
Processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters from coastal lagoons
Different approaches to processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters have distinct effects for fish, bacterial and archaea communities.
Abstract
Recommendation: posted 10 March 2023, validated 12 March 2023
Piccini, C. (2023) Processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters from coastal lagoons. Peer Community in Ecology, 100427. https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100427
Recommendation
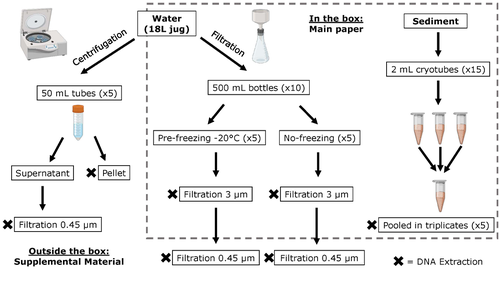
Coastal lagoons are among the most productive natural ecosystems on Earth. These relatively closed basins are important habitats and nursery for endemic and endangered species and are extremely vulnerable to nutrient input from the surrounding catchment; therefore, they are highly susceptible to anthropogenic influence, pollution and invasion (Pérez-Ruzafa et al., 2019). In general, coastal lagoons exhibit great spatial and temporal variability in their physicochemical water characteristics due to the sporadic mixing of freshwater with marine influx. One of the alternatives for monitoring communities or target species in aquatic ecosystems is the environmental DNA (eDNA), since overcomes some limitations from traditional methods and enables the investigation of multiple species from a single sample (Thomsen and Willerslev, 2015). In coastal lagoons, where the water turbidity is highly variable, there is a major challenge for monitoring the eDNA because filtering turbid water to obtain the eDNA is problematic (filters get rapidly clogged, there is organic and inorganic matter accumulation, etc.).
The study by Turba et al. (2023) analyzes different ways of dealing with eDNA sampling and processing in turbid waters and sediments of coastal lagoons, and offers guidelines to obtain unbiased results from the subsequent sequencing using 12S (fish) and 16S (Bacteria and Archaea) universal primers. They analyzed the effect on taxa detection of: i) freezing or not prior to filtering; ii) freezing prior to centrifugation to obtain a sample pellet; and iii) using frozen sediment samples as a proxy of what happens in the water. The authors propose these different alternatives (freeze, do not freeze, sediment sampling) because they consider that they are the easiest to carry out. They found that freezing before filtering using a 3 µm pore size filter had no effects on community composition for either primer, and therefore it is a worthwhile approach for comparison of fish, bacteria and archaea in this kind of system. However, significantly different bacterial community composition was found for sediment compared to water samples. Also, in sediment samples the replicates showed to be more heterogeneous, so the authors suggest increasing the number of replicates when using sediment samples. Something that could be a concern with the study is that the rarefaction curves based on sequencing effort for each protocol did not saturate in any case, this being especially evident in sediment samples. The authors were aware of this, used the slopes obtained from each curve as a measure of comparison between samples and considering that the sequencing depth did not meet their expectations, they managed to achieve their goal and to determine which protocol is the most promising for eDNA monitoring in coastal lagoons. Although there are details that could be adjusted in relation to this item, I consider that the approach is promising for this type of turbid system.
References
Pérez-Ruzafa A, Campillo S, Fernández-Palacios JM, García-Lacunza A, García-Oliva M, Ibañez H, Navarro-Martínez PC, Pérez-Marcos M, Pérez-Ruzafa IM, Quispe-Becerra JI, Sala-Mirete A, Sánchez O, Marcos C (2019) Long-Term Dynamic in Nutrients, Chlorophyll a, and Water Quality Parameters in a Coastal Lagoon During a Process of Eutrophication for Decades, a Sudden Break and a Relatively Rapid Recovery. Frontiers in Marine Science, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00026
Thomsen PF, Willerslev E (2015) Environmental DNA – An emerging tool in conservation for monitoring past and present biodiversity. Biological Conservation, 183, 4–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2014.11.019
Turba R, Thai GH, Jacobs DK (2023) Different approaches to processing environmental DNA samples in turbid waters have distinct effects for fish, bacterial and archaea communities. bioRxiv, 2022.06.17.495388, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.17.495388
The recommender in charge of the evaluation of the article and the reviewers declared that they have no conflict of interest (as defined in the code of conduct of PCI) with the authors or with the content of the article. The authors declared that they comply with the PCI rule of having no financial conflicts of interest in relation to the content of the article.
Funding was provided by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development of 632 Brazil (Rachel Turba) under Grant No. 209261/2014-5 and by NOAA Sea Grant 120651698:1. Funding for the CALeDNA sample processing, infrastructure, and personnel was provided by the 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 University of California Research Initiatives (UCRI) Catalyst grant CA-16-376437 and Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) Professors Grant GT10483
Reviewed by David Murray-Stoker , 23 Feb 2023
, 23 Feb 2023
I have provided my review in the attached PDF.
-David Murray-Stoker
Download the review https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100427.rev21Evaluation round #1
DOI or URL of the preprint: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.06.17.495388v1
Author's Reply, 05 Feb 2023
Decision by Claudia Piccini, posted 05 Oct 2022
Dear Dr. Turba,
Thank you for considering PCI Ecology as an option to publish your work and to help changing the scientific publication habits.
After carefully reading the comments from both reviewers, I recommend to make a revised version of the manuscript, mainly taking into account the suggestion of reviewer#1 about the manuscript structure and lenght (a short paper focused on eDNA from fishes or a paper comparing the different assessed compartments); and the reviewer #2 comments about writing the methodology in a more clear and straight way, considering the comments on data analysis.
We look forward to your revised version.
Best regards,
Claudia Piccini










