Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract▲ | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
28 Sep 2020
The dynamics of spawning acts by a semelparous fish and its associated energetic costsCédric Tentelier, Colin Bouchard, Anaïs Bernardin, Amandine Tauzin, Jean-Christophe Aymes, Frédéric Lange, Charlotte Recapet, Jacques Rives https://doi.org/10.1101/436295Extreme weight loss: when accelerometer could reveal reproductive investment in a semelparous fish speciesRecommended by Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont based on reviews by Aidan Jonathan Mark Hewison, Loïc Teulier and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Aidan Jonathan Mark Hewison, Loïc Teulier and 1 anonymous reviewer
Continuous observation of animal behaviour could be quite a challenge in the field, and the situation becomes even more complicated with aquatic species mostly active at night. In such cases, biologging techniques are real game changers in ecology, behavioural ecology or eco-physiology. An accelerating number of methodological applications of these tools in natural condition are thus published each year [1]. Biologging is not limited to movement ecology. For instance, fine grain information about energy expenditure can be inferred from body acceleration [2], and accelerometers has already proven useful in monitoring reproductive costs in some fish species [3,4]. The first part of the study by Tentelier et al. [5] is in line with this growing literature. It describes measurements of energy expenditure during reproduction in a fish species, Allis shad (Alosa Alosa), based on tail beat frequency and occurrence of spawning acts. The study has been convincingly conducted, and the results are important for fish biologists. But this is not the whole story: the authors added to this otherwise classical study a very original and insightful analysis which deserves closer interest. References [1] Börger L, Bijleveld AI, Fayet AL, Machovsky‐Capuska GE, Patrick SC, Street GM and Vander Wal E. (2020) Biologging special feature. J. Anim. Ecol. 89, 6–15. 10.1111/1365-2656.13163 | The dynamics of spawning acts by a semelparous fish and its associated energetic costs | Cédric Tentelier, Colin Bouchard, Anaïs Bernardin, Amandine Tauzin, Jean-Christophe Aymes, Frédéric Lange, Charlotte Recapet, Jacques Rives | <p>1. During the reproductive season, animals have to manage both their energetic budget and gamete stock. In particular, for semelparous capital breeders with determinate fecundity and no parental care other than gametic investment, the depletion... | Behaviour & Ethology, Freshwater ecology, Life history | Francois-Xavier Dechaume-Moncharmont | 2020-06-04 15:18:56 | View | ||
07 Oct 2019

Which pitfall traps and sampling efforts should be used to evaluate the effects of cropping systems on the taxonomic and functional composition of arthropod communities?Antoine Gardarin and Muriel Valantin-Morison https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3468920On the importance of experimental design: pitfall traps and arthropod communitiesRecommended by Ignasi Bartomeus based on reviews by Cécile ALBERT and Matthias Foellmer based on reviews by Cécile ALBERT and Matthias Foellmer
Despite the increasing refinement of statistical methods, a robust experimental design is still one of the most important cornerstones to answer ecological and evolutionary questions. However, there is a strong trade-off between a perfect design and its feasibility. A common mantra is that more data is always better, but how much is enough is complex to answer, specially when we want to capture the spatial and temporal variability of a given process. Gardarin and Valantin-Morison [1] make an effort to answer these questions for a practical case: How many pitfalls traps, of which type, and over which extent, do we need to detect shifts in arthropod community composition in agricultural landscapes. There is extense literature on how to approach these challenges using preliminary data in combination with simulation methods [e.g. 2], but practical cases are always welcomed to illustrate the complexity of the decisions to be made. A key challenge in this situation is the nature of simplified and patchy agricultural arthropod communities. In this context, small effect sizes are expected, but those small effects are relevant from an ecological point of view because small increases at low biodiversity may produce large gains in ecosystem functioning [3]. References [1] Gardarin, A. and Valantin-Morison, M. (2019). Which pitfall traps and sampling efforts should be used to evaluate the effects of cropping systems on the taxonomic and functional composition of arthropod communities? Zenodo, 3468920, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.3468920 | Which pitfall traps and sampling efforts should be used to evaluate the effects of cropping systems on the taxonomic and functional composition of arthropod communities? | Antoine Gardarin and Muriel Valantin-Morison | <p>1. Ground dwelling arthropods are affected by agricultural practices, and analyses of their responses to different crop management are required. The sampling efficiency of pitfall traps has been widely studied in natural ecosystems. In arable a... |  | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Biological control, Community ecology | Ignasi Bartomeus | 2019-01-08 09:40:14 | View | |
24 Mar 2023
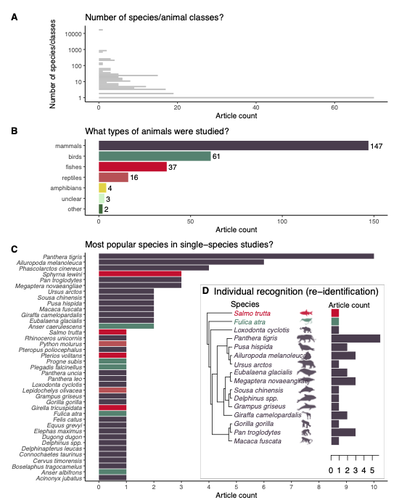
Rapid literature mapping on the recent use of machine learning for wildlife imageryShinichi Nakagawa, Malgorzata Lagisz, Roxane Francis, Jessica Tam, Xun Li, Andrew Elphinstone, Neil R. Jordan, Justine K. O’Brien, Benjamin J. Pitcher, Monique Van Sluys, Arcot Sowmya, Richard T. Kingsford https://doi.org/10.32942/X2H59DReview of machine learning uses for the analysis of images on wildlifeRecommended by Olivier Gimenez based on reviews by Falk Huettmann and 1 anonymous reviewerIn the field of ecology, there is a growing interest in machine (including deep) learning for processing and automatizing repetitive analyses on large amounts of images collected from camera traps, drones and smartphones, among others. These analyses include species or individual recognition and classification, counting or tracking individuals, detecting and classifying behavior. By saving countless times of manual work and tapping into massive amounts of data that keep accumulating with technological advances, machine learning is becoming an essential tool for ecologists. We refer to recent papers for more details on machine learning for ecology and evolution (Besson et al. 2022, Borowiec et al. 2022, Christin et al. 2019, Goodwin et al. 2022, Lamba et al. 2019, Nazir & Kaleem 2021, Perry et al. 2022, Picher & Hartig 2023, Tuia et al. 2022, Wäldchen & Mäder 2018). In their paper, Nakagawa et al. (2023) conducted a systematic review of the literature on machine learning for wildlife imagery. Interestingly, the authors used a method unfamiliar to ecologists but well-established in medicine called rapid review, which has the advantage of being quickly completed compared to a fully comprehensive systematic review while being representative (Lagisz et al., 2022). Through a rigorous examination of more than 200 articles, the authors identified trends and gaps, and provided suggestions for future work. Listing all their findings would be counterproductive (you’d better read the paper), and I will focus on a few results that I have found striking, fully assuming a biased reading of the paper. First, Nakagawa et al. (2023) found that most articles used neural networks to analyze images, in general through collaboration with computer scientists. A challenge here is probably to think of teaching computer vision to the generations of ecologists to come (Cole et al. 2023). Second, the images were dominantly collected from camera traps, with an increase in the use of aerial images from drones/aircrafts that raise specific challenges. Third, the species concerned were mostly mammals and birds, suggesting that future applications should aim to mitigate this taxonomic bias, by including, e.g., invertebrate species. Fourth, most papers were written by authors affiliated with three countries (Australia, China, and the USA) while India and African countries provided lots of images, likely an example of scientific colonialism which should be tackled by e.g., capacity building and the involvement of local collaborators. Last, few studies shared their code and data, which obviously impedes reproducibility. Hopefully, with the journals’ policy of mandatory sharing of codes and data, this trend will be reversed. REFERENCES Besson M, Alison J, Bjerge K, Gorochowski TE, Høye TT, Jucker T, Mann HMR, Clements CF (2022) Towards the fully automated monitoring of ecological communities. Ecology Letters, 25, 2753–2775. https://doi.org/10.1111/ele.14123 Borowiec ML, Dikow RB, Frandsen PB, McKeeken A, Valentini G, White AE (2022) Deep learning as a tool for ecology and evolution. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 13, 1640–1660. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13901 Christin S, Hervet É, Lecomte N (2019) Applications for deep learning in ecology. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 10, 1632–1644. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13256 Cole E, Stathatos S, Lütjens B, Sharma T, Kay J, Parham J, Kellenberger B, Beery S (2023) Teaching Computer Vision for Ecology. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2301.02211 Goodwin M, Halvorsen KT, Jiao L, Knausgård KM, Martin AH, Moyano M, Oomen RA, Rasmussen JH, Sørdalen TK, Thorbjørnsen SH (2022) Unlocking the potential of deep learning for marine ecology: overview, applications, and outlook†. ICES Journal of Marine Science, 79, 319–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/icesjms/fsab255 Lagisz M, Vasilakopoulou K, Bridge C, Santamouris M, Nakagawa S (2022) Rapid systematic reviews for synthesizing research on built environment. Environmental Development, 43, 100730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envdev.2022.100730 Lamba A, Cassey P, Segaran RR, Koh LP (2019) Deep learning for environmental conservation. Current Biology, 29, R977–R982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.016 Nakagawa S, Lagisz M, Francis R, Tam J, Li X, Elphinstone A, Jordan N, O’Brien J, Pitcher B, Sluys MV, Sowmya A, Kingsford R (2023) Rapid literature mapping on the recent use of machine learning for wildlife imagery. EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2H59D Nazir S, Kaleem M (2021) Advances in image acquisition and processing technologies transforming animal ecological studies. Ecological Informatics, 61, 101212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2021.101212 Perry GLW, Seidl R, Bellvé AM, Rammer W (2022) An Outlook for Deep Learning in Ecosystem Science. Ecosystems, 25, 1700–1718. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-022-00789-y Pichler M, Hartig F Machine learning and deep learning—A review for ecologists. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, n/a. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.14061 Tuia D, Kellenberger B, Beery S, Costelloe BR, Zuffi S, Risse B, Mathis A, Mathis MW, van Langevelde F, Burghardt T, Kays R, Klinck H, Wikelski M, Couzin ID, van Horn G, Crofoot MC, Stewart CV, Berger-Wolf T (2022) Perspectives in machine learning for wildlife conservation. Nature Communications, 13, 792. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-27980-y Wäldchen J, Mäder P (2018) Machine learning for image-based species identification. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 9, 2216–2225. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13075 | Rapid literature mapping on the recent use of machine learning for wildlife imagery | Shinichi Nakagawa, Malgorzata Lagisz, Roxane Francis, Jessica Tam, Xun Li, Andrew Elphinstone, Neil R. Jordan, Justine K. O’Brien, Benjamin J. Pitcher, Monique Van Sluys, Arcot Sowmya, Richard T. Kingsford | <p>1. Machine (especially deep) learning algorithms are changing the way wildlife imagery is processed. They dramatically speed up the time to detect, count, classify animals and their behaviours. Yet, we currently have a very few systematic liter... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Conservation biology | Olivier Gimenez | Anonymous | 2022-10-31 22:05:46 | View |
13 May 2024
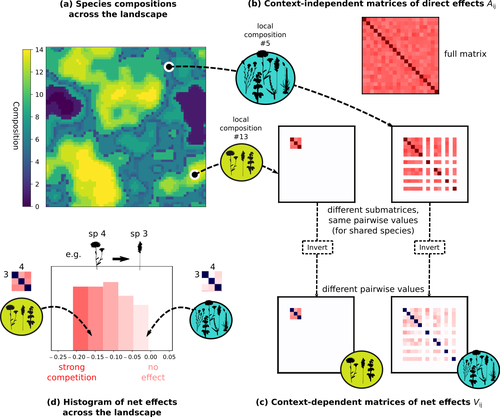
Getting More by Asking for Less: Linking Species Interactions to Species Co-Distributions in MetacommunitiesMatthieu Barbier, Guy Bunin, Mathew A. Leibold https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.04.543606Beyond pairwise species interactions: coarser inference of their joined effects is more relevantRecommended by François Munoz based on reviews by Frederik De Laender, Hao Ran Lai and Malyon Bimler based on reviews by Frederik De Laender, Hao Ran Lai and Malyon Bimler
Barbier et al. (2024) investigated the dynamics of species abundances depending on their ecological niche (abiotic component) and on (numerous) competitive interactions. In line with previous evidence and expectations (Barbier et al. 2018), the authors show that it is possible to robustly infer the mean and variance of interaction coefficients from species co-distributions, while it is not possible to infer the individual coefficient values. The authors devised a simulation framework representing multispecies dynamics in an heterogeneous environmental context (2D grid landscape). They used a Lotka-Volterra framework involving pairwise interaction coefficients and species-specific carrying capacities. These capacities depend on how well the species niche matches the local environmental conditions, through a Gaussian function of the distance of the species niche centers to the local environmental values. They considered two contrasted scenarios denoted as « Environmental tracking » and « Dispersal limited ». In the latter case, species are initially seeded over the environmental grid and cannot disperse to other cells, while in the former case they can disperse and possibly be more performant in other cells. The direct effects of species on one another are encoded in an interaction matrix A, and the authors further considered net interactions depending on the inverse of the matrix of direct interactions (Zelnik et al., 2024). The net effects are context-dependent, i.e., it involves the environment-dependent biotic capacities, even through the interaction terms can be defined between species as independent from local environment. The results presented here underline that the outcome of many individual competitive interactions can only be understood in terms of macroscopic properties. In essence, the results here echoe the mean field theories that investigate the dynamics of average ecological properties instead of the microscopic components (e.g., McKane et al. 2000). In a philosophical perspective, community ecology has long struggled with analyzing and inferring local determinants of species coexistence from species co-occurrence patterns, so that it was claimed that no universal laws can be derived in the discipline (Lawton 1999). Using different and complementary methods and perspectives, recent research has also shown that species assembly parameter values cannot be unambiguously inferred from species co-occurrences only, even in simple designs where an equilibrium can be reached (Poggiato et al. 2021). Although the roles of high-order competitive interactions and intransivity can lead to species coexistence, the simple view of a single loop of competitive interactions is easily challenged when further interactions and complexity is added (Gallien et al. 2024). But should we put so much emphasis on inferring individual interaction coefficients? In a quest to understand the emerging properties of elementary processes, ecological theory could go forward with a more macroscopic analysis and understanding of species coexistence in many communities. The authors referred several times to an interesting paper from Schaffer (1981), entitled « Ecological abstraction: the consequences of reduced dimensionality in ecological models ». It proposes that estimating individual species competition coefficients is not possible, but that competition can be assessed at the coarser level of organisation, i.e., between ecological guilds. This idea implies that the dimensionality of the competition equations should be greatly reduced to become tractable in practice. Taking together this claim with the results of the present Barbier et al. (2024) paper, it becomes clearer that the nature of competitive interactions can be addressed through « abstracted » quantities, as those of guilds or the moments of the individual competition coefficients (here the average and the standard deviation). Therefore the scope of Barbier et al. (2024) framework goes beyond statistical issues in parameter inference, but question the way we must think and represent the numerous competitive interactions in a simplified and robust way. References Barbier, Matthieu, Jean-François Arnoldi, Guy Bunin, et Michel Loreau. 2018. « Generic assembly patterns in complex ecological communities ». Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115 (9): 2156‑61. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1710352115 | Getting More by Asking for Less: Linking Species Interactions to Species Co-Distributions in Metacommunities | Matthieu Barbier, Guy Bunin, Mathew A. Leibold | <p>AbstractOne of the more difficult challenges in community ecology is inferring species interactions on the basis of patterns in the spatial distribution of organisms. At its core, the problem is that distributional patterns reflect the ‘realize... |  | Biogeography, Community ecology, Competition, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Species distributions, Statistical ecology, Theoretical ecology | François Munoz | 2023-10-21 14:14:16 | View | |
18 Dec 2020

Once upon a time in the far south: Influence of local drivers and functional traits on plant invasion in the harsh sub-Antarctic islandsManuele Bazzichetto, François Massol, Marta Carboni, Jonathan Lenoir, Jonas Johan Lembrechts, Rémi Joly, David Renault https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.19.210880A meaningful application of species distribution models and functional traits to understand invasion dynamicsRecommended by Joaquín Hortal based on reviews by Paula Matos and Peter ConveyPolar and subpolar regions are fragile environments, where the introduction of alien species may completely change ecosystem dynamics if the alien species become keystone species (e.g. Croll, 2005). The increasing number of human visits, together with climate change, are favouring the introduction and settling of new invaders to these regions, particularly in Antarctica (Hughes et al. 2015). Within this context, the joint use of Species Distribution Models (SDM) –to assess the areas potentially suitable for the aliens– with other measures of the potential to become successful invaders can inform on the need for devoting specific efforts to eradicate these new species before they become naturalized (e.g. Pertierra et al. 2016). References Austin, M. P., Nicholls, A. O., and Margules, C. R. (1990). Measurement of the realized qualitative niche: environmental niches of five Eucalyptus species. Ecological Monographs, 60(2), 161-177. doi: https://doi.org/10.2307/1943043 | Once upon a time in the far south: Influence of local drivers and functional traits on plant invasion in the harsh sub-Antarctic islands | Manuele Bazzichetto, François Massol, Marta Carboni, Jonathan Lenoir, Jonas Johan Lembrechts, Rémi Joly, David Renault | <p>Aim Here, we aim to: (i) investigate the local effect of environmental and human-related factors on alien plant invasion in sub-Antarctic islands; (ii) explore the relationship between alien species features and their dependence on anthropogeni... |  | Biogeography, Biological invasions, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Species distributions | Joaquín Hortal | 2020-07-21 21:13:08 | View | |
06 Sep 2019
Assessing metacommunity processes through signatures in spatiotemporal turnover of community compositionFranck Jabot, Fabien Laroche, Francois Massol, Florent Arthaud, Julie Crabot, Maxime Dubart, Simon Blanchet, Francois Munoz, Patrice David, Thibault Datry https://doi.org/10.1101/480335On the importance of temporal meta-community dynamics for our understanding of assembly processesRecommended by Werner Ulrich based on reviews by Joaquín Hortal and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Joaquín Hortal and 2 anonymous reviewers
The processes that trigger community assembly are still in the centre of ecological interest. While prior work mostly focused on spatial patterns of co-occurrence within a meta-community framework [reviewed in 1, 2] recent studies also include temporal patterns of community composition [e.g. 3, 4, 5, 6]. In this preprint [7], Franck Jabot and co-workers extend they prior approaches to quasi neutral community assembly [8, 9, 10] and develop an analytical framework of spatial and temporal diversity turnover. A simple and heuristic path model for beta diversity and an extended ecological drift model serve as starting points. The model can be seen as a counterpart to Ulrich et al. [5]. These authors implemented competitive hierarchies into their neutral meta-community model while the present paper focuses on environmental filtering. Most important, the model and parameterization of four empirical data sets on aquatic plant and animal meta-communities used by Jabot et al. returned a consistent high influence of environmental stochasticity on species turnover. Of course, this major result does not come to a surprise. As typical for this kind of models it depends also to a good deal on the initial model settings. It nevertheless makes a strong conceptual point for the importance of environmental variability over dispersal and richness effects. One interesting side effect regards the impact of richness differences (ΔS). Jabot et al. interpret this as a ‘nuisance variable’ as they do not have a stringent explanation. Of course, it might be a pure statistical bias introduced by the Soerensen metric of turnover that is normalized by richness. However, I suspect that there is more behind the ΔS effect. Richness differences are generally associated with respective differences in total abundances and introduce source – sink dynamics that inevitably shape subsequent colonization – extinction processes. It would be interesting to see whether ΔS alone is able to trigger observed patterns of community assembly and community composition. Such an analysis would require partitioning of species turnover into richness and nestedness effects [11]. I encourage Jabot et al. to undertake such an effort. References [1] Götzenberger, L. et al. (2012). Ecological assembly rules in plant communities—approaches, patterns and prospects. Biological reviews, 87(1), 111-127. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185X.2011.00187.x | Assessing metacommunity processes through signatures in spatiotemporal turnover of community composition | Franck Jabot, Fabien Laroche, Francois Massol, Florent Arthaud, Julie Crabot, Maxime Dubart, Simon Blanchet, Francois Munoz, Patrice David, Thibault Datry | <p>Although metacommunity ecology has been a major field of research in the last decades, with both conceptual and empirical outputs, the analysis of the temporal dynamics of metacommunities has only emerged recently and still consists mostly of r... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Community ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Werner Ulrich | 2018-11-29 14:58:54 | View | |
03 Mar 2022

Artificial reefs geographical location matters more than its age and depth for sessile invertebrate colonization in the Gulf of Lion (NorthWestern Mediterranean Sea)sylvain blouet, Katell Guizien, lorenzo Bramanti https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.08.463669A longer-term view on benthic communities on artificial reefs: it’s all about locationRecommended by James Davis Reimer based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersIn this study by Blouet, Bramanti, and Guizen (2022), the authors aim to tackle a long-standing data gap regarding research on marine benthic communities found on artificial reefs. The study is well thought out, and should serve as an important reference on this topic going forward. Blouet S, Bramanti L, Guizien K (2022) Artificial reefs geographical location matters more than shape, age and depth for sessile invertebrate colonization in the Gulf of Lion (NorthWestern Mediterranean Sea). bioRxiv, 2021.10.08.463669, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.08.463669 | Artificial reefs geographical location matters more than its age and depth for sessile invertebrate colonization in the Gulf of Lion (NorthWestern Mediterranean Sea) | sylvain blouet, Katell Guizien, lorenzo Bramanti | <p>Artificial reefs (ARs) have been used to support fishing activities. Sessile invertebrates are essential components of trophic networks within ARs, supporting fish productivity. However, colonization by sessile invertebrates is possible only af... |  | Biodiversity, Biogeography, Colonization, Ecological successions, Life history, Marine ecology | James Davis Reimer | 2021-10-11 10:21:36 | View | |
12 Jun 2019
Environmental heterogeneity drives tsetse fly population dynamics and controlCecilia H, Arnoux S, Picault S, Dicko A, Seck MT, Sall B, Bassene M, Vreysen M, Pagabeleguem S, Bance A, Bouyer J, Ezanno P https://doi.org/10.1101/493650Modeling jointly landscape complexity and environmental heterogeneity to envision new strategies for tsetse flies controlRecommended by Benjamin Roche based on reviews by Timothée Vergne and 1 anonymous reviewerToday, understanding spatio-temporal dynamics of pathogens is pivotal to understand their transmission and controlling them. First, understanding this dynamics can reveal the ecology of their transmission [1]. Indeed, such knowledge, based on data that are quite easy to access, can shed light on transmission modes, which could rely on different animal species that can be spatially distributed in a non-uniform way [2]. This is especially true for pathogens with complex life-cycles, despite that investigating such dynamics is very challenging and rely mostly on mathematical models. References [1] Grenfell, B. T., Bjørnstad, O. N., & Kappey, J. (2001). Travelling waves and spatial hierarchies in measles epidemics. Nature, 414(6865), 716-723. doi: 10.1038/414716a | Environmental heterogeneity drives tsetse fly population dynamics and control | Cecilia H, Arnoux S, Picault S, Dicko A, Seck MT, Sall B, Bassene M, Vreysen M, Pagabeleguem S, Bance A, Bouyer J, Ezanno P | <p>A spatially and temporally heterogeneous environment may lead to unexpected population dynamics. Knowledge still is needed on which of the local environment properties favour population maintenance at larger scale. For pathogen vectors, such as... |  | Biological control, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations | Benjamin Roche | 2018-12-14 12:13:39 | View | |
17 Mar 2021

Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslandsCatherine Picon-Cochard, Nathalie Vassal, Raphaël Martin, Damien Herfurth, Priscilla Note, Frédérique Louault https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.23.263137Resolving herbivore influences under climate variabilityRecommended by Jennifer Krumins based on reviews by 3 anonymous reviewersWe know that herbivory can have profound influences on plant communities with respect to their distribution and productivity (recently reviewed by Jia et al. 2018). However, the degree to which these effects are realized belowground in the rhizosphere is far less understood. Indeed, many independent studies and synthesis find that the environmental context can be more important than the direct effects of herbivore activity and its removal of plant biomass (Andriuzzi and Wall 2017, Schrama et al. 2013). In spite of dedicated attention, generalizable conclusions remain a bit elusive (Sitters and Venterink 2015). Picon-Cochard and colleagues (2021) help address this research conundrum in an elegant analysis that demonstrates the interaction between long-term cattle grazing and climatic variability on primary production aboveground and belowground. Over the course of two years, Picon-Cochard et al. (2021) measured above and belowground net primary productivity in French grasslands that had been subject to ten years of managed cattle grazing. When they compared these data with climatic trends, they find an interesting interaction among grazing intensity and climatic factors influencing plant growth. In short, and as expected, plants allocate more resources to root growth in dry years and more to above ground biomass in wet and cooler years. However, this study reveals the degree to which this is affected by cattle grazing. Grazed grasslands support warmer and dryer soils creating feedback that further and significantly promotes root growth over green biomass production. The implications of this work to understanding the capacity of grassland soils to store carbon is profound. This study addresses one brief moment in time of the long trajectory of this grazed ecosystem. The legacy of grazing does not appear to influence soil ecosystem functioning with respect to root growth except within the environmental context, in this case, climate. This supports the notion that long-term research in animal husbandry and grazing effects on landscapes is deeded. It is my hope that this study is one of many that can be used to synthesize many different data sets and build a deeper understanding of the long-term effects of grazing and herd management within the context of a changing climate. Herbivory has a profound influence upon ecosystem health and the distribution of plant communities (Speed and Austrheim 2017), global carbon storage (Chen and Frank 2020) and nutrient cycling (Sitters et al. 2020). The analysis and results presented by Picon-Cochard (2021) help to resolve the mechanisms that underly these complex effects and ultimately make projections for the future. References Andriuzzi WS, Wall DH. 2017. Responses of belowground communities to large aboveground herbivores: Meta‐analysis reveals biome‐dependent patterns and critical research gaps. Global Change Biology 23:3857-3868. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13675 Chen J, Frank DA. 2020. Herbivores stimulate respiration from labile and recalcitrant soil carbon pools in grasslands of Yellowstone National Park. Land Degradation & Development 31:2620-2634. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3656 Jia S, Wang X, Yuan Z, Lin F, Ye J, Hao Z, Luskin MS. 2018. Global signal of top-down control of terrestrial plant communities by herbivores. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115:6237-6242. doi: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1707984115 Picon-Cochard C, Vassal N, Martin R, Herfurth D, Note P, Louault F. 2021. Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslands. bioRxiv, 2020.08.23.263137, version 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Ecology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.08.23.263137 Schrama M, Veen GC, Bakker EL, Ruifrok JL, Bakker JP, Olff H. 2013. An integrated perspective to explain nitrogen mineralization in grazed ecosystems. Perspectives in Plant Ecology, Evolution and Systematics 15:32-44. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2012.12.001 Sitters J, Venterink HO. 2015. The need for a novel integrative theory on feedbacks between herbivores, plants and soil nutrient cycling. Plant and Soil 396:421-426. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2679-y Sitters J, Wubs EJ, Bakker ES, Crowther TW, Adler PB, Bagchi S, Bakker JD, Biederman L, Borer ET, Cleland EE. 2020. Nutrient availability controls the impact of mammalian herbivores on soil carbon and nitrogen pools in grasslands. Global Change Biology 26:2060-2071. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.15023 Speed JD, Austrheim G. 2017. The importance of herbivore density and management as determinants of the distribution of rare plant species. Biological Conservation 205:77-84. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocon.2016.11.030 | Intra and inter-annual climatic conditions have stronger effect than grazing intensity on root growth of permanent grasslands | Catherine Picon-Cochard, Nathalie Vassal, Raphaël Martin, Damien Herfurth, Priscilla Note, Frédérique Louault | <p>Background and Aims: Understanding how direct and indirect changes in climatic conditions, management, and species composition affect root production and root traits is of prime importance for the delivery of carbon sequestration services of gr... |  | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Botany, Community ecology, Ecosystem functioning | Jennifer Krumins | 2020-08-30 19:27:30 | View | |
20 Feb 2019
Differential immune gene expression associated with contemporary range expansion of two invasive rodents in SenegalNathalie Charbonnel, Maxime Galan, Caroline Tatard, Anne Loiseau, Christophe Diagne, Ambroise Dalecky, Hugues Parrinello, Stephanie Rialle, Dany Severac and Carine Brouat https://doi.org/10.1101/442160Are all the roads leading to Rome?Recommended by Simon Blanchet based on reviews by Nadia Aubin-Horth and 1 anonymous reviewerIdentifying the factors which favour the establishment and spread of non-native species in novel environments is one of the keys to predict - and hence prevent or control - biological invasions. This includes biological factors (i.e. factors associated with the invasive species themselves), and one of the prevailing hypotheses is that some species traits may explain their impressive success to establish and spread in novel environments [1]. In animals, most research studies have focused on traits associated with fecundity, age at maturity, level of affiliation to humans or dispersal ability for instance. The “composite picture” of the perfect (i.e. successful) invader that has gradually emerged is a small-bodied animal strongly affiliated to human activities with high fecundity, high dispersal ability and a super high level of plasticity. Of course, the story is not that simple, and actually a perfect invader sometimes – if not often- takes another form… Carrying on to identify what makes a species a successful invader or not is hence still an important research axis with major implications. References [1] Jeschke, J. M., & Strayer, D. L. (2006). Determinants of vertebrate invasion success in Europe and North America. Global Change Biology, 12(9), 1608-1619. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2006.01213.x | Differential immune gene expression associated with contemporary range expansion of two invasive rodents in Senegal | Nathalie Charbonnel, Maxime Galan, Caroline Tatard, Anne Loiseau, Christophe Diagne, Ambroise Dalecky, Hugues Parrinello, Stephanie Rialle, Dany Severac and Carine Brouat | <p>Background: Biological invasions are major anthropogenic changes associated with threats to biodiversity and health. What determines the successful establishment of introduced populations still remains unsolved. Here we explore the appealing as... |  | Biological invasions, Eco-immunology & Immunity, Population ecology | Simon Blanchet | 2018-10-14 12:21:52 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










