Latest recommendations

| Id | Title▼ | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
06 Mar 2020
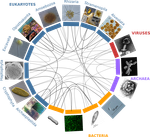
A community perspective on the concept of marine holobionts: current status, challenges, and future directionsSimon M. Dittami, Enrique Arboleda, Jean-Christophe Auguet, Arite Bigalke, Enora Briand, Paco Cárdenas, Ulisse Cardini, Johan Decelle, Aschwin Engelen, Damien Eveillard, Claire M.M. Gachon, Sarah Griffiths, Tilmann Harder, Ehsan Kayal, Elena Kazamia, Francois H. Lallier, Mónica Medina, Ezequiel M. Marzinelli, Teresa Morganti, Laura Núñez Pons, Soizic Pardo, José Pintado Valverde, Mahasweta Saha, Marc-André Selosse, Derek Skillings, Willem Stock, Shinichi Sunagawa, Eve Toulza, Alexey Vorobev, Cat... 10.5281/zenodo.3696771Marine holobiont in the high throughput sequencing eraRecommended by Sophie Arnaud-Haond and Corinne Vacher based on reviews by Sophie Arnaud-Haond and Aurélie TasiemskiThe concept of holobiont dates back to more than thirty years, it was primarily coined to hypothesize the importance of symbiotic associations to generate significant evolutionary novelties. Quickly adopted to describe the now well-studied system formed by zooxanthella associated corals, this concept expanded much further after the emergence of High-Throughput Sequencing and associated progresses in metabarcoding and metagenomics. References | A community perspective on the concept of marine holobionts: current status, challenges, and future directions | Simon M. Dittami, Enrique Arboleda, Jean-Christophe Auguet, Arite Bigalke, Enora Briand, Paco Cárdenas, Ulisse Cardini, Johan Decelle, Aschwin Engelen, Damien Eveillard, Claire M.M. Gachon, Sarah Griffiths, Tilmann Harder, Ehsan Kayal, Elena Kazam... | Host-microbe interactions play crucial roles in marine ecosystems. However, we still have very little understanding of the mechanisms that govern these relationships, the evolutionary processes that shape them, and their ecological consequences. T... |  | Marine ecology, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Symbiosis | Sophie Arnaud-Haond | 2019-02-05 17:57:11 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










