Latest recommendations

| Id | Title | Authors | Abstract | Picture | Thematic fields | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date▼ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
29 Sep 2023
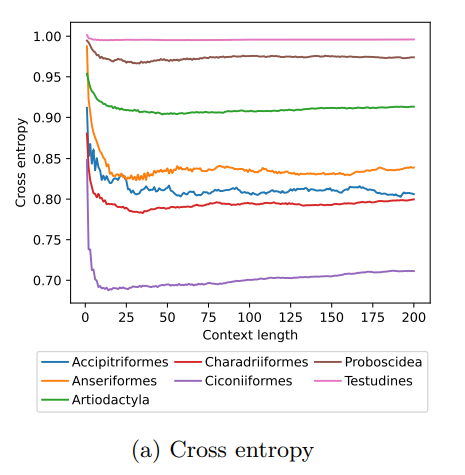
MoveFormer: a Transformer-based model for step-selection animal movement modellingOndřej Cífka, Simon Chamaillé-Jammes, Antoine Liutkus https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.05.531080A deep learning model to unlock secrets of animal movement and behaviourRecommended by Cédric Sueur based on reviews by Jacob Davidson and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jacob Davidson and 1 anonymous reviewer
The study of animal movement is essential for understanding their behaviour and how ecological or global changes impact their routines [1]. Recent technological advancements have improved the collection of movement data [2], but limited statistical tools have hindered the analysis of such data [3–5]. Animal movement is influenced not only by environmental factors but also by internal knowledge and memory, which are challenging to observe directly [6,7]. Routine movement behaviours and the incorporation of memory into models remain understudied. Researchers have developed ‘MoveFormer’ [8], a deep learning-based model that predicts future movements based on past context, addressing these challenges and offering insights into the importance of different context lengths and information types. The model has been applied to a dataset of over 1,550 trajectories from various species, and the authors have made the MoveFormer source code available for further research. Inspired by the step-selection framework and efforts to quantify uncertainty in movement predictions, MoveFormer leverages deep learning, specifically the Transformer architecture, to encode trajectories and understand how past movements influence current and future ones – a critical question in movement ecology. The results indicate that integrating information from a few days to two or three weeks before the movement enhances predictions. The model also accounts for environmental predictors and offers insights into the factors influencing animal movements. Its potential impact extends to conservation, comparative analyses, and the generalisation of uncertainty-handling methods beyond ecology, with open-source code fostering collaboration and innovation in various scientific domains. Indeed, this method could be applied to analyse other kinds of movements, such as arm movements during tool use [9], pen movements, or eye movements during drawing [10], to better understand anticipation in actions and their intentionality. References 1. Méndez, V.; Campos, D.; Bartumeus, F. Stochastic Foundations in Movement Ecology: Anomalous Diffusion, Front Propagation and Random Searches; Springer Series in Synergetics; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2014; ISBN 978-3-642-39009-8. | MoveFormer: a Transformer-based model for step-selection animal movement modelling | Ondřej Cífka, Simon Chamaillé-Jammes, Antoine Liutkus | <p style="text-align: justify;">The movement of animals is a central component of their behavioural strategies. Statistical tools for movement data analysis, however, have long been limited, and in particular, unable to account for past movement i... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Habitat selection | Cédric Sueur | 2023-03-22 16:32:14 | View | |
20 Feb 2024
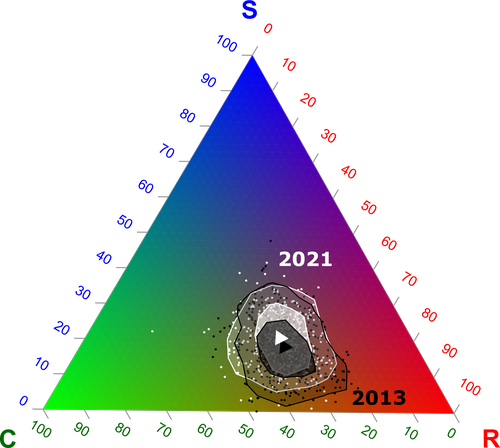
Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practicesIsis Poinas, Christine N Meynard, Guillaume Fried https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.03.530956Unravelling plant diversity in agricultural field margins in France: plant species better adapted to climate change need other agricultures to persistRecommended by Julia Astegiano based on reviews by Ignasi Bartomeus, Clelia Sirami and Diego Gurvich based on reviews by Ignasi Bartomeus, Clelia Sirami and Diego Gurvich
Agricultural field margin plants, often referred to as “spontaneous” species, are key for the stabilization of several social-ecological processes related to crop production such as pollination or pest control (Tamburini et al. 2020). Because of its beneficial function, increasing the diversity of field margin flora becomes as important as crop diversity in process-based agricultures such as agroecology. Contrary, supply-dependent intensive agricultures produce monocultures and homogenized environments that might benefit their productivity, which generally includes the control or elimination of the field margin flora (Emmerson et al. 2016, Aligner 2018). Considering that different agricultural practices are produced by (and produce) different territories (Moore 2020) and that they are also been shaped by current climate change, we urgently need to understand how agricultural intensification constrains the potential of territories to develop agriculture more resilient to such change (Altieri et al., 2015). Thus, studies unraveling how agricultural practices' effects on agricultural field margin flora interact with those of climate change is of main importance, as plant strategies better adapted to such social-ecological processes may differ. References Alignier, A., 2018. Two decades of change in a field margin vegetation metacommunity as a result of field margin structure and management practice changes. Agric., Ecosyst. & Environ., 251, 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2017.09.013 Altieri, M.A., Nicholls, C.I., Henao, A., Lana, M.A., 2015. Agroecology and the design of climate change-resilient farming systems. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 35, 869–890. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-015-0285-2 Emmerson, M., Morales, M. B., Oñate, J. J., Batary, P., Berendse, F., Liira, J., Aavik, T., Guerrero, I., Bommarco, R., Eggers, S., Pärt, T., Tscharntke, T., Weisser, W., Clement, L. & Bengtsson, J. (2016). How agricultural intensification affects biodiversity and ecosystem services. In Adv. Ecol. Res. 55, 43-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aecr.2016.08.005 Grime, J. P., 1977. Evidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory. The American Naturalist, 111(982), 1169–1194. https://doi.org/10.1086/283244 Grime, J. P., 1988. The C-S-R model of primary plant strategies—Origins, implications and tests. In L. D. Gottlieb & S. K. Jain, Plant Evolutionary Biology (pp. 371–393). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-009-1207-6_14 Moore, J., 2020. El capitalismo en la trama de la vida (Capitalism in The Web of Life). Traficantes de sueños, Madrid, Spain. Poinas, I., Fried, G., Henckel, L., & Meynard, C. N., 2023. Agricultural drivers of field margin plant communities are scale-dependent. Bas. App. Ecol. 72, 55-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2023.08.003 Poinas, I., Meynard, C. N., Fried, G., 2024. Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practices, bioRxiv, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.03.03.530956 Tamburini, G., Bommarco, R., Wanger, T.C., Kremen, C., Van Der Heijden, M.G., Liebman, M., Hallin, S., 2020. Agricultural diversification promotes multiple ecosystem services without compromising yield. Sci. Adv. 6, eaba1715. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aba1715 | Functional trade-offs: exploring the temporal response of field margin plant communities to climate change and agricultural practices | Isis Poinas, Christine N Meynard, Guillaume Fried | <p style="text-align: justify;">Over the past decades, agricultural intensification and climate change have led to vegetation shifts. However, functional trade-offs linking traits responding to climate and farming practices are rarely analyzed, es... |  | Agroecology, Biodiversity, Botany, Climate change, Community ecology | Julia Astegiano | 2023-03-04 15:40:35 | View | |
29 Aug 2023
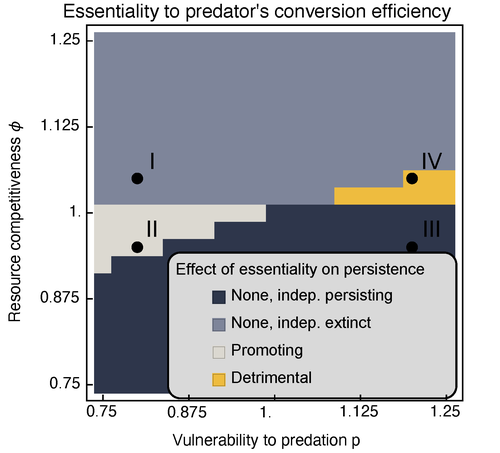
Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food websMichael Raatz https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525839High-order interactions in food webs may strongly impact persistence of speciesRecommended by Cédric Gaucherel based on reviews by Jean-Christophe POGGIALE and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Jean-Christophe POGGIALE and 1 anonymous reviewer
Michael Raatz (2023) provides here a relevant exploration of higher-order interactions, i.e. interactions involving more than two related species (Terry et al. 2019), in the case of food web and competition interactions. More precisely, he shows by modeling that essential resources may significantly mediate focal species' persistence. Simultaneously, the provision of essential resources may strongly affect the resulting community structure, by driving to extinction first the predator and then, depending on the higher-order interaction, potentially also the associated competitor. Today, all ecologists should be aware of the potential effects of high-order interactions on species' (and likely on ecosystem's) fate (Golubski et al. 2016, Grilli et al. 2017). Yet, we should soon be prepared to include any high-order interaction into any interaction network (i.e. not only between species, but also between species and abiotic components, and between biotic, anthropogenic and abiotic components too). For this purpose, we will need innovative approaches such as hypergraphs (Golubski et al. 2016) and discrete-event models (Gaucherel and Pommereau 2019, Thomas et al. 2022) able to manage highly complex interactions, with numerous interacting components and variables. Such a rigorous study is a necessary and preliminary step in taking into account such a higher complexity. References Gaucherel, C. and F. Pommereau. 2019. Using discrete systems to exhaustively characterize the dynamics of an integrated ecosystem. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 00:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.13242 Golubski, A. J., E. E. Westlund, J. Vandermeer, and M. Pascual. 2016. Ecological Networks over the Edge: Hypergraph Trait-Mediated Indirect Interaction (TMII) Structure trends in Ecology & Evolution 31:344-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2016.02.006 Grilli, J., G. Barabas, M. J. Michalska-Smith, and S. Allesina. 2017. Higher-order interactions stabilize dynamics in competitive network models. Nature 548:210-213. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23273 Raatz, M. 2023. Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.27.525839 Terry, J. C. D., R. J. Morris, and M. B. Bonsall. 2019. Interaction modifications lead to greater robustness than pairwise non-trophic effects in food webs. Journal of Animal Ecology 88:1732-1742. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.13057 Thomas, C., M. Cosme, C. Gaucherel, and F. Pommereau. 2022. Model-checking ecological state-transition graphs. PLoS Computational Biology 18:e1009657. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009657 | Provision of essential resources as a persistence strategy in food webs | Michael Raatz | <p style="text-align: justify;">Pairwise interactions in food webs, including those between predator and prey are often modulated by a third species. Such higher-order interactions are important structural components of natural food webs that can ... |  | Biodiversity, Coexistence, Competition, Ecological stoichiometry, Food webs, Interaction networks, Theoretical ecology | Cédric Gaucherel | 2023-02-23 17:48:26 | View | |
04 Apr 2023
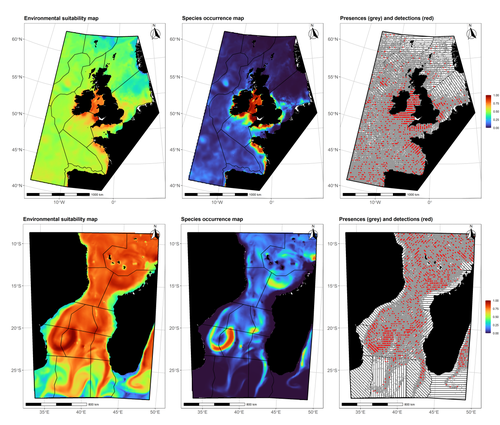
Data stochasticity and model parametrisation impact the performance of species distribution models: insights from a simulation studyCharlotte Lambert, Auriane Virgili https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.17.524386Species Distribution Models: the delicate balance between signal and noiseRecommended by Timothée Poisot based on reviews by Alejandra Zarzo Arias and 1 anonymous reviewer based on reviews by Alejandra Zarzo Arias and 1 anonymous reviewer
Species Distribution Models (SDMs) are one of the most commonly used tools to predict where species are, where they may be in the future, and, at times, what are the variables driving this prediction. As such, applying an SDM to a dataset is akin to making a bet: that the known occurrence data are informative, that the resolution of predictors is adequate vis-à-vis the scale at which their impact is expressed, and that the model will adequately capture the shape of the relationships between predictors and predicted occurrence. In this contribution, Lambert & Virgili (2023) perform a comprehensive assessment of different sources of complications to this process, using replicated simulations of two synthetic species. Their experimental process is interesting, in that both the data generation and the data analysis stick very close to what would happen in "real life". The use of synthetic species is particularly relevant to the assessment of SDM robustness, as they enable the design of species for which the shape of the relationship is given: in short, we know what the model should capture, and can evaluate the model performance against a ground truth that lacks uncertainty. Any simulation study is limited by the assumptions established by the investigators; when it comes to spatial data, the "shape" of the landscape, both in terms of auto-correlation and in where the predictors are available. Lambert & Virgili (2023) nicely circumvent these issues by simulating synthetic species against the empirical distribution of predictors; in other words, the species are synthetic, but the environment for which the prediction is made is real. This is an important step forward when compared to the use of e.g. neutral landscapes (With 1997), which can have statistical properties that are not representative of natural landscapes (see e.g. Halley et al., 2004). A striking point in the study by Lambert & Virgili (2023) is that they reveal a deep, indeed deeper than expected, stochasticity in SDMs; whether this is true in all models remains an open question, but does not invalidate their recommendation to the community: the interpretation of outcomes is a delicate exercise, especially because measures that inform on the goodness of the model fit do not capture the predictive quality of the model outputs. This preprint is both a call to more caution, and a call to more curiosity about the complex behavior of SDMs, while also providing a sensible template to perform future analyses of the potential issues with predictive models.
Halley, J. M., et al. (2004) “Uses and Abuses of Fractal Methodology in Ecology: Fractal Methodology in Ecology.” Ecology Letters, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 254–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00568.x. Lambert, Charlotte, and Auriane Virgili (2023). Data Stochasticity and Model Parametrisation Impact the Performance of Species Distribution Models: Insights from a Simulation Study. bioRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.01.17.524386 With, Kimberly A. (1997) “The Application of Neutral Landscape Models in Conservation Biology. Aplicacion de Modelos de Paisaje Neutros En La Biologia de La Conservacion.” Conservation Biology, vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 1069–80. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1739.1997.96210.x. | Data stochasticity and model parametrisation impact the performance of species distribution models: insights from a simulation study | Charlotte Lambert, Auriane Virgili | <p>Species distribution models (SDM) are widely used to describe and explain how species relate to their environment, and predict their spatial distributions. As such, they are the cornerstone of most of spatial planning efforts worldwide. SDM can... |  | Biogeography, Habitat selection, Macroecology, Marine ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Species distributions, Statistical ecology | Timothée Poisot | 2023-01-20 09:43:51 | View | |
31 Aug 2023
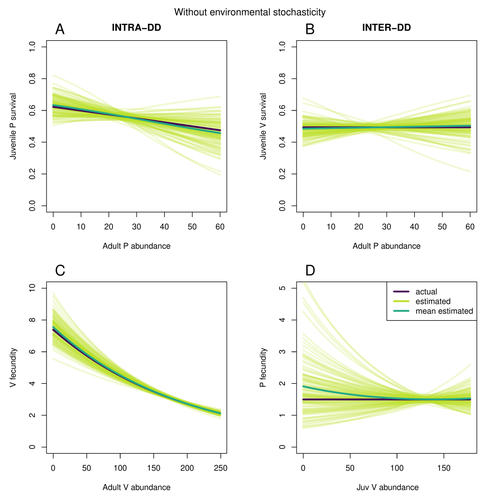
Assessing species interactions using integrated predator-prey modelsMatthieu Paquet, Frederic Barraquand https://doi.org/10.32942/X2RC7WAddressing the daunting challenge of estimating species interactions from count dataRecommended by Tim Coulson and David Alonso and David Alonso based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
Trophic interactions are at the heart of community ecology. Herbivores consume plants, predators consume herbivores, and pathogens and parasites infect, and sometimes kill, individuals of all species in a food web. Given the ubiquity of trophic interactions, it is no surprise that ecologists and evolutionary biologists strive to accurately characterize them. The outcome of an interaction between individuals of different species depends upon numerous factors such as the age, sex, and even phenotype of the individuals involved and the environment in which they are in. Despite this complexity, biologists often simplify an interaction down to a single number, an interaction coefficient that describes the average outcome of interactions between members of the populations of the species. Models of interacting species tend to be very simple, and interaction coefficients are often estimated from time series of population sizes of interacting species. Although biologists have long known that this approach is often approximate and sometimes unsatisfactory, work on estimating interaction strengths in more complex scenarios, and using ecological data beyond estimates of abundance, is still in its infancy. In their paper, Matthieu Paquet and Frederic Barraquand (2023) develop a demographic model of a predator and its prey. They then simulate demographic datasets that are typical of those collected by ecologists and use integrated population modelling to explore whether they can accurately retrieve the values interaction coefficients included in their model. They show that they can with good precision and accuracy. The work takes an important step in showing that accurate interaction coefficients can be estimated from the types of individual-based data that field biologists routinely collect, and it paves for future work in this area. As if often the case with exciting papers such as this, the work opens up a number of other avenues for future research. What happens as we move from demographic models of two species interacting such as those used by Paquet and Barraquand to more realistic scenarios including multiple species? How robust is the approach to incorrectly specified process or observation models, core components of integrated population modelling that require detailed knowledge of the system under study? Integrated population models have become a powerful and widely used tool in single-species population ecology. It is high time the techniques are extended to community ecology, and this work takes an important step in showing that this should and can be done. I would hope the paper is widely read and cited. References Paquet, M., & Barraquand, F. (2023). Assessing species interactions using integrated predator-prey models. EcoEvoRxiv, ver. 2 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.32942/X2RC7W | Assessing species interactions using integrated predator-prey models | Matthieu Paquet, Frederic Barraquand | <p style="text-align: justify;">Inferring the strength of species interactions from demographic data is a challenging task. The Integrated Population Modelling (IPM) approach, bringing together population counts, capture-recapture, and individual-... |  | Community ecology, Demography, Euring Conference, Food webs, Population ecology, Statistical ecology | Tim Coulson | Ilhan Özgen-Xian | 2023-01-05 17:02:22 | View |
13 May 2023

Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sourcesNils Radecker, Anders Meibom https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.07.519152Constraining the importance of heterotrophic vs autotrophic feeding in photosymbiotic cnidariansRecommended by Ulisse Cardini based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersThe symbiosis with autotrophic dinoflagellate algae has enabled heterotrophic Cnidaria to thrive in nutrient-poor tropical waters (Muscatine and Porter 1977; Stanley 2006). In particular, mixotrophy, i.e. the ability to acquire nutrients through both autotrophy and heterotrophy, confers a competitive edge in oligotrophic waters, allowing photosymbiotic Cnidaria to outcompete benthic organisms limited to a single diet (e.g., McCook 2001). However, the relative importance of autotrophy vs heterotrophy in sustaining symbiotic cnidarian’s nutrition is still the subject of intense research. In fact, figuring out the cellular mechanisms by which symbiotic Cnidaria acquire a balanced diet for their metabolism and growth is relevant to our understanding of their physiology under varying environmental conditions and in response to anthropogenic perturbations. In this study's long-term starvation experiment, Radecker & Meibom (2023) investigated the survival of the photosymbiotic sea anemone Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic feeding. After one year of heterotrophic starvation, Apitasia anemones remained fully viable but showed an 85 % reduction in biomass. Using 13C-bicarbonate and 15N-ammonium labeling, electron microscopy and NanoSIMS imaging, the authors could clearly show that the contribution of algal-derived nutrients to the host metabolism remained unaffected as a result of increased algal photosynthesis and more efficient carbon translocation. At the same time, the absence of heterotrophic feeding caused severe nitrogen limitation in the starved Apitasia anemones. Overall, this study provides valuable insights into nutrient exchange within the symbiosis between Cnidaria and dinoflagellate algae at the cellular level and sheds new light on the importance of heterotrophic feeding as a nitrogen acquisition strategy for holobiont growth in oligotrophic waters. REFERENCES McCook L (2001) Competition between corals and algal turfs along a gradient of terrestrial influence in the nearshore central Great Barrier Reef. Coral Reefs 19:419–425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003380000119 Muscatine L, Porter JW (1977) Reef corals: mutualistic symbioses adapted to nutrient-poor environments. Bioscience 27:454–460. https://doi.org/10.2307/1297526 Radecker N, Meibom A (2023) Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sources. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.07.519152 Stanley GD Jr (2006) Photosymbiosis and the evolution of modern coral reefs. Science 312:857–858. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1123701 | Symbiotic nutrient cycling enables the long-term survival of Aiptasia in the absence of heterotrophic food sources | Nils Radecker, Anders Meibom | <p style="text-align: justify;">Phototrophic Cnidaria are mixotrophic organisms that can complement their heterotrophic diet with nutrients assimilated by their algal endosymbionts. Metabolic models suggest that the translocation of photosynthates... |  | Eco-evolutionary dynamics, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Symbiosis | Ulisse Cardini | 2022-12-12 10:50:55 | View | |
11 Oct 2023

Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysisCédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.02.516908Disentangling microbial exopolymer dynamics in intertidal sedimentsRecommended by Ute Risse-Buhl and Nils Rädecker based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewers
The secretion of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) enables microorganisms to shape and interact with their environment [1]. EPS support cell adhesion and motility, offer protection from unfavorable conditions, and facilitate nutrient acquisition and transfer between microorganisms [2]. EPS production and consumption thus control the formation and structural organization of biofilms [3]. However, in marine environments, our understanding of the sources and composition of EPS is limited. References
| Identification of microbial exopolymer producers in sandy and muddy intertidal sediments by compound-specific isotope analysis | Cédric Hubas, Julie Gaubert-Boussarie, An-Sofie D’Hondt, Bruno Jesus, Dominique Lamy, Vona Meleder, Antoine Prins, Philippe Rosa, Willem Stock, Koen Sabbe | <p style="text-align: justify;">Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) refer to a wide variety of high molecular weight molecules secreted outside the cell membrane by biofilm microorganisms. In the present study, EPS from marine microphytobenth... |  | Biodiversity, Ecological stoichiometry, Ecosystem functioning, Food webs, Marine ecology, Microbial ecology & microbiology, Soil ecology | Ute Risse-Buhl | 2022-12-06 14:13:11 | View | |
16 Jun 2023
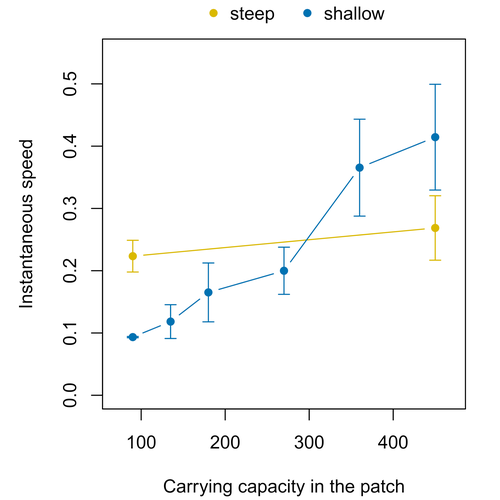
Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansionThibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255Combining stochastic models and experiments to understand dispersal in heterogeneous environmentsRecommended by Joaquín Hortal based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersDispersal is a key element of the natural dynamics of meta-communities, and plays a central role in the success of populations colonizing new landscapes. Understanding how demographic processes may affect the speed at which alien species spread through environmentally-heterogeneous habitat fragments is therefore of key importance to manage biological invasions. This requires studying together the complex interplay of dispersal and population processes, two inextricably related phenomena that can produce many possible outcomes. Stochastic models offer an opportunity to describe this kind of process in a meaningful way, but to ensure that they are realistic (sensu Levins 1966) it is also necessary to combine model simulations with empirical data (Snäll et al. 2007). Morel-Journel et al. (2023) put together stochastic models and experimental data to study how population density may affect the speed at which alien species spread through a heterogeneous landscape. They do it by focusing on what they call ‘colonisation debt’, which is merely the impact that population density at the invasion front may have on the speed at which the species colonizes patches of different carrying capacities. They investigate this issue through two largely independent approaches. First, a stochastic model of dispersal throughout the patches of a linear, 1-dimensional landscape, which accounts for different degrees of density-dependent growth. And second, a microcosm experiment of a parasitoid wasp colonizing patches with different numbers of host eggs. In both cases, they compare the velocity of colonization of patches with lower or higher carrying capacity than the previous one (i.e. what they call upward or downward gradients). Their results show that density-dependent processes influence the speed at which new fragments are colonized is significantly reduced by positive density dependence. When either population growth or dispersal rate depend on density, colonisation debt limits the speed of invasion, which turns out to be dependent on the strength and direction of the gradient between the conditions of the invasion front, and the newly colonized patches. Although this result may be quite important to understand the meta-population dynamics of dispersing species, it is important to note that in their study the environmental differences between patches do not take into account eventual shifts in the scenopoetic conditions (i.e. the values of the environmental parameters to which species niches’ respond to; Hutchinson 1978, see also Soberón 2007). Rather, differences arise from variations in the carrying capacity of the patches that are consecutively invaded, both in the in silico and microcosm experiments. That is, they account for potential differences in the size or quality of the invaded fragments, but not on the costs of colonizing fragments with different environmental conditions, which may also determine invasion speed through niche-driven processes. This aspect can be of particular importance in biological invasions or under climate change-driven range shifts, when adaptation to new environments is often required (Sakai et al. 2001; Whitney & Gabler 2008; Hill et al. 2011). The expansion of geographical distribution ranges is the result of complex eco-evolutionary processes where meta-community dynamics and niche shifts interact in a novel physical space and/or environment (see, e.g., Mestre et al. 2020). Here, the invasibility of native communities is determined by niche variations and how similar are the traits of alien and native species (Hui et al. 2023). Within this context, density-dependent processes will build upon and heterogeneous matrix of native communities and environments (Tischendorf et al. 2005), to eventually determine invasion success. What the results of Morel-Journel et al. (2023) show is that, when the invader shows density dependence, the invasion process can be slowed down by variations in the carrying capacity of patches along the dispersal front. This can be particularly useful to manage biological invasions; ongoing invasions can be at least partially controlled by manipulating the size or quality of the patches that are most adequate to the invader, controlling host populations to reduce carrying capacity. But further, landscape manipulation of such kind could be used in a preventive way, to account in advance for the effects of the introduction of alien species for agricultural exploitation or biological control, thereby providing an additional safeguard to practices such as the introduction of parasitoids to control plagues. These practical aspects are certainly worth exploring further, together with a more explicit account of the influence of the abiotic conditions and the characteristics of the invaded communities on the success and speed of biological invasions. REFERENCES Hill, J.K., Griffiths, H.M. & Thomas, C.D. (2011) Climate change and evolutionary adaptations at species' range margins. Annual Review of Entomology, 56, 143-159. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-120709-144746 Hui, C., Pyšek, P. & Richardson, D.M. (2023) Disentangling the relationships among abundance, invasiveness and invasibility in trait space. npj Biodiversity, 2, 13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s44185-023-00019-1 Hutchinson, G.E. (1978) An introduction to population biology. Yale University Press, New Haven, CT. Levins, R. (1966) The strategy of model building in population biology. American Scientist, 54, 421-431. Mestre, A., Poulin, R. & Hortal, J. (2020) A niche perspective on the range expansion of symbionts. Biological Reviews, 95, 491-516. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12574 Morel-Journel, T., Haond, M., Duan, L., Mailleret, L. & Vercken, E. (2023) Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion. bioRxiv, 2022.11.13.516255, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.13.516255 Snäll, T., B. O'Hara, R. & Arjas, E. (2007) A mathematical and statistical framework for modelling dispersal. Oikos, 116, 1037-1050. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15604.x Sakai, A.K., Allendorf, F.W., Holt, J.S., Lodge, D.M., Molofsky, J., With, K.A., Baughman, S., Cabin, R.J., Cohen, J.E., Ellstrand, N.C., McCauley, D.E., O'Neil, P., Parker, I.M., Thompson, J.N. & Weller, S.G. (2001) The population biology of invasive species. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 32, 305-332. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114037 Soberón, J. (2007) Grinnellian and Eltonian niches and geographic distributions of species. Ecology Letters, 10, 1115-1123. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01107.x Tischendorf, L., Grez, A., Zaviezo, T. & Fahrig, L. (2005) Mechanisms affecting population density in fragmented habitat. Ecology and Society, 10, 7. https://doi.org/10.5751/ES-01265-100107 Whitney, K.D. & Gabler, C.A. (2008) Rapid evolution in introduced species, 'invasive traits' and recipient communities: challenges for predicting invasive potential. Diversity and Distributions, 14, 569-580. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-4642.2008.00473.x | Colonisation debt: when invasion history impacts current range expansion | Thibaut Morel-Journel, Marjorie Haond, Lana Duan, Ludovic Mailleret, Elodie Vercken | <p>Demographic processes that occur at the local level, such as positive density dependence in growth or dispersal, are known to shape population range expansion, notably by linking carrying capacity to invasion speed. As a result of these process... |  | Biological invasions, Colonization, Dispersal & Migration, Experimental ecology, Landscape ecology, Population ecology, Spatial ecology, Metacommunities & Metapopulations, Theoretical ecology | Joaquín Hortal | Anonymous, Anonymous | 2022-11-16 15:52:08 | View |
12 Apr 2023
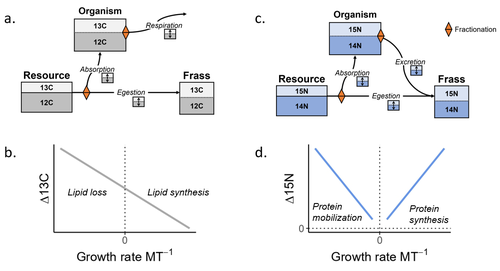
Feeding and growth variations affect δ13C and δ15N budgets during ontogeny in a lepidopteran larvaSamuel M. Charberet, Annick Maria, David Siaussat, Isabelle Gounand, Jérôme Mathieu https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.09.515573Refining our understanding how nutritional conditions affect 13C and 15N isotopic fractionation during ontogeny in a herbivorous insectRecommended by Gregor Kalinkat based on reviews by Anton Potapov and 1 anonymous reviewerUsing stable isotope fractionation to disentangle and understand the trophic positions of animals within the food webs they are embedded within has a long tradition in ecology (Post, 2002; Scheu, 2002). Recent years have seen increasing application of the method with several recent reviews summarizing past advancements in this field (e.g. Potapov et al., 2019; Quinby et al., 2020). In their new manuscript, Charberet and colleagues (2023) set out to refine our understanding of the processes that lead to nitrogen and carbon stable isotope fractionation by investigating how herbivorous insect larvae (specifically, the noctuid moth Spodoptera littoralis) respond to varying nutritional conditions (from starving to ad libitum feeding) in terms of stable isotopes enrichment. Though the underlying mechanisms have been experimentally investigated before in terrestrial invertebrates (e.g. in wolf spiders; Oelbermann & Scheu, 2002), the elegantly designed and adequately replicated experiments by Charberet and colleagues add new insights into this topic. Particularly, the authors provide support for the hypotheses that (A) 15N is disproportionately accumulated under fast growth rates (i.e. when fed ad libitum) and that (B) 13C is accumulated under low growth rates and starvation due to depletion of 13C-poor fat tissues. Applying this knowledge to field samples where feeding conditions are usually not known in detail is not straightforward, but the new findings could still help better interpretation of field data under specific conditions that make starvation for herbivores much more likely (e.g. droughts). Overall this study provides important methodological advancements for a better understanding of plant-herbivore interactions in a changing world. REFERENCES Charberet, S., Maria, A., Siaussat, D., Gounand, I., & Mathieu, J. (2023). Feeding and growth variations affect δ13C and δ15N budgets during ontogeny in a lepidopteran larva. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Ecology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.09.515573 Oelbermann, K., & Scheu, S. (2002). Stable Isotope Enrichment (δ 15N and δ 13C) in a Generalist Predator (Pardosa lugubris, Araneae: Lycosidae): Effects of Prey Quality. Oecologia, 130(3), 337–344. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100813 Post, D. M. (2002). Using stable isotopes to estimate trophic position: Models, methods, and assumptions. Ecology, 83(3), 703–718. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2002)083[0703:USITET]2.0.CO;2 Potapov, A. M., Tiunov, A. V., & Scheu, S. (2019). Uncovering trophic positions and food resources of soil animals using bulk natural stable isotope composition. Biological Reviews, 94(1), 37–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12434 Quinby, B. M., Creighton, J. C., & Flaherty, E. A. (2020). Stable isotope ecology in insects: A review. Ecological Entomology, 45(6), 1231–1246. https://doi.org/10.1111/een.12934 Scheu, S. (2002). The soil food web: Structure and perspectives. European Journal of Soil Biology, 38(1), 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1164-5563(01)01117-7 | Feeding and growth variations affect δ13C and δ15N budgets during ontogeny in a lepidopteran larva | Samuel M. Charberet, Annick Maria, David Siaussat, Isabelle Gounand, Jérôme Mathieu | <p style="text-align: justify;">Isotopes are widely used in ecology to study food webs and physiology. The fractionation observed between trophic levels in nitrogen and carbon isotopes, explained by isotopic biochemical selectivity, is subject to ... |  | Experimental ecology, Food webs, Physiology | Gregor Kalinkat | 2022-11-16 15:23:31 | View | |
24 Nov 2023
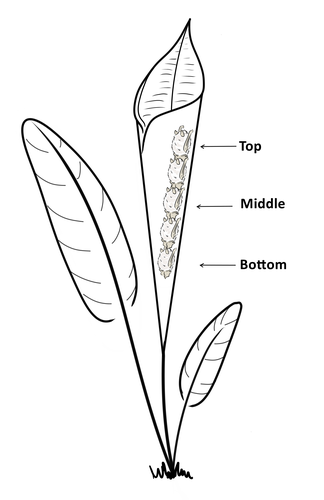
Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged batsGiada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223Consistent individual differences in habitat use in a tropical leaf roosting batRecommended by Corina Logan based on reviews by Annemarie van der Marel and 2 anonymous reviewersConsistent individual differences in habitat use are found across species and can play a role in who an individual mates with, their risk of predation, and their ability to compete with others (Stuber et al. 2022). However, the data informing such hypotheses come primarily from temperate regions (Stroud & Thompson 2019, Titley et al. 2017). This calls into question the generalizability of the conclusions from this research until further investigations can be conducted in tropical regions. Giacomini and colleagues (2023) tackled this task in an investigation of consistent individual differences in habitat use in the Central American tropics. They explored whether Spix’s disc-winged bats form positional hierarchies in roosts, which is an excellent start to learning more about the social behavior of this species - a species that is difficult to directly observe. They found that individual bats use their roosting habitat in predictable ways by positioning themselves consistently either in the bottom, middle, or top of the roost leaf. Individuals chose the same positions across time and across different roost sites. They also found that age and sex play a role in which sections individuals are positioned in. Their research shows that consistent individual differences in habitat use are present in a tropical system, and sets the stage for further investigations into social behavior in this species, particularly whether there is a dominance hierarchy among individuals and whether some positions in the roost are more protective and sought after than others. References Giacomini G, Chaves-Ramirez S, Hernandez-Pinson A, Barrantes JP, Chaverri G. (2023). Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats. bioRxiv, https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.11.04.515223 Stroud, J. T., & Thompson, M. E. (2019). Looking to the past to understand the future of tropical conservation: The importance of collecting basic data. Biotropica, 51(3), 293-299. https://doi.org/10.1111/btp.12665 Stuber, E. F., Carlson, B. S., & Jesmer, B. R. (2022). Spatial personalities: a meta-analysis of consistent individual differences in spatial behavior. Behavioral Ecology, 33(3), 477-486. https://doi.org/10.1093/beheco/arab147 Titley, M. A., Snaddon, J. L., & Turner, E. C. (2017). Scientific research on animal biodiversity is systematically biased towards vertebrates and temperate regions. PloS one, 12(12), e0189577. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189577 | Consistent individual positions within roosts in Spix's disc-winged bats | Giada Giacomini, Silvia Chaves-Ramirez, Andres Hernandez-Pinson, Jose Pablo Barrantes, Gloriana Chaverri | <p style="text-align: justify;">Individuals within both moving and stationary groups arrange themselves in a predictable manner; for example, some individuals are consistently found at the front of the group or in the periphery and others in the c... |  | Behaviour & Ethology, Social structure, Zoology | Corina Logan | 2022-11-05 17:39:35 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Julia Astegiano
Tim Coulson
Anna Eklof
Dominique Gravel
François Massol
Ben Phillips
Cyrille Violle










