Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture▲ | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
29 Nov 2019

Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersalAugust Sevchik, Corina Logan, Melissa Folsom, Luisa Bergeron, Aaron Blackwell, Carolyn Rowney, Dieter Lukas http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gdispersal.htmlInvestigate fine scale sex dispersal with spatial and genetic analysesRecommended by Sophie Beltran-Bech based on reviews by Sylvine Durand and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Sylvine Durand and 1 anonymous reviewer
The preregistration "Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersal" [1] presents the analysis plan that will be used to genetically and spatially investigate sex-biased dispersal in great-tailed grackles (Quiscalus mexicanus). References [1] Sevchik A., Logan C. J., Folsom M., Bergeron L., Blackwell A., Rowney C., and Lukas D. (2019). Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersal. In principle recommendation by Peer Community In Ecology. corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gdispersal.html | Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersal | August Sevchik, Corina Logan, Melissa Folsom, Luisa Bergeron, Aaron Blackwell, Carolyn Rowney, Dieter Lukas | In most bird species, females disperse prior to their first breeding attempt, while males remain close to the place they were hatched for their entire lives (Greenwood and Harvey (1982)). Explanations for such female bias in natal dispersal have f... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Life history, Preregistrations, Social structure, Zoology | Sophie Beltran-Bech | 2019-07-24 12:47:07 | View | |
01 Feb 2020

Touchy matter: the delicate balance between Morgan’s canon and open-minded description of advanced cognitive skills in the animalRecommended by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor based on reviews by Valérie Dufour and Alex Taylor
In a recent paper published in PNAS, Fayet et al. [1] reported scarce field observations of two Atlantic puffins (four years apart) apparently scratching their bodies using sticks, which was interpreted by the authors as evidence of tool use in this species. In a short response, Benjamin Farrar [2] raises serious concerns about this interpretation and proposes simpler, more parsimonious, mechanisms explaining the observed behaviour: a textbook case of Morgan's canon. References [1] Fayet, A. L., Hansen, E. S., and Biro, D. (2020). Evidence of tool use in a seabird. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(3), 1277–1279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918060117 | Evidence of tool use in a seabird? | Benjamin G. Farrar | Fayet, Hansen and Biro (1) provide two observations of Atlantic puffins, *Fratercula arctica*, performing self-directed actions while holding a stick in their beaks. The authors interpret this as evidence of tool use as they suggest that the stick... |  | Behaviour & Ethology | Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont | 2020-01-22 11:55:27 | View | |
13 May 2023

Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sourcesNils Radecker, Anders Meibom https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.07.519152Constraining the importance of heterotrophic vs autotrophic feeding in photosymbiotic cnidariansRecommended by Ulisse Cardini based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The symbiosis with autotrophic dinoflagellate algae has enabled heterotrophic Cnidaria to thrive in nutrient-poor tropical waters (Muscatine and Porter 1977; Stanley 2006). In particular, mixotrophy, i.e. the ability to acquire nutrients through both autotrophy and heterotrophy, confers a competitive edge in oligotrophic waters, allowing photosymbiotic Cnidaria to outcompete benthic organisms limited to a single diet (e.g., McCook 2001). However, the relative importance of autotrophy vs heterotrophy in sustaining symbiotic cnidarian’s nutrition is still the subject of intense research. In fact, figuring out the cellular mechanisms by which symbiotic Cnidaria acquire a balanced diet for their metabolism and growth is relevant to our understanding of their physiology under varying environmental conditions and in response to anthropogenic perturbations. In this study's long-term starvation experiment, Radecker & Meibom (2023) investigated the survival of the photosymbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic feeding. After one year of heterotrophic starvation, Apitasia anemones remained fully viable but showed an 85 % reduction in biomass. Using 13C-bicarbonate and 15N-ammonium labeling, electron microscopy and NanoSIMS imaging, the authors could clearly show that the contribution of algal-derived nutrients to the host metabolism remained unaffected as a result of increased algal photosynthesis and more efficient carbon translocation. At the same time, the absence of heterotrophic feeding caused severe nitrogen limitation in the starved Apitasia anemones. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into nutrient exchange within the symbiosis between Cnidaria and dinoflagellate algae at the cellular level and sheds new light on the importance of heterotrophic feeding as a nitrogen acquisition strategy for holobiont growth in oligotrophic waters. REFERENCES McCook L (2001) Competition between corals and algal turfs along a gradient of terrestrial influence in the nearshore central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 19:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003380000119 Muscatine L, Porter JW (1977) Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments. Bioscience 27:454–460. https://doi.org/10.2307/1297526 Radecker N, Meibom A (2023) Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sources. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.07.519152 Stanley GD Jr (2006) Photosymbiosis and the evolution of modern coral reefs. Science 312:857–858. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1123701 | Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sources | Nils Radecker, Anders Meibom | <p style="text-align: justify;">Phototrophic Cnidaria are mixotrophic organisms that can complement their heterotrophic diet with nutrients assimilated by their algal endosymbionts. Metabolic models suggest that the translocation of photosynthates... |  | Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Symbiosis | Ulisse Cardini | 2022-12-12 10:50:55 | View | |
26 Mar 2019
Is behavioral flexibility manipulatable and, if so, does it improve flexibility and problem solving in a new context?Corina Logan, Carolyn Rowney, Luisa Bergeron, Benjamin Seitz, Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Kelsey McCune http://corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/g_flexmanip.htmlCan context changes improve behavioral flexibility? Towards a better understanding of species adaptability to environmental changesRecommended by Aurélie Coulon based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin based on reviews by Maxime Dahirel and Andrea Griffin
Behavioral flexibility is a key for species adaptation to new environments. Predicting species responses to new contexts hence requires knowledge on the amount to and conditions in which behavior can be flexible. This is what Logan and collaborators propose to assess in a series of experiments on the great-tailed grackles, in a context of rapid range expansion. This pre-registration is integrated into this large research project and concerns more specifically the manipulability of the cognitive aspects of behavioral flexibility. Logan and collaborators will use reversal learning tests to test whether (i) behavioral flexibility is manipulatable, (ii) manipulating flexibility improves flexibility and problem solving in a new context, (iii) flexibility is repeatable within individuals, (iv) individuals are faster at problem solving as they progress through serial reversals. The pre-registration carefully details the hypotheses, their associated predictions and alternatives, and the plan of statistical analyses, including power tests. The ambitious program presented in this pre-registration has the potential to provide important pieces to better understand the mechanisms of species adaptability to new environments. | Is behavioral flexibility manipulatable and, if so, does it improve flexibility and problem solving in a new context? | Corina Logan, Carolyn Rowney, Luisa Bergeron, Benjamin Seitz, Aaron Blaisdell, Zoe Johnson-Ulrich, Kelsey McCune | This is one of the first studies planned for our long-term research on the role of behavioral flexibility in rapid geographic range expansions. Behavioral flexibility, the ability to adapt behavior to new circumstances, is thought to play an impor... | Behaviour & Ethology, Preregistrations, Zoology | Aurélie Coulon | 2018-07-03 13:23:10 | View | ||
11 Mar 2022
Comment on “Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities”Ethan Bass, André Kessler https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/xsbtmDoes information theory inform chemical arms race communication?Recommended by Rodrigo Medel based on reviews by Claudio Ramirez and 2 anonymous reviewersOne of the long-standing questions in evolutionary ecology is on the mechanisms involved in arms race coevolution. One way to address this question is to understand the conditions under which one species evolves traits in response to the presence of a second species and so on. However, specialized pairwise interactions are by far less common in nature than interactions involving a higher number of interacting species (Bascompte, Jordano 2013). While interactions between large sets of species are the norm rather than the exception in mutualistic (pollination, seed dispersal), and antagonist (herbivory, parasitism) relationships, few is known on the way species identify, process, and respond to information provided by other interacting species under field conditions (Schaefer, Ruxton 2011). Zu et al. (2020) addressed this general question by developing an interesting information theory-based approach that hypothesized conditional entropy in chemical communication plays a role as proxy of fitness in plant-herbivore communities. More specifically, plant fitness was assumed to be related to the efficiency to code signals by plant species, and herbivore fitness to the capacity to decode plant signals. In this way, from the plant perspective, the elaboration of plant signals that elude decoding by herbivores is expected to be favored, as herbivores are expected to attack plants with simple chemical signals. The empirical observation upon which the model was tested was the redundancy in volatile organic compounds (VOC) found across plant species in a plant-herbivore community. Interestingly, Zu et al.’s model predicted successfully that VOC redundancy in the plant community associates with increased conditional entropy, which conveys herbivore confusion and plant protection against herbivory. In this way, plant species that evolve VOCs already present in the community might be benefitted, ultimately leading to the patterns of VOC redundancy commonly observed in nature. Bass & Kessler performed a series of interesting observations on Zu et al. (2020), that can be organized along three lines of reasoning. First, from an evolutionary perspective, Bass & Kessler note the important point that accepting that conditional information entropy, estimated from the contribution of every plant species to volatile redundancy implies that average plant fitness seems to depend on community-level properties (i.e., what the other species in the community are doing) rather than on population-level characteristics (I.e., what the individuals belonging a population are doing). While the level at which selection acts upon is a longstanding debate (e.g., Goodnight, 1990; Williams, 1992), the model seems to contradict one of the basic tenets of Darwinian evolution. The extent to which this important observation invalidates the contribution of Zu et al. (2020) is open to scrutiny. However, one can indulge the evolutionary criticism by arguing that every theoretical model performs a number of assumptions to preserve the simplicity of analyses. Furthermore, even accepting the criticism, the overall information-based framework is valuable as it provides a fresh perspective to the way coding and decoding chemical information in plant-herbivore interactions may result in arm race coevolution. The question to be assessed by members of the scientific community is how strong the evolutionary assumptions are to be acceptable. A second line of reasoning involves consideration of additional routes of chemical information transfer. If chemical volatiles are involved in another ecological function unrelated to arm race (as they are) such as toxicity, crypsis, aposematism, etc., the conditional information indices considered as proxy to plant and herbivore fitness may be only secondarily related to arms race. This is an interesting observation, which suggests that VOC production may have more than one ecological function, as it often happens in “pleiotropic” traits (Strauss, Irwin 2004). This is an exciting avenue for future research. Finally, a third category of comments involves the relationship between conditional information entropy and plant and herbivore fitness. Bass & Kessler developed a Bayesian treatment of the community-level information developed by Zu et al. (2020) that permitted to estimate fitness on a species rather than community level. Their results revealed that community conditional entropies fail to align with species-level indices, suggesting that conclusions of Strauss & Irwin (2004) are not commensurate with fitness at the species level, where the analysis seems to be pertinent. In general, I strongly recommend Bass & Kessler’s contribution as it provides a series of observations and new perspectives to Zu et al. (2020). Rather than restricting their manuscript to blind criticisms, Bass & Kessler provides new interesting perspectives, which is always welcome as it improves the value and scope of the original work. References Bascompte J, Jordano P (2013) Mutualistic Networks. Princeton University Press. https://doi.org/10.23943/princeton/9780691131269.001.0001 Bass E, Kessler A (2022) Comment on “Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities.” EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 8 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/xsbtm Goodnight CJ (1990) Experimental Studies of Community Evolution I: The Response to Selection at the Community Level. Evolution, 44, 1614–1624. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1990.tb03850.x Schaefer HM, Ruxton GD (2011) Plant-Animal Communication. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:osobl/9780199563609.001.0001 Strauss SY, Irwin RE (2004) Ecological and Evolutionary Consequences of Multispecies Plant-Animal Interactions. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 35, 435–466. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.35.112202.130215 Williams GC (1992) Natural Selection: Domains, Levels, and Challenges. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York. Zu P, Boege K, del-Val E, Schuman MC, Stevenson PC, Zaldivar-Riverón A, Saavedra S (2020) Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities. Science, 368, 1377–1381. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba2965 | Comment on “Information arms race explains plant-herbivore chemical communication in ecological communities” | Ethan Bass, André Kessler | <p style="text-align: justify;">Zu et al (Science, 19 Jun 2020, p. 1377) propose that an ‘information arms-race’ between plants and herbivores explains plant-herbivore communication at the community level. However, the analysis presented here show... |  | Chemical ecology, Community ecology, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Evolutionary ecology, Herbivory, Interaction networks, Theoretical ecology | Rodrigo Medel | 2021-10-02 06:06:07 | View | |
20 Oct 2021

Eco-evolutionary dynamics further weakens mutualistic interaction and coexistence under population declineAvril Weinbach, Nicolas Loeuille, Rudolf P. Rohr https://doi.org/10.1101/570580Doomed by your partner: when mutualistic interactions are like an evolutionary millstone around a species’ neckRecommended by Sylvain Billiard based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Mutualistic interactions are the weird uncles of population and community ecology. They are everywhere, from the microbes aiding digestion in animals’ guts to animal-pollination services in ecosystems; They increase productivity through facilitation; They fascinate us when small birds pick the teeth of a big-mouthed crocodile. Yet, mutualistic interactions are far less studied and understood than competition or predation. Possibly because we are naively convinced that there is no mystery here: isn’t it obvious that mutualistic interactions necessarily facilitate species coexistence? Since mutualistic species benefit from one another, if one species evolves, the other should just follow, isn’t that so? It is not as simple as that, for several reasons. First, because simple mutualistic Lotka-Volterra models showed that most of the time mutualistic systems should drift to infinity and be unstable (e.g. Goh 1979). This is not what happens in natural populations, so something is missing in simple models. At a larger scale, that of communities, this is even worse, since we are still far from understanding the link between the topology of mutualistic networks and the stability of a community. Second, interactions are context-dependent: mutualistic species exchange resources, and thus from the point of view of one species the interaction is either beneficial or not, depending on the net gain of energy (e.g. Holland and DeAngelis 2010). In other words, considering interactions as mutualistic per se is too caricatural. Third, since evolution is blind, the evolutionary response of a species to an environmental change can have any effect on its mutualistic partner, and not necessarily a neutral or positive effect. This latter reason is particularly highlighted by the paper by A. Weinbach et al. (2021). Weinbach et al. considered a simple two-species mutualistic Lotka-Volterra model and analyzed the evolutionary dynamics of a trait controlling for the rate of interaction between the two species by using the classical Adaptive Dynamics framework. They showed that, depending on the form of the trade-off between this interaction trait and its effect on the intrinsic growth rate, several situations can occur at evolutionary equilibrium: species can stably coexist and maintain their interaction, or the interaction traits can evolve to zero where species can coexist without any interactions. Weinbach et al. then investigated the fate of the two-species system if a partner species is strongly affected by environmental change, for instance, a large decrease of its growth rate. Because of the supposed trade-off between the interaction trait and the growth rate, the interaction trait in the focal species tends to decrease as an evolutionary response to the decline of the partner species. If environmental change is too large, the interaction trait can evolve to zero and can lead the partner species to extinction. An “evolutionary murder”. Even though Weinbach et al. interpreted the results of their model through the lens of plant-pollinators systems, their model is not specific to this case. On the contrary, it is very general, which has advantages and caveats. By its generality, the model is informative because it is a proof of concept that the evolution of mutualistic interactions can have unexpected effects on any category of mutualistic systems. Yet, since the model lacks many specificities of plant-pollinator interactions, it is hard to evaluate how their result would apply to plant-pollinators communities. I wanted to recommend this paper as a reminder that it is certainly worth studying the evolution of mutualistic interactions, because i) some unexpected phenomenons can occur, ii) we are certainly too naive about the evolution and ecology of mutualistic interactions, and iii) one can wonder to what extent we will be able to explain the stability of mutualistic communities without accounting for the co-evolutionary dynamics of mutualistic species. References Goh BS (1979) Stability in Models of Mutualism. The American Naturalist, 113, 261–275. http://www.jstor.org/stable/2460204. Holland JN, DeAngelis DL (2010) A consumer–resource approach to the density-dependent population dynamics of mutualism. Ecology, 91, 1286–1295. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-1163.1 Weinbach A, Loeuille N, Rohr RP (2021) Eco-evolutionary dynamics further weakens mutualistic interaction and coexistence under population decline. bioRxiv, 570580, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/570580 | Eco-evolutionary dynamics further weakens mutualistic interaction and coexistence under population decline | Avril Weinbach, Nicolas Loeuille, Rudolf P. Rohr | <p style="text-align: justify;">With current environmental changes, evolution can rescue declining populations, but what happens to their interacting species? Mutualistic interactions can help species sustain each other when their environment wors... |  | Coexistence, Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Evolutionary ecology, Interaction networks, Pollination, Theoretical ecology | Sylvain Billiard | 2019-09-05 11:29:45 | View | |
20 Sep 2018
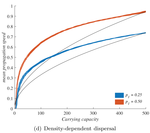
When higher carrying capacities lead to faster propagationMarjorie Haond, Thibaut Morel-Journel, Eric Lombaert, Elodie Vercken, Ludovic Mailleret & Lionel Roques https://doi.org/10.1101/307322When the dispersal of the many outruns the dispersal of the fewRecommended by Matthieu Barbier based on reviews by Yuval Zelnik and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Yuval Zelnik and 1 anonymous reviewer
Are biological invasions driven by a few pioneers, running ahead of their conspecifics? Or are these pioneers constantly being caught up by, and folded into, the larger flux of propagules from the established populations behind them? References [1] Levins, R., & Culver, D. (1971). Regional Coexistence of Species and Competition between Rare Species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 68(6), 1246–1248. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1246 | When higher carrying capacities lead to faster propagation | Marjorie Haond, Thibaut Morel-Journel, Eric Lombaert, Elodie Vercken, Ludovic Mailleret & Lionel Roques | <p>This preprint has been reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Ecology (https://dx.doi.org/10.24072/pci.ecology.100004). Finding general patterns in the expansion of natural populations is a major challenge in ecology and invasion biology... |  | Biological invasions, Colonization, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Matthieu Barbier | Yuval Zelnik | 2018-04-25 10:18:48 | View |
15 Jun 2020

Investigating the rare behavior of male parental care in great-tailed gracklesFolsom MA, MacPherson M, Lukas D, McCune KB, Bergeron L, Bond A, Blackwell A, Rowney C, Logan CJ https://github.com/corinalogan/grackles/blob/master/Files/Preregistrations/gmalecare.RmdStudying a rare behavior in a polygamous bird: male parental care in great-tailed gracklesRecommended by Marie-Jeanne Holveck based on reviews by Matthieu Paquet and André C FerreiraThe Great-tailed grackle (Quiscalus mexicanus) is a polygamous bird species that is originating from Central America and rapidly expanding its geographic range toward the North, and in which females were long thought to be the sole nest builders and caretakers of the young. In their pre-registration [1], Folsom and collaborators report repeated occurrences of male parental care and develop hypotheses aiming at better understanding the occurrence and the fitness consequences of this very rarely observed male behavior. They propose to assess if male parental care correlates with the circulating levels of several relevant hormones, increases offspring survival, is a local adaptation, and is a mating strategy, in surveying three populations located in Arizona (middle of the geographic range expansion), California (northern edge of the geographic range), and in Central America (core of the range). This study is part of a 5-year bigger project. References [1] Folsom MA, MacPherson M, Lukas D, McCune KB, Bergeron L, Bond A, Blackwell A, Rowney C, Logan CJ. 2020. Investigating the rare behavior of male parental care in great-tailed grackles. corinalogan.com/Preregistrations/gmalecare.html In principle acceptance by PCI Ecology of the version on 15 June 2020 corinalogan/grackles/blob/master/Files/Preregistrations/gmalecare.Rmd. | Investigating the rare behavior of male parental care in great-tailed grackles | Folsom MA, MacPherson M, Lukas D, McCune KB, Bergeron L, Bond A, Blackwell A, Rowney C, Logan CJ | This is a PREREGISTRATION submitted for pre-study peer review. Our planned data collection START DATE is May 2020, therefore it would be ideal if the peer review process could be completed before then. Abstract: Great-tailed grackles (Quiscalus... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Biological invasions, Preregistrations, Zoology | Marie-Jeanne Holveck | 2019-12-05 17:38:47 | View | |
16 Nov 2020
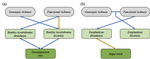
Intraspecific diversity loss in a predator species alters prey community structure and ecosystem functionsAllan Raffard, Julien Cucherousset, José M. Montoya, Murielle Richard, Samson Acoca-Pidolle, Camille Poésy, Alexandre Garreau, Frédéric Santoul & Simon Blanchet. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.06.10.144337Hidden diversity: how genetic richness affects species diversity and ecosystem processes in freshwater pondsRecommended by Frederik De Laender based on reviews by Andrew Barnes and Jes HinesBiodiversity loss can have important consequences for ecosystem functions, as exemplified by a large body of literature spanning at least three decades [1–3]. While connections between species diversity and ecosystem functions are now well-defined and understood, the importance of diversity within species is more elusive. Despite a surge in theoretical work on how intraspecific diversity can affect coexistence in simple community types [4,5], not much is known about how intraspecific diversity drives ecosystem processes in more complex community types. One particular challenge is that intraspecific diversity can be expressed as observable variation of functional traits, or instead subsist as genetic variation of which the consequences for ecosystem processes are harder to grasp. References [1] Tilman D, Downing JA (1994) Biodiversity and stability in grasslands. Nature, 367, 363–365. https://doi.org/10.1038/367363a0 | Intraspecific diversity loss in a predator species alters prey community structure and ecosystem functions | Allan Raffard, Julien Cucherousset, José M. Montoya, Murielle Richard, Samson Acoca-Pidolle, Camille Poésy, Alexandre Garreau, Frédéric Santoul & Simon Blanchet. | <p>Loss in intraspecific diversity can alter ecosystem functions, but the underlying mechanisms are still elusive, and intraspecific biodiversity-ecosystem function relationships (iBEF) have been restrained to primary producers. Here, we manipulat... |  | Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning, Experimental ecology, Food webs, Freshwater ecology | Frederik De Laender | Andrew Barnes | 2020-06-15 09:04:53 | View |
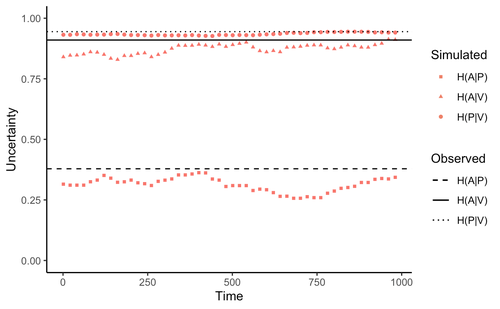
13 Mar 2021

Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersalSevchik, A., Logan, C. J., McCune, K. B., Blackwell, A., Rowney, C. and Lukas, D https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/t6behDispersal: from “neutral” to a state- and context-dependent viewRecommended by Emanuel A. Fronhofer based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersTraditionally, dispersal has often been seen as “random” or “neutral” as Lowe & McPeek (2014) have put it. This simplistic view is likely due to dispersal being intrinsically difficult to measure empirically as well as “random” dispersal being a convenient simplifying assumption in theoretical work. Clobert et al. (2009), and many others, have highlighted how misleading this assumption is. Rather, dispersal seems to be usually a complex reaction norm, depending both on internal as well as external factors. One such internal factor is the sex of the dispersing individual. A recent review of the theoretical literature (Li & Kokko 2019) shows that while ideas explaining sex-biased dispersal go back over 40 years this state-dependency of dispersal is far from comprehensively understood. Sevchik et al. (2021) tackle this challenge empirically in a bird species, the great-tailed grackle. In contrast to most bird species, where females disperse more than males, the authors report genetic evidence indicating male-biased dispersal. The authors argue that this difference can be explained by the great-tailed grackle’s social and mating-system. Dispersal is a central life-history trait (Bonte & Dahirel 2017) with major consequences for ecological and evolutionary processes and patterns. Therefore, studies like Sevchik et al. (2021) are valuable contributions for advancing our understanding of spatial ecology and evolution. Importantly, Sevchik et al. also lead to way to a more open and reproducible science of ecology and evolution. The authors are among the pioneers of preregistering research in their field and their way of doing research should serve as a model for others. References Bonte, D. & Dahirel, M. (2017) Dispersal: a central and independent trait in life history. Oikos 126: 472-479. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.03801 Clobert, J., Le Galliard, J. F., Cote, J., Meylan, S. & Massot, M. (2009) Informed dispersal, heterogeneity in animal dispersal syndromes and the dynamics of spatially structured populations. Ecol. Lett.: 12, 197-209. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2008.01267.x Li, X.-Y. & Kokko, H. (2019) Sex-biased dispersal: a review of the theory. Biol. Rev. 94: 721-736. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12475 Lowe, W. H. & McPeek, M. A. (2014) Is dispersal neutral? Trends Ecol. Evol. 29: 444-450. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2014.05.009 Sevchik, A., Logan, C. J., McCune, K. B., Blackwell, A., Rowney, C. & Lukas, D. (2021) Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersal. EcoEvoRxiv, osf.io/t6beh, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer community in Ecology. doi: https://doi.org/10.32942/osf.io/t6beh | Investigating sex differences in genetic relatedness in great-tailed grackles in Tempe, Arizona to infer potential sex biases in dispersal | Sevchik, A., Logan, C. J., McCune, K. B., Blackwell, A., Rowney, C. and Lukas, D | <p>In most bird species, females disperse prior to their first breeding attempt, while males remain closer to the place they hatched for their entire lives. Explanations for such female bias in natal dispersal have focused on the resource-defense ... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Dispersal & Migration, Zoology | Emanuel A. Fronhofer | 2020-08-24 17:53:06 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










