
CHEN Huihuang
- Aquatic EcoHealth Group, Institute of Urban Environment Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xiamen, China
- Climate change, Community ecology, Ecological stoichiometry, Ecotoxicology, Freshwater ecology, Meta-analyses, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Molecular ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Statistical ecology, Theoretical ecology
- recommender
Recommendations: 2
Reviews: 0
Recommendations: 2

Delayed dichromatism in waterfowl as a convenient tool for assessing vital rates
A cost-effective and non-invasive approach to estimating population dynamics in waterfowl
Recommended by Huihuang Chen based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThis article highlights a novel non-invasive method based on the "apparent sex ratios" that exploits delayed sexual importance in waterfowl populations. Unlike traditional capture-mark-recapture (CMR) technique, which is costly, invasive, and may disturb the target species, this method infers key population dynamics, such as adult survival rate and recruitment rate, by monitoring sex ratios in counts conducted during winter. Juvenile males that resemble adult females before molting provide a unique opportunity to estimate these vital rates. This method is cost-effective, minimizes disturbance to the species, and is particularly suitable for studying protected or invasive species.
References
Adrien Tableau, Iain Henderson, Sébastien Reeber, Matthieu Guillemain, Jean-François Maillard, Alain Caizergues (2024) Delayed dichromatism in waterfowl as a convenient tool for assessing vital rates. bioRxiv, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.06.04.597326
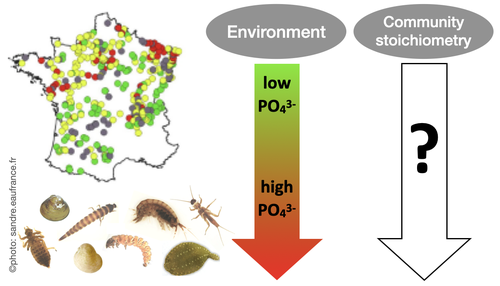
Effects of water nutrient concentrations on stream macroinvertebrate community stoichiometry: a large-scale study
The influence of water phosphorus and nitrogen loads on stream macroinvertebrate community stoichiometry
Recommended by Huihuang Chen based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Jun Zuo and 1 anonymous reviewerThe manuscript by Beck et al. (2024) investigates the effects of water phosphorus and nitrogen loads on stream macroinvertebrate community stoichiometry across France. Utilizing data from over 1300 standardized sampling events, this research finds that community stoichiometry is significantly influenced by water phosphorus concentration, with the strongest effects at low nitrogen levels.
The results demonstrate that the assumptions of Ecological Stoichiometry Theory apply at the community level for at least two dominant taxa and across a broad spatial scale, with probable implications for nutrient cycling and ecosystem functionality.
This manuscript contributes to ecological theory, particularly by extending Ecological Stoichiometry Theory to include community-level interactions, clarifying the impact of nutrient concentrations on community structure and function, and informing nutrient management and conservation strategies.
In summary, this study not only addresses a gap in community-level stoichiometric research but also delivers crucial empirical support for advancing ecological science and promoting environmental stewardship.
References
Beck M, Billoir E, Usseglio-Polatera P, Meyer A, Gautreau E and Danger M (2024) Effects of water nutrient concentrations on stream macroinvertebrate community stoichiometry: a large-scale study. bioRxiv, 2024.02.01.574823, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.02.01.574823