
RAMIREZ Claudio
- Instituto de Ciencias Biológicas, Universidad de Talca, Talca, Chile
- Agroecology, Behaviour & Ethology, Herbivory
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
Comment on “Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities”
Does information theory inform chemical arms race communication?
Recommended by Rodrigo Medel based on reviews by Claudio Ramirez and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the long-standing questions in evolutionary ecology is on the mechanisms involved in arms race coevolution. One way to address this question is to understand the conditions under which one species evolves traits in response to the presence of a second species and so on. However, specialized pairwise interactions are by far less common in nature than interactions involving a higher number of interacting species (Bascompte, Jordano 2013). While interactions between large sets of species are the norm rather than the exception in mutualistic (pollination, seed dispersal), and antagonist (herbivory, parasitism) relationships, few is known on the way species identify, process, and respond to information provided by other interacting species under field conditions (Schaefer, Ruxton 2011).
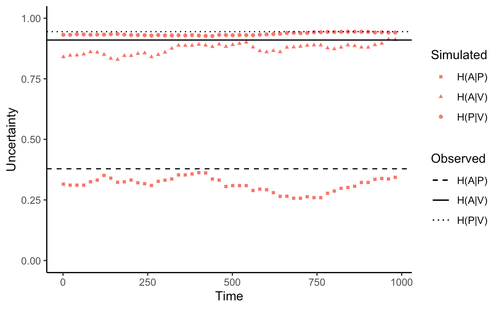
Zu et al. (2020) addressed this general question by developing an interesting information theory-based approach that hypothesized conditional entropy in chemical communication plays a role as proxy of fitness in plant-herbivore communities. More specifically, plant fitness was assumed to be related to the efficiency to code signals by plant species, and herbivore fitness to the capacity to decode plant signals. In this way, from the plant perspective, the elaboration of plant signals that elude decoding by herbivores is expected to be favored, as herbivores are expected to attack plants with simple chemical signals. The empirical observation upon which the model was tested was the redundancy in volatile organic compounds (VOC) found across plant species in a plant-herbivore community. Interestingly, Zu et al.’s model predicted successfully that VOC redundancy in the plant community associates with increased conditional entropy, which conveys herbivore confusion and plant protection against herbivory. In this way, plant species that evolve VOCs already present in the community might be benefitted, ultimately leading to the patterns of VOC redundancy commonly observed in nature.
Bass & Kessler performed a series of interesting observations on Zu et al. (2020), that can be organized along three lines of reasoning. First, from an evolutionary perspective, Bass & Kessler note the important point that accepting that conditional information entropy, estimated from the contribution of every plant species to volatile redundancy implies that average plant fitness seems to depend on community-level properties (i.e., what the other species in the community are doing) rather than on population-level characteristics (I.e., what the individuals belonging a population are doing). While the level at which selection acts upon is a longstanding debate (e.g., Goodnight, 1990; Williams, 1992), the model seems to contradict one of the basic tenets of Darwinian evolution. The extent to which this important observation invalidates the contribution of Zu et al. (2020) is open to scrutiny. However, one can indulge the evolutionary criticism by arguing that every theoretical model performs a number of assumptions to preserve the simplicity of analyses. Furthermore, even accepting the criticism, the overall information-based framework is valuable as it provides a fresh perspective to the way coding and decoding chemical information in plant-herbivore interactions may result in arm race coevolution. The question to be assessed by members of the scientific community is how strong the evolutionary assumptions are to be acceptable. A second line of reasoning involves consideration of additional routes of chemical information transfer. If chemical volatiles are involved in another ecological function unrelated to arm race (as they are) such as toxicity, crypsis, aposematism, etc., the conditional information indices considered as proxy to plant and herbivore fitness may be only secondarily related to arms race. This is an interesting observation, which suggests that VOC production may have more than one ecological function, as it often happens in “pleiotropic” traits (Strauss, Irwin 2004). This is an exciting avenue for future research. Finally, a third category of comments involves the relationship between conditional information entropy and plant and herbivore fitness. Bass & Kessler developed a Bayesian treatment of the community-level information developed by Zu et al. (2020) that permitted to estimate fitness on a species rather than community level. Their results revealed that community conditional entropies fail to align with species-level indices, suggesting that conclusions of Strauss & Irwin (2004) are not commensurate with fitness at the species level, where the analysis seems to be pertinent. In general, I strongly recommend Bass & Kessler’s contribution as it provides a series of observations and new perspectives to Zu et al. (2020). Rather than restricting their manuscript to blind criticisms, Bass & Kessler provides new interesting perspectives, which is always welcome as it improves the value and scope of the original work.
References
Bascompte J, Jordano P (2013) Mutualistic Networks. Princeton University Press. https://doi.org/10.23943/princeton/9780691131269.001.0001
Bass E, Kessler A (2022) Comment on “Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities.” EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/xsbtm
Goodnight CJ (1990) Experimental Studies of Community Evolution I: The Response to Selection at the Community Level. Evolution, 44, 1614–1624. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1990.tb03850.x
Schaefer HM, Ruxton GD (2011) Plant-Animal Communication. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199563609.001.0001
Strauss SY, Irwin RE (2004) Ecological and Evolutionary Consequences of Multispecies Plant-Animal Interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 435–466. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.112202.130215
Williams GC (1992) Natural Selection: Domains, Levels, and Challenges. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York.
Zu P, Boege K, del-Val E, Schuman MC, Stevenson PC, Zaldivar-Riverón A, Saavedra S (2020) Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities. Science, 368, 1377–1381. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba2965