
LORENZO MONTERO Leda
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
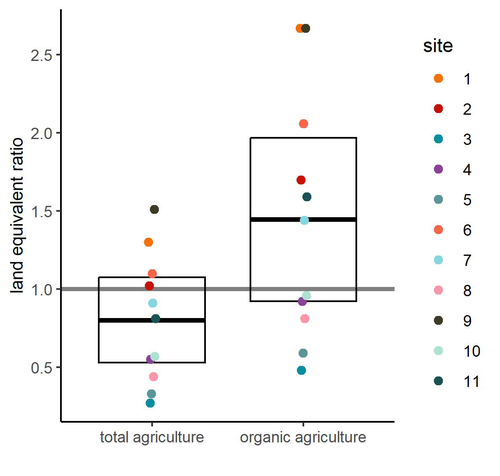
Crop productivity of Central European Permaculture is within the range of organic and conventional agriculture.
Permaculture, a promising alternative to conventional agriculture
Recommended by Aleksandra Walczyńska based on reviews by Julia Astegiano, Paulina Kramarz, Leda Lorenzo Montero and 1 anonymous reviewerAs mankind develops increasingly efficient and productive methods of agriculture and food production, we have reached a point where intensive agriculture threatens several aspects of life on Earth, negatively affecting biodiversity, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles and water reservoirs, while producing considerable amounts of greenhouse gases (Krebs and Bach, 2018). There was a need to develop farming methods that were friendly to both nature and people, producing good quality, healthy food without destroying the environment. The idea of permaculture, a concept of sustainable agriculture based on methods learned directly from nature, originated in the 1960s, invented and developed by Bruce Charles Mollison and David Holmgren (Mollison and Holmgren 1979, Mollison et al. 1991, Holmgren 2002). Although the idea of permaculture has attracted scientific interest, the representation in published studies is unbalanced in favour of positive ecological and sociological effects, with much less presence of rigorous experimental testing (Ferguson and Lovell 2014, Reiff et al. 2024a).
Reiff et al. (2024b) provided the first large-scale empirical evidence of permaculture production outcomes for Central Europe. Based on results from 11 commercial permaculture sites, situated mostly in Germany but also in Switzerland and Luxembourg, the authors found that food production from permaculture sites was on average comparable to that from conventional and organic agriculture. The authors were very thorough in pointing out the issues that could potentially affect their results and which need further testing.
Among these, the authors highlight the considerable variability between the 11 sites studied, which may suggest that different permacultures should differ in details according to their specificity - an interesting issue that definitely requires further study. The other factor that the authors point out that could have influenced the results and led to an underestimation of the real potential is the age of the permaculture sites. The sites from the study were relatively young, and their potential can be expected to increase with time.
It is important to note that the results are mostly applicable to vegetables, as vegetable production accounted for 94% of production in the permaculture sites (followed by tree crops, 6%, and soft fruit production, 0.5%). There is therefore a need to include other types of crops produced in further studies of this type.
To date, the results informing permaculture food production are urgently needed and should cover the potentially wide range of geographical regions and crops produced. The results of Reiff et al. (2025) show that rigorous testing of this issue is demanding, but the authors provide a very sound "road map" of further steps.
Literature:
Ferguson R. S. and Lovell S. T. 2014. Permaculture for agroecology: design, movement, practice, and worldview. A review. Agronomy for Sustainable Development 34, 251-274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-013-0181-6
Holmgren D. 2002. Permaculture: Principles & Pathways Beyond Sustainability. Holmgren Design Services, pp. 320.
Krebs J. and Bach S. 2018. Permaculture – scientific evidence of principles for the agroecological design of farming systems. Sustainability 10, 3218, https://doi.org/10.3390/su10093218
Mollison B. C. and Holmgren D. 1979. Permaculture One: A Perennial Agricultural System for Human Settlements. Tagari Publications, pp. 136.
Mollison B. C., Slay, R. M. and Jeeves A. 1991. Introduction to permaculture. Tagari Publications, pp. 198.
Reiff J., Jungkunst H. F., Mauser K. M., Kampel S., Regending S., Rösch V., Zaller J. G. and Entling M. H. 2024a. Permaculture enhances carbon stocks, soil quality and biodiversity in Central Europe. Communications Earth & Environment 5, 305. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43247-024-01405-8
Reiff J., Jungkunst H. F., Antes N. and Entling M. H. 2024b. Crop productivity of Central European Permaculture is within the range of organic and conventional agriculture. bioRxiv, ver.2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.09.09.611985