, 257–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10441-012-9144-6. [5] Gravel D, Guichard F, Hochberg ME (2011) Species coexistence in a variable world. Ecology Letters, 14, 828–839. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01643.x. [6] Hubbell SP (2001) The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography (MPB-32). Princeton University Press. [7] Leibold MA, McPeek MA (2006) Coexistence of the Niche and Neutral Perspectives in Community Ecology. Ecology, 87, 1399–1410. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87[1399:COTNAN]2.0.CO;2. [8] Pielou EC (1977) The Latitudinal Spans of Seaweed Species and Their Patterns of Overlap. Journal of Biogeography, 4, 299–311. https://doi.org/10.2307/3038189. [9] Holt RD (2006) Emergent neutrality. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 21, 531–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.08.003. [10] Scheffer M, Nes EH van (2006) Self-organized similarity, the evolutionary emergence of groups of similar species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103, 6230–6235. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508024103. [11] Gravel D, Canham CD, Beaudet M, Messier C (2006) Reconciling niche and neutrality: the continuum hypothesis. Ecology Letters, 9, 399–409. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2006.00884.x. [12] Vergnon R, Dulvy NK, Freckleton RP (2009) Niches versus neutrality: uncovering the drivers of diversity in a species-rich community. Ecology Letters, 12, 1079–1090. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2009.01364.x. [13] Mutshinda CM, Finkel ZV, Widdicombe CE, Irwin AJ (2016) Ecological equivalence of species within phytoplankton functional groups. Functional Ecology, 30, 1714–1722. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12641. [14] Graco-Roza C, Segura AM, Kruk C, Domingos P, Soininen J, Marinho MM (2021) Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly. bioRxiv, 869966, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/869966
| Clumpy coexistence in phytoplankton: The role of functional similarity in community assembly | Caio Graco-Roza, Angel M. Segura, Carla Kruk, Patricia Domingos, Janne Soininen, Marcelo M. Marinho | <p style="text-align: justify;">Emergent neutrality (EN) suggests that species must be sufficiently similar or sufficiently different in their niches to avoid interspecific competition. Such a scenario results in a transient pattern with clumps an... |  | Coexistence, Community ecology, Theoretical ecology | Cédric Hubas | 2020-01-23 16:11:32 | View | |
02 Aug 2021

Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimationAline Migné, Gwendoline Duong, Dominique Menu, Dominique Davoult & François Gévaert https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03079617Towards a better understanding of the effects of self-shading on Fucus serratus populationsRecommended by Cédric Hubas based on reviews by Gwenael Abril, Francesca Rossi and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Gwenael Abril, Francesca Rossi and 1 anonymous reviewer
The importance of the vertical structure of vegetation cover for the functioning, management and conservation of ecosystems has received particular attention from ecologists in the last decades. Canopy architecture has many implications for light extinction coefficient, temperature variation reduction, self-shading which are all key parameters for the structuring and functioning of different ecosystems such as grasslands [1,2], forests [3,4], phytoplankton communities [5, 6], macroalgal populations [7] and even underwater animal forests such as octocoral communities [8]. This research topic, therefore, benefits from a large body of literature and the facilitative role of self-shadowing is no longer in question. However, it is always puzzling to note that some of the most common ecosystems turn out to be amongst the least known. This is precisely the case of the Fucus serratus communities which are widespread in Northeast Atlantic along the Atlantic coast of Europe from Svalbard to Portugal, as well as Northwest Atlantic & Gulf of St. Lawrence, easily accessible at low tide, but which have comparatively received less attention than more emblematic macro-algal communities such as Laminariales. The lack of attention paid to these most common Fucales is particularly critical as some species such as F. serratus are proving to be particularly vulnerable to environmental change, leading to a predicted northward retreat from its current southern boundary [9]. In the present study [10], the authors showed the importance of the vegetation cover in resisting tide-induced environmental stresses. The canopy of F. serratus mitigates stress levels experienced in the lower layers during emersion, while various acclimation strategies take over to maintain the photosynthetic apparatus in optimal conditions. They hereby highlight adaptation mechanisms to the extreme environment represented by the intertidal zone. These adaptation strategies were expected and similar mechanisms had been shown at the cellular level previously [11]. The earliest studies on the subject have shown that the structure of the bottom, the movement of water, and light availability all "influence the distribution of Fucaceae and disturb the regularity of their fine zonation, which itself is caused by the most important factor, desiccation", as Zaneveld states in his review [12]. He observed that the causes of the zonal distribution of marine algae are numerous, and identified several points of interest such as the relative period of emersion, the rapidity of desiccation, the loss of water, and the thickness of the cell walls. The present study thus highlights the existence of facilitative mechanisms associated with F. serratus canopy and nicely confirms previous work with in situ observations. It also highlights the importance of the vegetative cover in combating desiccation and introduces the dampening effect as a facilitating mechanism. The effect of the vegetation cover can sometimes even be felt beyond its immediate area of influence. A recent study shows that ground-level ozone is significantly reduced by the combined effects of canopy shading and turbulence [4]. Below the canopy, the light intensity becomes sufficiently low which inhibits ozone formation due to the decrease in the rates of hydroxyl radical formation and the rates of conversion of nitrogen dioxide to nitrogen oxide by photolysis. In addition, reductions in light levels associated with foliage promote ozone-destroying reactions between plant-emitted species, such as nitric oxide and/or alkenes, and ozone itself. The reduction in diffusivity slows the upward transport of surface emitted species, partially decoupling the area under the canopy from the rest of the atmosphere. By analogy with the work of Makar et al [4], and in the light of the results provided by the authors of this study, one may wonder whether the canopy dampening of F. serratus communities (and other common fucoids widely distributed on our coasts) might not also influence atmospheric chemistry, both at the Earth's surface and in the atmospheric boundary layer. The lack of accumulation of reactive oxygen species under the canopy found by the authors is consistent with this hypothesis and suggests that the damping effect of F. serratus may well have much wider consequences than expected. References [1] Jurik TW, Kliebenstein H (2000) Canopy Architecture, Light Extinction and Self-Shading of a Prairie Grass, Andropogon Gerardii. The American Midland Naturalist, 144, 51–65. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3083010 [2] Mitchley J, Willems JH (1995) Vertical canopy structure of Dutch chalk grasslands in relation to their management. Vegetatio, 117, 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00033256 [3] Kane VR, Gillespie AR, McGaughey R, Lutz JA, Ceder K, Franklin JF (2008) Interpretation and topographic compensation of conifer canopy self-shadowing. Remote Sensing of Environment, 112, 3820–3832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2008.06.001 [4] Makar PA, Staebler RM, Akingunola A, Zhang J, McLinden C, Kharol SK, Pabla B, Cheung P, Zheng Q (2017) The effects of forest canopy shading and turbulence on boundary layer ozone. Nature Communications, 8, 15243. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15243 [5] Shigesada N, Okubo A (1981) Analysis of the self-shading effect on algal vertical distribution in natural waters. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 12, 311–326. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276919 [6] Barros MP, Pedersén M, Colepicolo P, Snoeijs P (2003) Self-shading protects phytoplankton communities against H2O2-induced oxidative damage. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 30, 275–282. https://doi.org/10.3354/ame030275 [7] Ørberg SB, Krause-Jensen D, Mouritsen KN, Olesen B, Marbà N, Larsen MH, Blicher ME, Sejr MK (2018) Canopy-Forming Macroalgae Facilitate Recolonization of Sub-Arctic Intertidal Fauna and Reduce Temperature Extremes. Frontiers in Marine Science, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2018.00332 [8] Nelson H, Bramanti L (2020) From Trees to Octocorals: The Role of Self-Thinning and Shading in Underwater Animal Forests. In: Perspectives on the Marine Animal Forests of the World (eds Rossi S, Bramanti L), pp. 401–417. Springer International Publishing, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57054-5_12 [9] Jueterbock A, Kollias S, Smolina I, Fernandes JMO, Coyer JA, Olsen JL, Hoarau G (2014) Thermal stress resistance of the brown alga Fucus serratus along the North-Atlantic coast: Acclimatization potential to climate change. Marine Genomics, 13, 27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margen.2013.12.008 [10] Migné A, Duong G, Menu D, Davoult D, Gévaert F (2021) Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimation. HAL, hal-03079617, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-03079617 [11] Lichtenberg M, Kühl M (2015) Pronounced gradients of light, photosynthesis and O2 consumption in the tissue of the brown alga Fucus serratus. New Phytologist, 207, 559–569. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13396 [12] Zaneveld JS (1937) The Littoral Zonation of Some Fucaceae in Relation to Desiccation. Journal of Ecology, 25, 431–468. https://doi.org/10.2307/2256204 | Dynamics of Fucus serratus thallus photosynthesis and community primary production during emersion across seasons: canopy dampening and biochemical acclimation | Aline Migné, Gwendoline Duong, Dominique Menu, Dominique Davoult & François Gévaert | <p style="text-align: justify;">The brown alga <em>Fucus serratus</em> forms dense stands on the sheltered low intertidal rocky shores of the Northeast Atlantic coast. In the southern English Channel, these stands have proved to be highly producti... |  | Marine ecology | Cédric Hubas | 2021-01-05 16:24:02 | View | |
09 Dec 2019

Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive successAinhoa Magrach, Francisco P. Molina, Ignasi Bartomeus https://doi.org/10.1101/629931Improving our knowledge of species interaction networksRecommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Michael Lattorff, Nicolas Deguines and 3 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Michael Lattorff, Nicolas Deguines and 3 anonymous reviewers
Ecosystems shelter a huge number of species, continuously interacting. Each species interact in various ways, with trophic interactions, but also non-trophic interactions, not mentioning the abiotic and anthropogenic interactions. In particular, pollination, competition, facilitation, parasitism and many other interaction types are simultaneously present at the same place in terrestrial ecosystems [1-2]. For this reason, we need today to improve our understanding of such complex interaction networks to later anticipate their responses. This program is a huge challenge facing ecologists and they today join their forces among experimentalists, theoreticians and modelers. While some of us struggle in theoretical and modeling dimensions [3-4], some others perform brilliant works to observe and/or experiment on the same ecological objects [5-6]. References [1] Campbell, C., Yang, S., Albert, R., and Shea, K. (2011). A network model for plant–pollinator community assembly. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 108(1), 197-202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1008204108 | Niche complementarity among pollinators increases community-level plant reproductive success | Ainhoa Magrach, Francisco P. Molina, Ignasi Bartomeus | <p>Declines in pollinator diversity and abundance have been reported across different regions, with implications for the reproductive success of plant species. However, research has focused primarily on pairwise plant-pollinator interactions, larg... |  | Ecosystem functioning, Interaction networks, Pollination, Terrestrial ecology | Cédric Gaucherel | Nicolas Deguines | 2019-05-07 17:03:23 | View |
29 Aug 2023
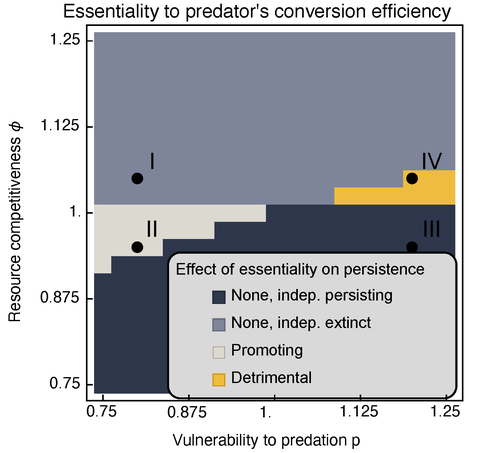
Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food websMichael Raatz https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525839High-order interactions in food webs may strongly impact persistence of speciesRecommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Jean-Christophe POGGIALE and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jean-Christophe POGGIALE and 1 anonymous reviewer
Michael Raatz (2023) provides here a relevant exploration of higher-order interactions, i.e. interactions involving more than two related species (Terry et al. 2019), in the case of food web and competition interactions. More precisely, he shows by modeling that essential resources may significantly mediate focal species' persistence. Simultaneously, the provision of essential resources may strongly affect the resulting community structure, by driving to extinction first the predator and then, depending on the higher-order interaction, potentially also the associated competitor. Today, all ecologists should be aware of the potential effects of high-order interactions on species' (and likely on ecosystem's) fate (Golubski et al. 2016, Grilli et al. 2017). Yet, we should soon be prepared to include any high-order interaction into any interaction network (i.e. not only between species, but also between species and abiotic components, and between biotic, anthropogenic and abiotic components too). For this purpose, we will need innovative approaches such as hypergraphs (Golubski et al. 2016) and discrete-event models (Gaucherel and Pommereau 2019, Thomas et al. 2022) able to manage highly complex interactions, with numerous interacting components and variables. Such a rigorous study is a necessary and preliminary step in taking into account such a higher complexity. References Gaucherel, C. and F. Pommereau. 2019. Using discrete systems to exhaustively characterize the dynamics of an integrated ecosystem. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 00:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13242 Golubski, A. J., E. E. Westlund, J. Vandermeer, and M. Pascual. 2016. Ecological Networks over the Edge: Hypergraph Trait-Mediated Indirect Interaction (TMII) Structure trends in Ecology & Evolution 31:344-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.006 Grilli, J., G. Barabas, M. J. Michalska-Smith, and S. Allesina. 2017. Higher-order interactions stabilize dynamics in competitive network models. Nature 548:210-213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23273 Raatz, M. 2023. Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525839 Terry, J. C. D., R. J. Morris, and M. B. Bonsall. 2019. Interaction modifications lead to greater robustness than pairwise non-trophic effects in food webs. Journal of Animal Ecology 88:1732-1742. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.13057 Thomas, C., M. Cosme, C. Gaucherel, and F. Pommereau. 2022. Model-checking ecological state-transition graphs. PLoS Computational Biology 18:e1009657. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009657 | Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs | Michael Raatz | <p style="text-align: justify;">Pairwise interactions in food webs, including those between predator and prey are often modulated by a third species. Such higher-order interactions are important structural components of natural food webs that can ... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Competition, Ecological stoichiometry, Food webs, Interaction networks, Theoretical ecology | Cédric Gaucherel | 2023-02-23 17:48:26 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










