Direct submissions to PCI Ecology from bioRxiv.org are possible using the B2J service
Latest recommendations
| Id | Title * | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
15 Jul 2023
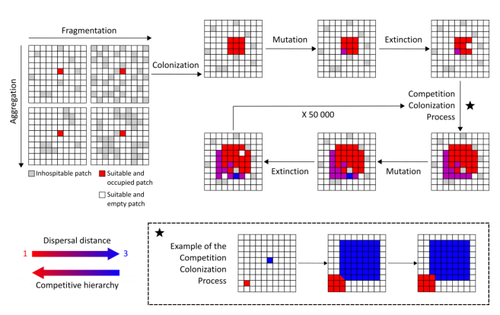
Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulationsBasile Finand, Thibaud Monnin, Nicolas Loeuille https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.06.08.495260The spatial dynamics of habitat fragmentation drives the evolution of dispersal and metapopulation persistenceRecommended by Frédéric Guichard based on reviews by Eva Kisdi, David Murray-Stoker, Shripad Tuljapurkar and 1 anonymous reviewerThe persistence of populations facing the destruction of their habitat is a multifaceted question that has mobilized theoreticians and empiricists alike for decades. As an ecological question, persistence has been studied as the spatial rescue of populations via dispersal into remaining suitable habitats. The spatial aggregation of habitat destruction has been a key component of these studies, and it has been applied to the problem of coexistence by integrating competition-colonization tradeoffs. There is a rich ecological literature on this topic, both from theoretical and field studies (Fahrig 2003). The relationship between life-history strategies of species and their resilience to spatially structured habitat fragmentation is also an important component of conservation strategies through the management of land use, networks of protected areas, and the creation of corridors. In the context of environmental change, the ability of species to adapt to changes in landscape configuration and availability can be treated as an eco-evolutionary process by considering the possibility of evolutionary rescue (Heino and Hanski 2001; Bell 2017). However, eco-evolutionary dynamics considering spatially structured changes in landscapes and life-history tradeoffs remains an outstanding question. Finand et al. (2023) formulate the problem of persistence in fragmented landscapes over evolutionary time scales by studying models for the evolution of dispersal in relation to habitat fragmentation and spatial aggregation. Their simulations were conducted on a spatial grid where individuals can colonize suitable patch as a function of their competitive rank that decreases as a function of their (ii) dispersal distance trait. Simulations were run under fixed habitat fragmentation (proportion of unsuitable habitat) and aggregation, and with an explicit rate of habitat destruction to study evolutionary rescue. Their results reveal a balance between the selection for high dispersal under increasing habitat fragmentation and selection for lower dispersal in response to habitat aggregation. This balance leads to the coexistence of polymorphic dispersal strategies in highly aggregated landscapes with low fragmentation where high dispersers inhabit aggregated habitats while low dispersers are found in isolated habitats. The authors then integrate the spatial rescue mechanism to the problem of evolutionary rescue in response to temporally increasing fragmentation. There they show how rapid evolution allows for evolutionary rescue through the evolution of high dispersal. They also show the limits to this evolutionary rescue to cases where both aggregation and fragmentation are not too high. Interestingly, habitat aggregation prevents evolutionary rescue by directly affecting the evolutionary potential of dispersal. The study is based on simple scenarios that ignore the complexity of relationships between dispersal, landscape properties, and species interactions. This simplicity is the strength of the study, revealing basic mechanisms that can now be tested against other life-history tradeoffs and species interactions. Finand et al. (2023) provide a novel foundation for the study of eco-evolutionary dynamics in metacommunities exposed to spatially structured habitat destruction. They point to important assumptions that must be made along the way, including the relationships between dispersal distance and fecundity (they assume a positive relationship), and the nature of life-history tradeoffs between dispersal rate and local competitive abilities.
Bell, G. 2017. Evolutionary Rescue. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 48:605–627. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110316-023011 | Evolution of dispersal and the maintenance of fragmented metapopulations | Basile Finand, Thibaud Monnin, Nicolas Loeuille | <p>Because it affects dispersal risk and modifies competition levels, habitat fragmentation directly constrains dispersal evolution. When dispersal is traded-off against competitive ability, increased fragmentation is often expected to select high... |  | Colonization, Competition, Dispersal & Migration, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Frédéric Guichard | 2022-06-10 13:51:15 | View | |
14 Jul 2023
Field margins as substitute habitat for the conservation of birds in agricultural wetlandsMallet Pierre, Béchet Arnaud, Sirami Clélia, Mesléard François, Blanchon Thomas, Calatayud François, Dagonet Thomas, Gaget Elie, Leray Carole, Galewski Thomas https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.05.490780Searching for conservation opportunities at the marginsRecommended by Ana S. L. Rodrigues based on reviews by Scott Wilson and Elena D Concepción based on reviews by Scott Wilson and Elena D Concepción
In a progressively human-dominated planet (Venter et al., 2016), the fate of many species will depend on the extent to which they can persist in anthropogenic landscapes. In Western Europe, where only small areas of primary habitat remain (e.g. Sabatini et al., 2018), semi-natural areas are crucial habitats to many native species, yet they are threatened by the expansion of human activities, including agricultural expansion and intensification (Rigal et al., 2023). A new study by Mallet and colleagues (Mallet et al., 2023) investigates the extent to which bird species in the Camargue region are able to use the margins of agricultural fields as substitutes for their preferred semi-natural habitats. Located in the delta of the Rhône River in Southern France, the Camargue is internationally recognized for its biodiversity value, classified as a Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO and as a Wetland of International Importance under the Ramsar Convention (IUCN & UN-WCMC, 2023). Mallet and colleagues tested three specific hypotheses: that grass strips (grassy field boundaries, including grassy tracks or dirt roads used for moving agricultural machinery) can function as substitute habitats for grassland species; that reed strips along drainage ditches (common in the rice paddy landscapes of the Camargue) can function as substitute habitats to wetland species; and that hedgerows can function as substitute habitats to species that favour woodland edges. They did so by measuring how the local abundances of 14 bird species (nine typical of forest edges, 3 of grasslands, and two of reedbeds) respond to increasing coverage of either the three types of field margins or of the three types of semi-natural habitat. This is an elegant study design, yet – as is often the case with real field data – results are not as simple as expected. Indeed, for most species (11 out of 14) local abundances did not increase significantly with the area of their supposed primary habitat, undermining the assumption that they are strongly associated with (or dependent on) those habitats. Among the three species that did respond positively to the area of their primary habitat, one (a forest edge species) responded positively but not significantly to the area of field margins (hedgerows), providing weak evidence to the habitat compensation hypothesis. For the other two (grassland and a wetland species), abundance responded even more strongly to the area of field margins (grass and reed strips, respectively) than to the primary habitat, suggesting that the field margins are not so much a substitute but valuable habitats in their own right. It would have been good conservation news if field margins were found to be suitable habitat substitutes to semi-natural habitats, or at least reasonable approximations, to most species. Given that these margins have functional roles in agricultural landscapes (marking boundaries, access areas, water drainage), they could constitute good win-win solutions for reconciling biodiversity conservation with agricultural production. Alas, the results are more complicated than that, with wide variation in species responses that could not have been predicted from presumed habitat affinities. These results illustrate the challenges of conservation practice in complex landscapes formed by mosaics of variable land use types. With species not necessarily falling neatly into habitat guilds, it becomes even more challenging to plan strategically how to manage landscapes to optimize their conservation. The results presented here suggest that species’ abundances may be responding to landscape variables not taken into account in the analyses, such as connectivity between habitat patches, or maybe positive and negative edge effects between land use types. That such uncertainties remain even in a well-studied region as the Camargue, and for such a well-studied taxon such as birds, only demonstrates the continued importance of rigorous field studies testing explicit hypotheses such as this one by Mallet and colleagues. References IUCN, & UN-WCMC (2023). Protected Planet. Protected Planet. https://www.protectedplanet.net/en Mallet, P., Béchet, A., Sirami, C., Mesléard, F., Blanchon, T., Calatayud, F., Dagonet, T., Gaget, E., Leray, C., & Galewski, T. (2023). Field margins as substitute habitat for the conservation of birds in agricultural wetlands. bioRxiv, 2022.05.05.490780, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.05.05.490780 Rigal, S., Dakos, V., Alonso, H., Auniņš, A., Benkő, Z., Brotons, L., Chodkiewicz, T., Chylarecki, P., de Carli, E., del Moral, J. C. et al. (2023). Farmland practices are driving bird population decline across Europe. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120, e2216573120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2216573120 Sabatini, F. M., Burrascano, S., Keeton, W. S., Levers, C., Lindner, M., Pötzschner, F., Verkerk, P. J., Bauhus, J., Buchwald, E., Chaskovsky, O., Debaive, N. et al. (2018). Where are Europe’s last primary forests? Diversity and Distributions, 24, 1426–1439. https://doi.org/10.1111/ddi.12778 Venter, O., Sanderson, E. W., Magrach, A., Allan, J. R., Beher, J., Jones, K. R., Possingham, H. P., Laurance, W. F., Wood, P., Fekete, B. M., Levy, M. A., & Watson, J. E. M. (2016). Sixteen years of change in the global terrestrial human footprint and implications for biodiversity conservation. Nature Communications, 7, 12558. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12558 | Field margins as substitute habitat for the conservation of birds in agricultural wetlands | Mallet Pierre, Béchet Arnaud, Sirami Clélia, Mesléard François, Blanchon Thomas, Calatayud François, Dagonet Thomas, Gaget Elie, Leray Carole, Galewski Thomas | <p style="text-align: justify;">Breeding birds in agricultural landscapes have declined considerably since the 1950s and the beginning of agricultural intensification in Europe. Given the increasing pressure on agricultural land, it is necessary t... | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Conservation biology, Landscape ecology | Ana S. L. Rodrigues | 2022-05-09 10:48:49 | View | ||
13 Jul 2023
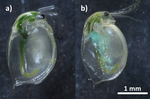
Parasites make hosts more profitable but less available to predatorsLoïc Prosnier, Nicolas Loeuille, Florence D. Hulot, David Renault, Christophe Piscart, Baptiste Bicocchi, Muriel Deparis, Matthieu Lam, Vincent Médoc https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.08.479552Indirect effects of parasitism include increased profitability of prey to optimal foragersRecommended by Luis Schiesari based on reviews by Thierry DE MEEUS and Eglantine Mathieu-BégnéEven though all living organisms are, at the same time, involved in host-parasite interactions and embedded in complex food webs, the indirect effects of parasitism are only beginning to be unveiled. Prosnier et al. investigated the direct and indirect effects of parasitism making use of a very interesting biological system comprising the freshwater zooplankton Daphnia magna and its highly specific parasite, the iridovirus DIV-1 (Daphnia-iridescent virus 1). Daphnia are typically semitransparent, but once infected develop a white phenotype with a characteristic iridescent shine due to the enlargement of white fat cells. In a combination of infection trials and comparison of white and non-white phenotypes collected in natural ponds, the authors demonstrated increased mortality and reduced lifetime fitness in infected Daphnia. Furthermore, white phenotypes had lower mobility, increased reflectance, larger body sizes and higher protein content than non-white phenotypes. As a consequence, total energy content was effectively doubled in white Daphnia when compared to non-white broodless Daphnia. Next the authors conducted foraging trials with Daphnia predators Notonecta (the backswimmer) and Phoxinus (the European minnow). Focusing on Notonecta, unchanged search time and increased handling time were more than compensated by the increased energy content of white Daphnia. White Daphnia were 24% more profitable and consistently preferred by Notonecta, as the optimal foraging theory would predict. The authors argue that menu decisions of optimal foragers in the field might be different, however, as the prevalence – and therefore availability - of white phenotypes in natural populations is very low. The study therefore contributes to our understanding of the trophic context of parasitism. One shortcoming of the study is that the authors rely exclusively on phenotypic signs for determining infection. On their side, DIV-1 is currently known to be highly specific to Daphnia, their study site is well within DIV-1 distributional range, and the symptoms of infection are very conspicuous. Furthermore, the infection trial – in which non-white Daphnia were exposed to white Daphnia homogenates - effectively caused several lethal and sublethal effects associated with DIV-1 infection, including iridescence. However, the infection trial also demonstrated that part of the exposed individuals developed intermediate traits while still keeping the non-white, non-iridescent phenotype. Thus, there may be more subtleties to the association of DIV-1 infection of Daphnia with ecological and evolutionary consequences, such as costs to resistance or covert infection, that the authors acknowledge, and that would be benefitted by coupling experimental and observational studies with the determination of actual infection and viral loads. References Prosnier L., N. Loeuille, F.D. Hulot, D. Renault, C. Piscart, B. Bicocchi, M, Deparis, M. Lam, & V. Médoc. (2023). Parasites make hosts more profitable but less available to predators. BioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.08.479552 | Parasites make hosts more profitable but less available to predators | Loïc Prosnier, Nicolas Loeuille, Florence D. Hulot, David Renault, Christophe Piscart, Baptiste Bicocchi, Muriel Deparis, Matthieu Lam, Vincent Médoc | <p>Parasites are omnipresent, and their eco-evolutionary significance has aroused much interest from scientists. Parasites may affect their hosts in many ways by altering host density, vulnerability to predation, and energy content, thus modifying... |  | Community ecology, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Epidemiology, Experimental ecology, Food webs, Foraging, Freshwater ecology, Host-parasite interactions, Life history, Parasitology, Statistical ecology | Luis Schiesari | 2022-05-20 10:15:41 | View | |
16 Jun 2023
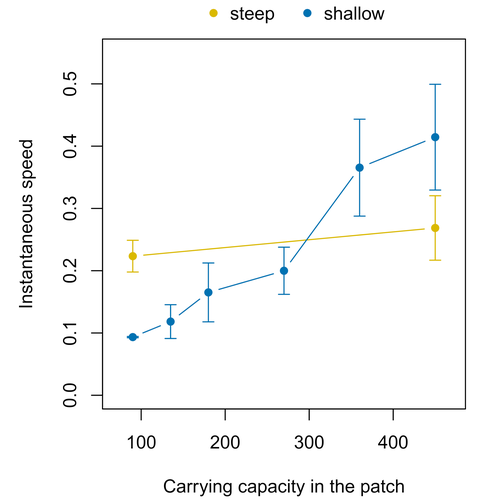
Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansionThibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255Combining stochastic models and experiments to understand dispersal in heterogeneous environmentsRecommended by Joaquín Hortal based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Dispersal is a key element of the natural dynamics of meta-communities, and plays a central role in the success of populations colonizing new landscapes. Understanding how demographic processes may affect the speed at which alien species spread through environmentally-heterogeneous habitat fragments is therefore of key importance to manage biological invasions. This requires studying together the complex interplay of dispersal and population processes, two inextricably related phenomena that can produce many possible outcomes. Stochastic models offer an opportunity to describe this kind of process in a meaningful way, but to ensure that they are realistic (sensu Levins 1966) it is also necessary to combine model simulations with empirical data (Snäll et al. 2007). Morel-Journel et al. (2023) put together stochastic models and experimental data to study how population density may affect the speed at which alien species spread through a heterogeneous landscape. They do it by focusing on what they call ‘colonisation debt’, which is merely the impact that population density at the invasion front may have on the speed at which the species colonizes patches of different carrying capacities. They investigate this issue through two largely independent approaches. First, a stochastic model of dispersal throughout the patches of a linear, 1-dimensional landscape, which accounts for different degrees of density-dependent growth. And second, a microcosm experiment of a parasitoid wasp colonizing patches with different numbers of host eggs. In both cases, they compare the velocity of colonization of patches with lower or higher carrying capacity than the previous one (i.e. what they call upward or downward gradients). Their results show that density-dependent processes influence the speed at which new fragments are colonized is significantly reduced by positive density dependence. When either population growth or dispersal rate depend on density, colonisation debt limits the speed of invasion, which turns out to be dependent on the strength and direction of the gradient between the conditions of the invasion front, and the newly colonized patches. Although this result may be quite important to understand the meta-population dynamics of dispersing species, it is important to note that in their study the environmental differences between patches do not take into account eventual shifts in the scenopoetic conditions (i.e. the values of the environmental parameters to which species niches’ respond to; Hutchinson 1978, see also Soberón 2007). Rather, differences arise from variations in the carrying capacity of the patches that are consecutively invaded, both in the in silico and microcosm experiments. That is, they account for potential differences in the size or quality of the invaded fragments, but not on the costs of colonizing fragments with different environmental conditions, which may also determine invasion speed through niche-driven processes. This aspect can be of particular importance in biological invasions or under climate change-driven range shifts, when adaptation to new environments is often required (Sakai et al. 2001; Whitney & Gabler 2008; Hill et al. 2011). The expansion of geographical distribution ranges is the result of complex eco-evolutionary processes where meta-community dynamics and niche shifts interact in a novel physical space and/or environment (see, e.g., Mestre et al. 2020). Here, the invasibility of native communities is determined by niche variations and how similar are the traits of alien and native species (Hui et al. 2023). Within this context, density-dependent processes will build upon and heterogeneous matrix of native communities and environments (Tischendorf et al. 2005), to eventually determine invasion success. What the results of Morel-Journel et al. (2023) show is that, when the invader shows density dependence, the invasion process can be slowed down by variations in the carrying capacity of patches along the dispersal front. This can be particularly useful to manage biological invasions; ongoing invasions can be at least partially controlled by manipulating the size or quality of the patches that are most adequate to the invader, controlling host populations to reduce carrying capacity. But further, landscape manipulation of such kind could be used in a preventive way, to account in advance for the effects of the introduction of alien species for agricultural exploitation or biological control, thereby providing an additional safeguard to practices such as the introduction of parasitoids to control plagues. These practical aspects are certainly worth exploring further, together with a more explicit account of the influence of the abiotic conditions and the characteristics of the invaded communities on the success and speed of biological invasions. REFERENCES Hill, J.K., Griffiths, H.M. & Thomas, C.D. (2011) Climate change and evolutionary adaptations at species' range margins. Annual Review of Entomology, 56, 143-159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144746 Hui, C., Pyšek, P. & Richardson, D.M. (2023) Disentangling the relationships among abundance, invasiveness and invasibility in trait space. npj Biodiversity, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-023-00019-1 Hutchinson, G.E. (1978) An introduction to population biology. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT. Levins, R. (1966) The strategy of model building in population biology. American Scientist, 54, 421-431. Mestre, A., Poulin, R. & Hortal, J. (2020) A niche perspective on the range expansion of symbionts. Biological Reviews, 95, 491-516. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12574 Morel-Journel, T., Haond, M., Duan, L., Mailleret, L. & Vercken, E. (2023) Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion. bioRxiv, 2022.11.13.516255, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255 Snäll, T., B. O'Hara, R. & Arjas, E. (2007) A mathematical and statistical framework for modelling dispersal. Oikos, 116, 1037-1050. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15604.x Sakai, A.K., Allendorf, F.W., Holt, J.S., Lodge, D.M., Molofsky, J., With, K.A., Baughman, S., Cabin, R.J., Cohen, J.E., Ellstrand, N.C., McCauley, D.E., O'Neil, P., Parker, I.M., Thompson, J.N. & Weller, S.G. (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 305-332. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114037 Soberón, J. (2007) Grinnellian and Eltonian niches and geographic distributions of species. Ecology Letters, 10, 1115-1123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01107.x Tischendorf, L., Grez, A., Zaviezo, T. & Fahrig, L. (2005) Mechanisms affecting population density in fragmented habitat. Ecology and Society, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-01265-100107 Whitney, K.D. & Gabler, C.A. (2008) Rapid evolution in introduced species, 'invasive traits' and recipient communities: challenges for predicting invasive potential. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 569-580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2008.00473.x | Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion | Thibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken | <p>Demographic processes that occur at the local level, such as positive density dependence in growth or dispersal, are known to shape population range expansion, notably by linking carrying capacity to invasion speed. As a result of these process... |  | Biological invasions, Colonization, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Landscape ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Joaquín Hortal | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-11-16 15:52:08 | View |
07 Jun 2023
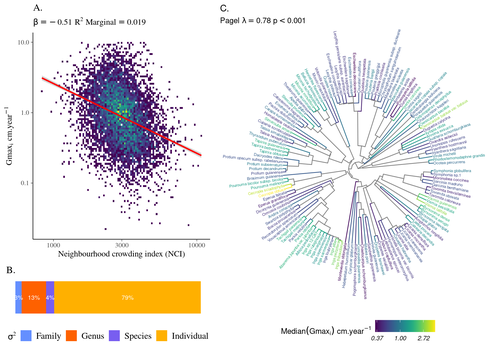
High intraspecific growth variability despite strong evolutionary heritage in a neotropical forestSylvain Schmitt, Bruno Hérault, Géraldine Derroire https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.27.501745Environmental and functional determinants of tree performance in a neotropical forest: the imprint of evolutionary legacy on growth strategiesRecommended by François Munoz based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker, Camille Girard and Jelena Pantel based on reviews by David Murray-Stoker, Camille Girard and Jelena Pantel
The hyperdiverse tropical forests have long fascinated ecologists because the fact that so many species persist at a low density at a local scale remains hard to explain. Both niche-based and neutral hypotheses have been tested, primarily based on analyzing the taxonomic composition of tropical forest plots (Janzen 1970; Hubbell 2001). Studies of the functional and phylogenetic structure of tropical tree communities have further aimed to better assess the importance of niche-based processes. For instance, Baraloto et al. (2012) found that co-occurring species were functionally and phylogenetically more similar in a neotropical forest, suggesting a role of environmental filtering. Likewise, Schmitt et al. (2021) found the influence of environmental filtering on the functional composition of an Indian rainforest. Yet these studies evidenced non-random trait-environment association based on the composition of assemblages only (in terms of occurrences and abundances). A major challenge remains to further address whether and how tree performance varies among species and individuals in tropical forests. Functional traits are related to components of individual fitness (Violle et al. 2007). Recently, more and more emphasis has been put on examining the relationship between functional trait values and demographic parameters (Salguero-Gómez et al. 2018), in order to better understand how functional trait values determine species population dynamics and abundances in assemblages. Fortunel et al. (2018) found an influence of functional traits on species growth variation related to topography, and less clearly to neighborhood density (crowding). Poorter et al. (2018) observed 44% of trait variation within species in a neotropical forest. Although individual trait values would be expected to be better predictors of performance than average values measured at the species level, Poorter et al still found a poor relationship. Schmitt et al. (2023) examined how abiotic conditions and biotic interactions (considering neighborhood density) influenced the variation of individual potential tree growth, in a tropical forest plot located in French Guiana. They also considered the link between species-averaged values of growth potential and functional traits. Schmitt et al. (2023) found substantial variation in growth potential within species, that functional traits explained 40% of the variation of species-averaged growth and, noticeably, that the taxonomic structure (used as random effect in their model) explained a third of the variation in individual growth. Although functional traits of roots, wood and leaves could predict a significant part of species growth potential, much variability of tree growth occurred within species. Intraspecific trait variation can thus be huge in response to changing abiotic and biotic contexts across individuals. The information on phylogenetic relationships can still provide a proxy of the integrated phenotypic variation that is under selection across the phylogeny, and determine a variation in growth strategies among individuals. The similarity of the phylogenetic structure suggests a joint selection of these growth strategies and related functional traits during events of convergent evolution. Baraloto et al. (2012) already noted that phylogenetic distance can be a proxy of niche overlap in tropical tree communities. Here, Schmitt et al. further demonstrate that evolutionary heritage is significantly related to individual growth variation, and plead for better acknowledging this role in future studies. While the role of fitness differences in tropical tree community dynamics remained to be assessed, the present study provides new evidence that individual growth does vary depending on evolutionary relationships, which can reflect the roles of selection and adaptation on growth strategies. Therefore, investigating both the influence of functional traits and phylogenetic relationships on individual performance remains a promising avenue of research, for functional and community ecology in general. REFERENCES Baraloto, Christopher, Olivier J. Hardy, C. E. Timothy Paine, Kyle G. Dexter, Corinne Cruaud, Luke T. Dunning, Mailyn-Adriana Gonzalez, et al. 2012. « Using functional traits and phylogenetic trees to examine the assembly of tropical tree communities ». Journal of Ecology, 100: 690‑701. | High intraspecific growth variability despite strong evolutionary heritage in a neotropical forest | Sylvain Schmitt, Bruno Hérault, Géraldine Derroire | <p style="text-align: justify;">Individual tree growth is a key determinant of species performance and a driver of forest dynamics and composition. Previous studies on tree growth unravelled the variation in species growth as a function of demogra... |  | Community ecology, Demography, Population ecology | François Munoz | Jelena Pantel, David Murray-Stoker | 2022-08-01 14:29:04 | View |
31 May 2023
Conservation networks do not match the ecological requirements of amphibiansMatutini Florence, Jacques Baudry, Marie-Josée Fortin, Guillaume Pain, Joséphine Pithon https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500425Amphibians under scrutiny - When human-dominated landscape mosaics are not in full compliance with their ecological requirementsRecommended by Sandrine Charles based on reviews by Peter Vermeiren and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Peter Vermeiren and 1 anonymous reviewer
Among vertebrates, amphibians are one of the most diverse groups with more than 7,000 known species. Amphibians occupy various ecosystems, including forests, wetlands, and freshwater habitats. Amphibians are known to be highly sensitive to changes in their environment, particularly to water quality and habitat degradation, so that monitoring abundance of amphibian populations can provide early warning signs of ecosystem disturbances that may also affect other organisms including humans (Bishop et al., 2012). Accordingly, efforts in habitat preservation and sustainable land and water management are necessary to safeguard amphibian populations. In this context, Matutini et al. (2023) compared ecological requirements of amphibian species with the quality of agricultural landscape mosaics. Doing so, they identified critical gaps in existing conservation tools that include protected areas, green infrastructures, and inventoried sites. Matutini et al. (2023) focused on nine amphibian species in the Pays-de-la-Loire region where the landscape has been fashioned over the years by human activities. Three of the chosen amphibian species are living in a dense hedgerow mosaic landscape, while five others are more generalists. Matutini et al. (2023) established multi-species habitat suitability maps, together with their levels of confidence, by combining single species maps with a probabilistic stacking method at 500-m resolution. From these maps, habitats were classified in five categories, from not suitable to highly suitable. Then, the circuit theory was used to map the potential connections between each highly suitable patch at the regional scale. Finally, comparing suitability maps with existing conservation tools, Matutini et al. (2023) were able to assess their coverage and efficiency. Whatever their species status (endangered or not), Matutini et al. (2023) highlighted some discrepancies between the ecological requirements of amphibians in terms of habitat quality and the conservation tools of the landscape mosaic within which they are evolving. More specifically, Matutini et al. (2023) found that protected areas and inventoried sites covered only a small proportion of highly suitable habitats, while green infrastructures covered around 50% of the potential habitat for amphibian species. Such a lack of coverage and efficiency of protected areas brings to light that geographical sites with amphibian conservation challenges are known but not protected. Regarding the landscape fragmentation, Matutini et al. (2023) found that generalist amphibian species have a more homogeneous distribution of suitable habitats at the regional scale. They also identified two bottlenecks between two areas of suitable habitats, a situation that could prove critical to amphibian movements if amphibians were forced to change habitats to global change. In conclusion, Matutini et al. (2023) bring convincing arguments in support of land-use species-conservation planning based on a better consideration of human-dominated landscape mosaics in full compliance with ecological requirements of the species that inhabit the regions concerned. ReferencesBishop, P.J., Angulo, A., Lewis, J.P., Moore, R.D., Rabb, G.B., Moreno, G., 2012. The Amphibian Extinction Crisis - what will it take to put the action into the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan? Sapiens - Surveys and Perspectives Integrating Environment and Society 5, 1–16. http://journals.openedition.org/sapiens/1406 Matutini, F., Baudry, J., Fortin, M.-J., Pain, G., Pithon, J., 2023. Conservation networks do not match ecological requirements of amphibians. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.18.500425 | Conservation networks do not match the ecological requirements of amphibians | Matutini Florence, Jacques Baudry, Marie-Josée Fortin, Guillaume Pain, Joséphine Pithon | <p style="text-align: justify;">1. Amphibians are among the most threatened taxa as they are highly sensitive to habitat degradation and fragmentation. They are considered as model species to evaluate habitats quality in agricultural landscapes. I... | Biodiversity, Biogeography, Human impact, Landscape ecology, Macroecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Species distributions, Terrestrial ecology | Sandrine Charles | 2022-09-20 14:40:03 | View | ||
29 May 2023

Using integrated multispecies occupancy models to map co-occurrence between bottlenose dolphins and fisheries in the Gulf of Lion, French Mediterranean SeaValentin Lauret, Hélène Labach, Léa David, Matthieu Authier, Olivier Gimenez https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/npd6uMapping co-occurence of human activities and wildlife from multiple data sourcesRecommended by Paul Caplat based on reviews by Mason Fidino and 1 anonymous reviewerTwo fields of research have grown considerably over the past twenty years: the investigation of human-wildlife conflicts (e.g. see Treves & Santiago-Ávila 2020), and multispecies occupancy modelling (Devarajan et al. 2020). In their recent study, Lauret et al. (2023) combined both in an elegant methodological framework, applied to the study of the co-occurrence of fishing activities and bottlenose dolphins in the French Mediterranean. A common issue with human-wildlife conflicts (and, in particular, fishery by-catch) is that data is often only available from those conflicts or interactions, limiting the validity of the predictions (Kuiper et al. 2022). Lauret et al. use independent data sources informing the occurrence of fishing vessels and dolphins, combined in a Bayesian multispecies occupancy model where vessels are "the other species". I particularly enjoyed that approach, as integration of human activities in ecological models can be extremely complex, but can also translate in phenomena that can be captured as one would of individuals of a species, as long as the assumptions are made clearly. Here, the model is made more interesting by accounting for environmental factors (seabed depth) borrowing an approach from Generalized Additive Models in the Bayesian framework. While not pretending to provide (yet) practical recommendations to help conserve bottlenose dolphins (and other wildlife conflicts), this study and the associated code are a promising step in that direction. REFERENCES Devarajan, K., Morelli, T.L. & Tenan, S. (2020), Multi-species occupancy models: review, roadmap, and recommendations. Ecography, 43: 1612-1624. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.04957 Kuiper, T., Loveridge, A.J. and Macdonald, D.W. (2022), Robust mapping of human–wildlife conflict: controlling for livestock distribution in carnivore depredation models. Anim. Conserv., 25: 195-207. https://doi.org/10.1111/acv.12730 Lauret V, Labach H, David L, Authier M, & Gimenez O (2023) Using integrated multispecies occupancy models to map co-occurrence between bottlenose dolphins and fisheries in the Gulf of Lion, French Mediterranean Sea. Ecoevoarxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/npd6u Treves, A. & Santiago-Ávila, F.J. (2020). Myths and assumptions about human-wildlife conflict and coexistence. Conserv. Biol. 34, 811–818. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13472 | Using integrated multispecies occupancy models to map co-occurrence between bottlenose dolphins and fisheries in the Gulf of Lion, French Mediterranean Sea | Valentin Lauret, Hélène Labach, Léa David, Matthieu Authier, Olivier Gimenez | <p style="text-align: justify;">In the Mediterranean Sea, interactions between marine species and human activities are prevalent. The coastal distribution of bottlenose dolphins (<em>Tursiops truncatus</em>) and the predation pressure they put on ... |  | Marine ecology, Population ecology, Species distributions | Paul Caplat | 2022-10-21 11:13:36 | View | |
26 May 2023
Using repeatability of performance within and across contexts to validate measures of behavioral flexibilityMcCune KB, Blaisdell AP, Johnson-Ulrich Z, Lukas D, MacPherson M, Seitz BM, Sevchik A, Logan CJ https://doi.org/10.32942/X2R59KDo reversal learning methods measure behavioral flexibility?Recommended by Aurélie Coulon based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Aparajitha Ramesh based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Aparajitha Ramesh
Assessing the reliability of the methods we use in actually measuring the intended trait should be one of our first priorities when designing a study – especially when the trait in question is not directly observable and is measured through a proxy. This is the case for cognitive traits, which are often quantified through measures of behavioral performance. Behavioral flexibility is of particular interest in the context of great environmental changes that a lot of populations have to experiment. This type of behavioral performance is often measured through reversal learning experiments (Bond 2007). In these experiments, individuals first learn a preference, for example for an object of a certain type of form or color, associated with a reward such as food. The characteristics of the rewarded object then change, and the individuals hence have to learn these new characteristics (to get the reward). The time needed by the individual to make this change in preference has been considered a measure of behavioral flexibility. Although reversal learning experiments have been widely used, their construct validity to assess behavioral flexibility has not been thoroughly tested. This was the aim of McCune and collaborators' (2023) study, through the test of the repeatability of individual performance within and across contexts of reversal learning, in the great-tailed grackle. This manuscript presents a post-study of the preregistered study* (Logan et al. 2019) that was peer-reviewed and received an In Principle Recommendation for PCI Ecology (Coulon 2019; the initial preregistration was split into 3 post-studies).
The first hypothesis was tested by measuring the repeatability of the time needed by individuals to switch color preference in a color reversal learning task (colored tubes), over serial sessions of this task. The second one was tested by measuring the time needed by individuals to switch solutions, within 3 different contexts: (1) colored tubes, (2) plastic and (3) wooden multi-access boxes involving several ways to access food. Despite limited sample sizes, the results of these experiments suggest that there is both temporal and contextual repeatability of behavioral flexibility performance of great-tailed grackles, as measured by reversal learning experiments. Those results are a first indication of the construct validity of reversal learning experiments to assess behavioral flexibility. As highlighted by McCune and collaborators, it is now necessary to assess the discriminant validity of these experiments, i.e. checking that a different performance is obtained with tasks (experiments) that are supposed to measure different cognitive abilities. Coulon, A. (2019) Can context changes improve behavioral flexibility? Towards a better understanding of species adaptability to environmental changes. Peer Community in Ecology, 100019. https://doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100019 Logan, CJ, Lukas D, Bergeron L, Folsom M, & McCune, K. (2019). Is behavioral flexibility related to foraging and social behavior in a rapidly expanding species? In Principle Acceptance by PCI Ecology of the Version on 6 Aug 2019. http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_flexmanip.html McCune KB, Blaisdell AP, Johnson-Ulrich Z, Lukas D, MacPherson M, Seitz BM, Sevchik A, Logan CJ (2023) Using repeatability of performance within and across contexts to validate measures of behavioral flexibility. EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2R59K | Using repeatability of performance within and across contexts to validate measures of behavioral flexibility | McCune KB, Blaisdell AP, Johnson-Ulrich Z, Lukas D, MacPherson M, Seitz BM, Sevchik A, Logan CJ | <p style="text-align: justify;">Research into animal cognitive abilities is increasing quickly and often uses methods where behavioral performance on a task is assumed to represent variation in the underlying cognitive trait. However, because thes... | Behaviour & Ethology, Evolutionary ecology, Preregistrations, Zoology | Aurélie Coulon | 2022-08-15 20:56:42 | View | ||
24 May 2023
Evolutionary determinants of reproductive seasonality: a theoretical approachLugdiwine Burtschell, Jules Dezeure, Elise Huchard, Bernard Godelle https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504761When does seasonal reproduction evolve?Recommended by Tim Coulson based on reviews by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont, Nigel Yoccoz and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont, Nigel Yoccoz and 1 anonymous reviewer
Have you ever wondered why some species breed seasonally while others do not? You might think it is all down to lattitude and the harshness of winters but it turns out it is quite a bit more complicated than that. A consequence of this is that climate change may result in the evolution of the degree of seasonal reproduction, with some species perhaps becoming less seasonal and others more so even in the same habitat. Burtschell et al. (2023) investigated how various factors influence seasonal breeding by building an individual-based model of a baboon population from which they calculated the degree of seasonality for the fittest reproductive strategy. They then altered key aspects of their model to examine how these changes impacted the degree of seasonality in the reproductive strategy. What they found is fascinating. The degree of seasonality in reproductive strategy is expected to increase with increased seasonality in the environment, decreased food availability, increased energy expenditure, and how predictable resource availability is. Interestingly, neither female cycle length nor extrinsic infant mortality influenced the degree of seasonality in reproduction. What this means in reality for seasonal species is more challenging to understand. Some environments appear to be becoming more seasonal yet less predictable, and some species appear to be altering their daily energy budgets in response to changing climate in quite complex ways. As with pretty much everything in biology, Burtschell et al.'s work reveals much nuance and complexity, and that predicting how species might alter their reproductive timing is fraught with challenges. The paper is very well written. With a simpler model it may have proven possible to achieve analytical solutions, but this is a very minor gripe. The reviewers were positive about the paper, and I have little doubt it will be well-cited. REFERENCES Burtschell L, Dezeure J, Huchard E, Godelle B (2023) Evolutionary determinants of reproductive seasonality: a theoretical approach. bioRxiv, 2022.08.22.504761, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.08.22.504761 | Evolutionary determinants of reproductive seasonality: a theoretical approach | Lugdiwine Burtschell, Jules Dezeure, Elise Huchard, Bernard Godelle | <p style="text-align: justify;">Reproductive seasonality is a major adaptation to seasonal cycles and varies substantially among organisms. This variation, which was long thought to reflect a simple latitudinal gradient, remains poorly understood ... |  | Evolutionary ecology, Life history, Theoretical ecology | Tim Coulson | Nigel Yoccoz | 2022-08-23 21:37:28 | View |
17 May 2023
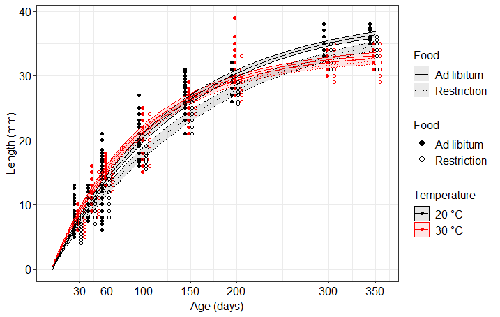
Distinct impacts of food restriction and warming on life history traits affect population fitness in vertebrate ectothermsSimon Bazin, Claire Hemmer-Brepson, Maxime Logez, Arnaud Sentis, Martin Daufresne https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-03738584v3Effect of food conditions on the Temperature-Size RuleRecommended by Aleksandra Walczyńska based on reviews by Wolf Blanckenhorn and Wilco VerberkTemperature-size rule (TSR) is a phenomenon of plastic changes in body size in response to temperature, originally observed in more than 80% of ectothermic organisms representing various groups (Atkinson 1994). In particular, ectotherms were observed to grow faster and reach smaller size at higher temperature and grow slower and achieve larger size at lower temperature. This response has fired the imagination of researchers since its invention, due to its counterintuitive pattern from an evolutionary perspective (Berrigan and Charnov 1994). The main question to be resolved is: why do organisms grow fast and achieve smaller sizes under more favourable conditions (= relatively higher temperature), while they grow longer and achieve larger sizes under less favourable conditions (relatively lower temperature), if larger size means higher fitness, while longer development may be risky? This evolutionary conundrum still awaits an ultimate explanation (Angilletta Jr et al. 2004; Angilletta and Dunham 2003; Verberk et al. 2021). Although theoretical modelling has shown that such a growth pattern can be achieved as a response to temperature alone, with a specific combination of energetic parameters and external mortality (Kozłowski et al. 2004), it has been suggested that other temperature-dependent environmental variables may be the actual drivers of this pattern. One of the most frequently invoked variable is the relative oxygen availability in the environment (e.g., Atkinson et al. 2006; Audzijonyte et al. 2019; Verberk et al. 2021; Woods 1999), which decreases with temperature increase. Importantly, this effect is more pronounced in aquatic systems (Forster et al. 2012). However, other temperature-dependent parameters are also being examined in the context of their possible effect on TSR induction and strength. Food availability is among the interfering factors in this regard. In aquatic systems, nutritional conditions are generally better at higher temperature, while a range of relatively mild thermal conditions is considered. However, there are no conclusive results so far on how nutritional conditions affect the plastic body size response to acute temperature changes. A study by Bazin et al. (2023) examined this particular issue, the effects of food and temperature on TSR, in medaka fish. An important value of the study was to relate the patterns found to fitness. This is a rare and highly desirable approach since evolutionary significance of any results cannot be reliably interpreted unless shown as expressed in light of fitness. The authors compared the body size of fish kept at 20°C and 30°C under conditions of food abundance or food restriction. The results showed that the TSR (smaller body size at 30°C compared to 20°C) was observed in both food treatments, but the effect was delayed during fish development under food restriction. Regarding the relevance to fitness, increased temperature resulted in more eggs laid but higher mortality, while food restriction increased survival but decreased the number of eggs laid in both thermal treatments. Overall, food restriction seemed to have a more severe effect on development at 20°C than at 30°C, contrary to the authors’ expectations. I found this result particularly interesting. One possible interpretation, also suggested by the authors, is that the relative oxygen availability, which was not controlled for in this study, could have affected this pattern. According to theoretical predictions confirmed in quite many empirical studies so far, oxygen restriction is more severe at higher temperatures. Perhaps for these particular two thermal treatments and in the case of the particular species studied, this restriction was more severe for organismal performance than the food restriction. This result is an example that all three variables, temperature, food and oxygen, should be taken into account in future studies if the interrelationship between them is to be understood in the context of TSR. It also shows that the reasons for growing smaller in warm may be different from those for growing larger in cold, as suggested, directly or indirectly, in some previous studies (Hessen et al. 2010; Leiva et al. 2019). Since medaka fish represent predatory vertebrates, the results of the study contribute to the issue of global warming effect on food webs, as the authors rightly point out. This is an important issue because the general decrease in the size or organisms in the aquatic environment with global warming is a fact (e.g., Daufresne et al. 2009), while the question of how this might affect entire communities is not trivial to resolve (Ohlberger 2013). REFERENCES Angilletta Jr, M. J., T. D. Steury & M. W. Sears, 2004. Temperature, growth rate, and body size in ectotherms: fitting pieces of a life–history puzzle. Integrative and Comparative Biology 44:498-509. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/44.6.498 Angilletta, M. J. & A. E. Dunham, 2003. The temperature-size rule in ectotherms: Simple evolutionary explanations may not be general. American Naturalist 162(3):332-342. https://doi.org/10.1086/377187 Atkinson, D., 1994. Temperature and organism size – a biological law for ectotherms. Advances in Ecological Research 25:1-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60212-3 Atkinson, D., S. A. Morley & R. N. Hughes, 2006. From cells to colonies: at what levels of body organization does the 'temperature-size rule' apply? Evolution & Development 8(2):202-214 https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-142X.2006.00090.x Audzijonyte, A., D. R. Barneche, A. R. Baudron, J. Belmaker, T. D. Clark, C. T. Marshall, J. R. Morrongiello & I. van Rijn, 2019. Is oxygen limitation in warming waters a valid mechanism to explain decreased body sizes in aquatic ectotherms? Global Ecology and Biogeography 28(2):64-77 https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12847 Bazin, S., Hemmer-Brepson, C., Logez, M., Sentis, A. & Daufresne, M. 2023. Distinct impacts of food restriction and warming on life history traits affect population fitness in vertebrate ectotherms. HAL, ver.3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-03738584v3 Berrigan, D. & E. L. Charnov, 1994. Reaction norms for age and size at maturity in response to temperature – a puzzle for life historians. Oikos 70:474-478. https://doi.org/10.2307/3545787 Daufresne, M., K. Lengfellner & U. Sommer, 2009. Global warming benefits the small in aquatic ecosystems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 106(31):12788-93 https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0902080106 Forster, J., A. G. Hirst & D. Atkinson, 2012. Warming-induced reductions in body size are greater in aquatic than terrestrial species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 109(47):19310-19314. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1210460109 Hessen, D. O., P. D. Jeyasingh, M. Neiman & L. J. Weider, 2010. Genome streamlining and the elemental costs of growth. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 25(2):75-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2009.08.004 Kozłowski, J., M. Czarnoleski & M. Dańko, 2004. Can optimal resource allocation models explain why ectotherms grow larger in cold? Integrative and Comparative Biology 44(6):480-493. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/44.6.480 Leiva, F. P., P. Calosi & W. C. E. P. Verberk, 2019. Scaling of thermal tolerance with body mass and genome size in ectotherms: a comparison between water- and air-breathers. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B 374:20190035. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2019.0035 Ohlberger, J., 2013. Climate warming and ectotherm body szie - from individual physiology to community ecology. Functional Ecology 27:991-1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12098 Verberk, W. C. E. P., D. Atkinson, K. N. Hoefnagel, A. G. Hirst, C. R. Horne & H. Siepel, 2021. Shrinking body sizes in response to warming: explanations for the temperature-size rule with special emphasis on the role of oxygen. Biological Reviews 96:247-268. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12653 Woods, H. A., 1999. Egg-mass size and cell size: effects of temperature on oxygen distribution. American Zoologist 39:244-252. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/39.2.244 | Distinct impacts of food restriction and warming on life history traits affect population fitness in vertebrate ectotherms | Simon Bazin, Claire Hemmer-Brepson, Maxime Logez, Arnaud Sentis, Martin Daufresne | <p>The reduction of body size with warming has been proposed as the third universal response to global warming, besides geographical and phenological shifts. Observed body size shifts in ectotherms are mostly attributed to the temperature size rul... |  | Climate change, Experimental ecology, Freshwater ecology, Phenotypic plasticity, Population ecology | Aleksandra Walczyńska | 2022-07-27 09:28:29 | View |
FOLLOW US
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Vasilis Dakos (Representative)
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










