
TULJAPURKAR Shripad
- Biology, Stanford University, Stanford, United States of America
- Allometry, Climate change, Coexistence, Competition, Demography, Dispersal & Migration, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Evolutionary ecology, Human impact, Life history, Molecular ecology, Ontogeny, Population ecology, Soil ecology, Theoretical ecology, Zoology
- recommender
Recommendations: 0
Review: 1
Review: 1
Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulations
The spatial dynamics of habitat fragmentation drives the evolution of dispersal and metapopulation persistence
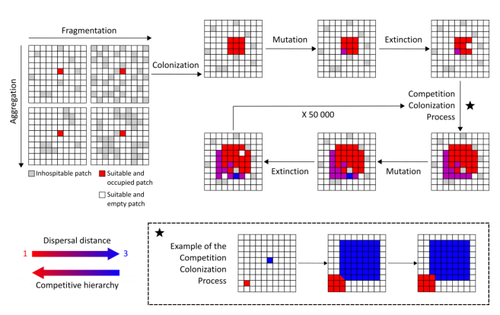
Recommended by Frédéric Guichard based on reviews by Eva Kisdi, David Murray-Stoker, Shripad Tuljapurkar and 1 anonymous reviewerThe persistence of populations facing the destruction of their habitat is a multifaceted question that has mobilized theoreticians and empiricists alike for decades. As an ecological question, persistence has been studied as the spatial rescue of populations via dispersal into remaining suitable habitats. The spatial aggregation of habitat destruction has been a key component of these studies, and it has been applied to the problem of coexistence by integrating competition-colonization tradeoffs. There is a rich ecological literature on this topic, both from theoretical and field studies (Fahrig 2003). The relationship between life-history strategies of species and their resilience to spatially structured habitat fragmentation is also an important component of conservation strategies through the management of land use, networks of protected areas, and the creation of corridors. In the context of environmental change, the ability of species to adapt to changes in landscape configuration and availability can be treated as an eco-evolutionary process by considering the possibility of evolutionary rescue (Heino and Hanski 2001; Bell 2017). However, eco-evolutionary dynamics considering spatially structured changes in landscapes and life-history tradeoffs remains an outstanding question. Finand et al. (2023) formulate the problem of persistence in fragmented landscapes over evolutionary time scales by studying models for the evolution of dispersal in relation to habitat fragmentation and spatial aggregation. Their simulations were conducted on a spatial grid where individuals can colonize suitable patch as a function of their competitive rank that decreases as a function of their (ii) dispersal distance trait. Simulations were run under fixed habitat fragmentation (proportion of unsuitable habitat) and aggregation, and with an explicit rate of habitat destruction to study evolutionary rescue.
Their results reveal a balance between the selection for high dispersal under increasing habitat fragmentation and selection for lower dispersal in response to habitat aggregation. This balance leads to the coexistence of polymorphic dispersal strategies in highly aggregated landscapes with low fragmentation where high dispersers inhabit aggregated habitats while low dispersers are found in isolated habitats. The authors then integrate the spatial rescue mechanism to the problem of evolutionary rescue in response to temporally increasing fragmentation. There they show how rapid evolution allows for evolutionary rescue through the evolution of high dispersal. They also show the limits to this evolutionary rescue to cases where both aggregation and fragmentation are not too high. Interestingly, habitat aggregation prevents evolutionary rescue by directly affecting the evolutionary potential of dispersal. The study is based on simple scenarios that ignore the complexity of relationships between dispersal, landscape properties, and species interactions. This simplicity is the strength of the study, revealing basic mechanisms that can now be tested against other life-history tradeoffs and species interactions. Finand et al. (2023) provide a novel foundation for the study of eco-evolutionary dynamics in metacommunities exposed to spatially structured habitat destruction. They point to important assumptions that must be made along the way, including the relationships between dispersal distance and fecundity (they assume a positive relationship), and the nature of life-history tradeoffs between dispersal rate and local competitive abilities.
References
Bell, G. 2017. Evolutionary Rescue. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 48:605–627. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-023011
Fahrig, L. 2003. Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Biodiversity. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 34:487–515. https://doi.org/10.2307/30033784
Finand, B., T. Monnin, and N. Loeuille. 2023. Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulations. bioRxiv, 2022.06.08.495260, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.08.495260
Heino, M., and I. Hanski. 2001. Evolution of Migration Rate in a Spatially Realistic Metapopulation Model. The American Naturalist 157:495–511. https://doi.org/10.1086/319927